
A thermally insulated container is divided into two parts by a screen. In one part the pressure and temperature are $P$ and $T$ for an ideal gas filled. In the second part it is vacuum. If now a small hole is created in the screen, then the temperature of the gas will
A. decrease
B. increase
C. remains same
D. none of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:
This problem is based on thermodynamics; we know that pressure and temperature vary with the given conditions of the system and surroundings. As the gas is expanding from a small hole against a vacuum, therefore, the process will be free expansion i.e., $\Delta W = 0$. Hence, use the first law of thermodynamics to state the answer for the given problem.
Formula used:
First Law of the thermodynamics used in this problem is defined as: -
$\Delta U + \Delta W = \Delta Q$
and, for ideal gas internal energy is the function of temperature i.e., $U = f\left( T \right)$
Complete step by step solution:
Let us illustrate the given problem by a diagram given as follows: -
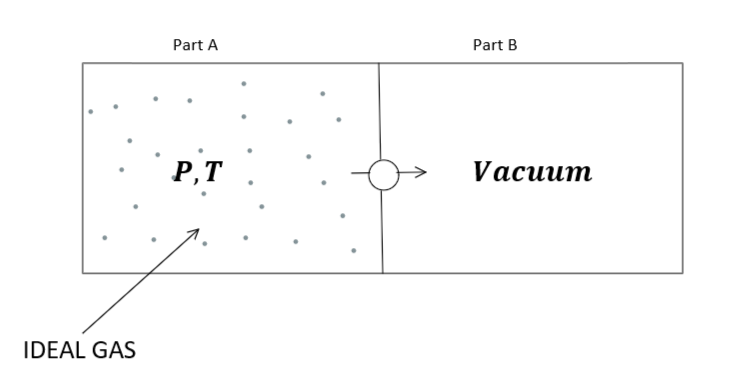
It is given that the container is thermally insulated which means $\Delta Q = 0$.
Additionally, the process of the gas expanding against a vacuum (surroundings) is known as free expansion, and for this process, work done by gas will be: -
$\Delta W = \int {PdV} = 0$
Now we know that the First Law of Thermodynamics is the application of conservation of energy and according to the first law: -
$\Delta U + \Delta W\, = \Delta Q\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,...\,(1)$
where $\Delta U = $ Change in the Internal Energy of the system
$\Delta Q = $ Heat Added to the system
$\Delta W = $ Work done
From the equation $(1)$, we get
$0 = \Delta U + 0 \Rightarrow \Delta U = 0$
i.e., ${U_{final}} = {U_{initial}}$
or, $U{\text{ }} = constant$
Since the given gas is ideal and for an ideal gas, the internal energy is the function of temperature.
i.e., $U = f\left( T \right)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,...\,(2)$.
As, $U = constant$
Therefore, from the equation $(2)$
$T = constant$
Thus, in the given scenario, the temperature of the gas will remain constant.
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note:
In this problem, to determine the effect on the temperature of an ideal gas when it is freely expanding against a vacuum from a small hole (in a container that is thermally insulated), use $\Delta Q = 0$ and $\Delta W = 0$ in the first law of thermodynamics and then apply the condition of an ideal gas $U = f\left( T \right)$ to state the final answer.
This problem is based on thermodynamics; we know that pressure and temperature vary with the given conditions of the system and surroundings. As the gas is expanding from a small hole against a vacuum, therefore, the process will be free expansion i.e., $\Delta W = 0$. Hence, use the first law of thermodynamics to state the answer for the given problem.
Formula used:
First Law of the thermodynamics used in this problem is defined as: -
$\Delta U + \Delta W = \Delta Q$
and, for ideal gas internal energy is the function of temperature i.e., $U = f\left( T \right)$
Complete step by step solution:
Let us illustrate the given problem by a diagram given as follows: -

It is given that the container is thermally insulated which means $\Delta Q = 0$.
Additionally, the process of the gas expanding against a vacuum (surroundings) is known as free expansion, and for this process, work done by gas will be: -
$\Delta W = \int {PdV} = 0$
Now we know that the First Law of Thermodynamics is the application of conservation of energy and according to the first law: -
$\Delta U + \Delta W\, = \Delta Q\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,...\,(1)$
where $\Delta U = $ Change in the Internal Energy of the system
$\Delta Q = $ Heat Added to the system
$\Delta W = $ Work done
From the equation $(1)$, we get
$0 = \Delta U + 0 \Rightarrow \Delta U = 0$
i.e., ${U_{final}} = {U_{initial}}$
or, $U{\text{ }} = constant$
Since the given gas is ideal and for an ideal gas, the internal energy is the function of temperature.
i.e., $U = f\left( T \right)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,...\,(2)$.
As, $U = constant$
Therefore, from the equation $(2)$
$T = constant$
Thus, in the given scenario, the temperature of the gas will remain constant.
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note:
In this problem, to determine the effect on the temperature of an ideal gas when it is freely expanding against a vacuum from a small hole (in a container that is thermally insulated), use $\Delta Q = 0$ and $\Delta W = 0$ in the first law of thermodynamics and then apply the condition of an ideal gas $U = f\left( T \right)$ to state the final answer.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




