
ABC is a right angled isosceles triangle with \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\]. If D is a point on AB, so that \[\angle DCB = {15^ \circ }\] and if AD = 35 cm, then find CD.
A. \[35\sqrt 2 \]cm
B. \[70\sqrt 2 \]cm
C. \[\dfrac{{35\sqrt 3 }}{2}\] cm
D. \[35\sqrt 6 \] cm
E. \[\dfrac{{35\sqrt 2 }}{2}\] cm
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: First we will draw a triangle according to the question. Then we will find the side BC and \[\angle CDB\]. Then we will apply sine law on triangle BCD to calculate the value of CD.
Formula used:
\[\sin {15^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[\sin {75^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\]
Sine law:
\[\dfrac{{\sin A}}{a} = \dfrac{{\sin B}}{b} = \dfrac{{\sin C}}{c}\]
Complete step by step solution:
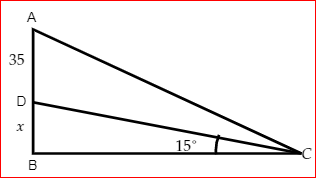
Image :Triangle ABC
Given that, the triangle is a right angled isosceles triangle with \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\].Two sides and two angles of an isosceles triangle are the same.
Thus AB = BC, since AC is hypotenuse and a hypotenuse of a triangle always greater than the rest two legs.
Assume that, DB = x.
So, AB = x+35
Since AB = BC, so BC = x+35.
Since BDC is triangle and \[\angle CBD = {90^ \circ }\] and \[\angle DCB = {15^ \circ }\], thus \[\angle CDB = {180^ \circ } - {15^ \circ } - {90^ \circ } = {75^ \circ }\].
Now we apply sine law on triangle BDC:
\[\dfrac{{\sin B}}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sin C}}{{DB}} = \dfrac{{\sin D}}{{BC}}\]
Now putting the value of unknown:
\[\dfrac{{\sin {{90}^ \circ }}}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sin {{15}^ \circ }}}{x} = \dfrac{{\sin {{75}^ \circ }}}{{35 + x}}\] …..(i)
Taking last two ratios
\[\dfrac{{\sin {{15}^ \circ }}}{x} = \dfrac{{\sin {{75}^ \circ }}}{{35 + x}}\]
Substituting \[\sin {15^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\] and \[\sin {75^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}}}{x} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}}}{{35 + x}}\]
Cross multiply
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\left( {35 + x} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}x\]
Cancel out \[2\sqrt 2 \] from both sides
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)\left( {35 + x} \right) = \left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)x\]
\[ \Rightarrow 35\sqrt 3 + \sqrt 3 x - 35 - x = \sqrt 3 x + x\]
Calculate the value of x
\[ \Rightarrow 2x = 35\sqrt 3 - 35\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{35\sqrt 3 - 35}}{2}\]
Taking first two ratios of (i)
\[\dfrac{{\sin {{90}^ \circ }}}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sin {{15}^ \circ }}}{x}\]
Substitute the value of \[\sin {15^ \circ }\] and x
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}}}{{\dfrac{{35\sqrt 3 - 35}}{2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} \times \dfrac{2}{{35\sqrt 3 - 35}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} \times \dfrac{2}{{35\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{DC}} = \dfrac{1}{{35\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow DC = 35\sqrt 2 \]
Hence option A is the correct option.
Note: Students often make mistakes to find the equal sides of the isosceles triangle ABC. They equate AB = AC. But the hypotenuse of a triangle is always greater than the legs. So, AB = BC.
Formula used:
\[\sin {15^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[\sin {75^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\]
Sine law:
\[\dfrac{{\sin A}}{a} = \dfrac{{\sin B}}{b} = \dfrac{{\sin C}}{c}\]
Complete step by step solution:

Image :Triangle ABC
Given that, the triangle is a right angled isosceles triangle with \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\].Two sides and two angles of an isosceles triangle are the same.
Thus AB = BC, since AC is hypotenuse and a hypotenuse of a triangle always greater than the rest two legs.
Assume that, DB = x.
So, AB = x+35
Since AB = BC, so BC = x+35.
Since BDC is triangle and \[\angle CBD = {90^ \circ }\] and \[\angle DCB = {15^ \circ }\], thus \[\angle CDB = {180^ \circ } - {15^ \circ } - {90^ \circ } = {75^ \circ }\].
Now we apply sine law on triangle BDC:
\[\dfrac{{\sin B}}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sin C}}{{DB}} = \dfrac{{\sin D}}{{BC}}\]
Now putting the value of unknown:
\[\dfrac{{\sin {{90}^ \circ }}}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sin {{15}^ \circ }}}{x} = \dfrac{{\sin {{75}^ \circ }}}{{35 + x}}\] …..(i)
Taking last two ratios
\[\dfrac{{\sin {{15}^ \circ }}}{x} = \dfrac{{\sin {{75}^ \circ }}}{{35 + x}}\]
Substituting \[\sin {15^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\] and \[\sin {75^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}}}{x} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}}}{{35 + x}}\]
Cross multiply
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\left( {35 + x} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}x\]
Cancel out \[2\sqrt 2 \] from both sides
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)\left( {35 + x} \right) = \left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)x\]
\[ \Rightarrow 35\sqrt 3 + \sqrt 3 x - 35 - x = \sqrt 3 x + x\]
Calculate the value of x
\[ \Rightarrow 2x = 35\sqrt 3 - 35\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{35\sqrt 3 - 35}}{2}\]
Taking first two ratios of (i)
\[\dfrac{{\sin {{90}^ \circ }}}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sin {{15}^ \circ }}}{x}\]
Substitute the value of \[\sin {15^ \circ }\] and x
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}}}{{\dfrac{{35\sqrt 3 - 35}}{2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} \times \dfrac{2}{{35\sqrt 3 - 35}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} \times \dfrac{2}{{35\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{DC}} = \dfrac{1}{{35\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow DC = 35\sqrt 2 \]
Hence option A is the correct option.
Note: Students often make mistakes to find the equal sides of the isosceles triangle ABC. They equate AB = AC. But the hypotenuse of a triangle is always greater than the legs. So, AB = BC.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




