
When a wheel rolls on a level road, the direction of frictional force at the point of contact of wheel and ground is:
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Static friction holds a wheel or a ball on the surface. A torque has to be applied to the wheel in order to start the rolling motion. The frictional force prevents the wheel from sliding and thus initiates the rolling motion. Static friction opposes the motion that would take place. Apply this logic to obtain the direction of frictional force.
Complete step by step solution:
Frictional force is the opposing force which plays between two surfaces and it destroys the relative motion between them. Frictional force is a non-conservative force. The force produced by two surfaces that contact and slide against each other, that force is called the frictional force. These forces are affected by the nature of the surface and amount of force acting on them.
In case of a bicycle, the front wheel of the bicycle is connected to a rod passing through its centre. The force acting on the wheel about its central axis by the force coming from the rest of the bicycle is zero. Front wheel obtains linear velocity by pedalling but it cannot rotate it.
Wheel or ball can also be rolled by pushing on it. The frictional force prevents the wheel from sliding forward at the point of contact. Here, the frictional force prevents the wheel from sliding forward and it is in the opposite direction.
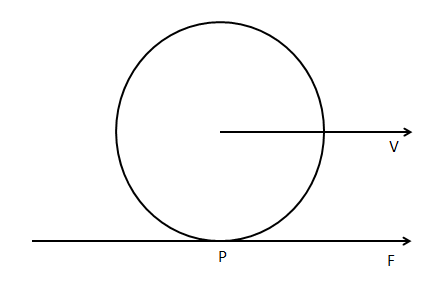
So, in the case of the wheel, the point P which is in contact with the ground tries to go backward due to rotation. Frictional force will oppose this motion. Hence it will move forward.
Hence the direction of frictional force at the point P of the wheel is in forward direction.
Note: Frictional force opposes the motion. Here static friction holds a wheel or a ball on the surface. Frictional force is equal and opposite in direction to the applied force parallel to the contacting surfaces. The resistance due to the rolling body on a surface is called rolling friction. Torque is a force that acts on a body that is undergoing rotation.
Complete step by step solution:
Frictional force is the opposing force which plays between two surfaces and it destroys the relative motion between them. Frictional force is a non-conservative force. The force produced by two surfaces that contact and slide against each other, that force is called the frictional force. These forces are affected by the nature of the surface and amount of force acting on them.
In case of a bicycle, the front wheel of the bicycle is connected to a rod passing through its centre. The force acting on the wheel about its central axis by the force coming from the rest of the bicycle is zero. Front wheel obtains linear velocity by pedalling but it cannot rotate it.
Wheel or ball can also be rolled by pushing on it. The frictional force prevents the wheel from sliding forward at the point of contact. Here, the frictional force prevents the wheel from sliding forward and it is in the opposite direction.

So, in the case of the wheel, the point P which is in contact with the ground tries to go backward due to rotation. Frictional force will oppose this motion. Hence it will move forward.
Hence the direction of frictional force at the point P of the wheel is in forward direction.
Note: Frictional force opposes the motion. Here static friction holds a wheel or a ball on the surface. Frictional force is equal and opposite in direction to the applied force parallel to the contacting surfaces. The resistance due to the rolling body on a surface is called rolling friction. Torque is a force that acts on a body that is undergoing rotation.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




