
A tangential force $2N$ acts at the rim of a ring of radius $15m$ and causes the ring to turn through an angle $60^\circ $ the work done by the force will be:
A) $5\pi $
B) $10\pi $
C) $15\pi $
D) $20\pi $
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint: A power which follows up on a moving body toward a digression to the way of the body, its impact being to increment or lessen the speed; - recognized from an ordinary power, which acts at right points to the digression and alters the course of the movement without changing the speed.
Net force implies ascertaining the subsequent force from n diverse contributing powers.
In material science and mechanics, force is what might be compared to direct power. It is likewise alluded to as the occasion, snapshot of power, rotational power, or turning impact, contingent upon the field of study.
The idea began with the investigations by Archimedes of the use of switches.
Force is a proportion of the power that can make an item pivot about a hub.
Similarly, as power is the thing that makes an article quicken in direct kinematics, force is the thing that makes an item gain precise speeding up.
Force is a vector amount.
Formula used:
The formula of torque $T$ is
$\overrightarrow T = \overrightarrow r \times \overrightarrow F $
$\overrightarrow F $= force, $\overrightarrow r $ = the lever arm and
The angle $\theta $, between the lever arm $r$ and force $F$ is known, the magnitude of the torque can be calculated as $\overrightarrow T = \overrightarrow r \times \overrightarrow F \sin \theta $
Complete step by step answer:
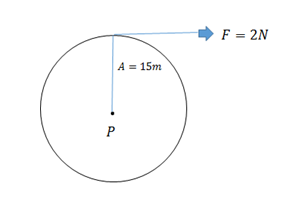
Let A tangential force $2N$, radius $15m$, an angle $60^\circ $
Net torque, $\overrightarrow T = \overrightarrow r \times \overrightarrow F $
$ \Rightarrow 15m\mathop j\limits^ \wedge \times 2N\mathop i\limits^ \wedge $
$ \Rightarrow 30Nm$
Since, we already know that $\left( {\because \sin 60^\circ = \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$ $\left( {\because \overrightarrow T = 30Nm} \right)$ $\left( {\because \sin 60^\circ = \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
Work done,
$W = \overrightarrow T \times \Delta \overrightarrow \theta $
$ \Rightarrow W = 30 \times \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
$ \Rightarrow W = 10\pi $
Hence the answer is $\left( B \right)$
Note: A surface containing the essential foci of focuses in a plane opposite to the optical hub of an astigmatic framework. Spiral power by and large methods a power applied an outspread way towards the middle or away from the middle. In outward siphons, spiral power (additionally outspread push) is the term used to assign the power following up on the siphon rotor. The extraneous increasing speed is a proportion of the pace of progress in the size of the speed vector, for example, speed, and the typical increasing speed is a proportion of the pace of altering the course of the speed vector.
Net force implies ascertaining the subsequent force from n diverse contributing powers.
In material science and mechanics, force is what might be compared to direct power. It is likewise alluded to as the occasion, snapshot of power, rotational power, or turning impact, contingent upon the field of study.
The idea began with the investigations by Archimedes of the use of switches.
Force is a proportion of the power that can make an item pivot about a hub.
Similarly, as power is the thing that makes an article quicken in direct kinematics, force is the thing that makes an item gain precise speeding up.
Force is a vector amount.
Formula used:
The formula of torque $T$ is
$\overrightarrow T = \overrightarrow r \times \overrightarrow F $
$\overrightarrow F $= force, $\overrightarrow r $ = the lever arm and
The angle $\theta $, between the lever arm $r$ and force $F$ is known, the magnitude of the torque can be calculated as $\overrightarrow T = \overrightarrow r \times \overrightarrow F \sin \theta $
Complete step by step answer:


Let A tangential force $2N$, radius $15m$, an angle $60^\circ $
Net torque, $\overrightarrow T = \overrightarrow r \times \overrightarrow F $
$ \Rightarrow 15m\mathop j\limits^ \wedge \times 2N\mathop i\limits^ \wedge $
$ \Rightarrow 30Nm$
Since, we already know that $\left( {\because \sin 60^\circ = \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$ $\left( {\because \overrightarrow T = 30Nm} \right)$ $\left( {\because \sin 60^\circ = \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
Work done,
$W = \overrightarrow T \times \Delta \overrightarrow \theta $
$ \Rightarrow W = 30 \times \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
$ \Rightarrow W = 10\pi $
Hence the answer is $\left( B \right)$
Note: A surface containing the essential foci of focuses in a plane opposite to the optical hub of an astigmatic framework. Spiral power by and large methods a power applied an outspread way towards the middle or away from the middle. In outward siphons, spiral power (additionally outspread push) is the term used to assign the power following up on the siphon rotor. The extraneous increasing speed is a proportion of the pace of progress in the size of the speed vector, for example, speed, and the typical increasing speed is a proportion of the pace of altering the course of the speed vector.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Other Pages
CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 - Kinetic Theory - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 Waves - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 7 Gravitation - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties Of Solids - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties Of Matter - 2025-26




