
Acetic anhydride is obtained from acetyl chloride by the reaction of
A.\[{{\rm{P}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}\]
B. \[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]
C. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COONa}}\]
D. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Acetic anhydride also called ethanoic anhydride is a chemical species possessing the formula of \[{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CO}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\] . The common abbreviation of this compound is \[{\rm{A}}{{\rm{c}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\]. In the synthesis of many organic compounds, it is widely used as a reagent.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let’s understand what acetyl chloride is. Acetyl chloride belongs to the class of acyl chloride that we get from acetic acid. Acetyl chloride also belongs to the group of acid halides. It has no colour. It is a liquid of volatile nature. And it is a corrosive substance.
The structure of acetyl chloride is,
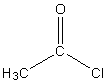
Image: Acetyl chloride
The structure of acetic anhydride is,
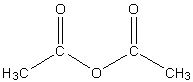
Image: Acetic anhydride
Now, we have to understand the conversion of acetyl chloride to acetic anhydride. When sodium acetate undergoes a reaction with acetyl chloride, the formation of acetic anhydride takes place. In this reaction, a molecule of Sodium chloride (NaCl) is extracted. The chemical reaction is as follows:
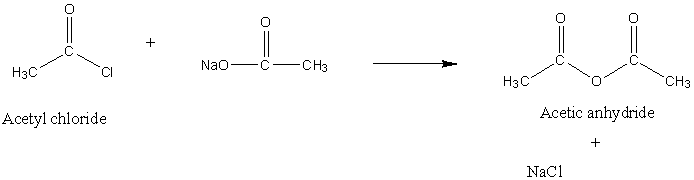
Image: Formation of acetic anhydride due to the reaction of sodium acetate and acetyl chloride
Hence, option C is right.
Additional Information: Acyl chlorides are the organic species derived from carboxylic acid. In acyl chlorides, the OH group of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an atom of chloride.
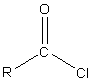
Image: Acyl chloride
Note: Grignard reagent is one of the important compounds in organic chemistry. It is beneficial for the preparation of various organic compounds such as acetals, amides, amino compounds, etc. It is used for the manufacture of many compounds that are useful in the pharmaceutical field.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let’s understand what acetyl chloride is. Acetyl chloride belongs to the class of acyl chloride that we get from acetic acid. Acetyl chloride also belongs to the group of acid halides. It has no colour. It is a liquid of volatile nature. And it is a corrosive substance.
The structure of acetyl chloride is,

Image: Acetyl chloride
The structure of acetic anhydride is,

Image: Acetic anhydride
Now, we have to understand the conversion of acetyl chloride to acetic anhydride. When sodium acetate undergoes a reaction with acetyl chloride, the formation of acetic anhydride takes place. In this reaction, a molecule of Sodium chloride (NaCl) is extracted. The chemical reaction is as follows:

Image: Formation of acetic anhydride due to the reaction of sodium acetate and acetyl chloride
Hence, option C is right.
Additional Information: Acyl chlorides are the organic species derived from carboxylic acid. In acyl chlorides, the OH group of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an atom of chloride.

Image: Acyl chloride
Note: Grignard reagent is one of the important compounds in organic chemistry. It is beneficial for the preparation of various organic compounds such as acetals, amides, amino compounds, etc. It is used for the manufacture of many compounds that are useful in the pharmaceutical field.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




