
A student obtained a clear image of window grills on the screen. But the teacher told him to get the image of a tree far away, instead of the window. To get a clear image the lens must be:
A) Moved towards the screen
B) Moved away from the screen
C) Moved very close to the screen
D) None of these.
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: from the above question it is clear that the distance of the tree from the lens is greater than the distance of the window grills. Now a lens is kept between the window grills and a screen and the student getting a clear image of the grills. The lens should be converging as the tree is far away from the grills. In the converging lens, the nearer the object the more distance the image from the lens. Therefore for the faraway tree, the image will be near the lens.
Complete solution:
Step 1: First let us understand how a converging lens forms the image and how the position of the object affects the position of the image. Consider the following diagram.
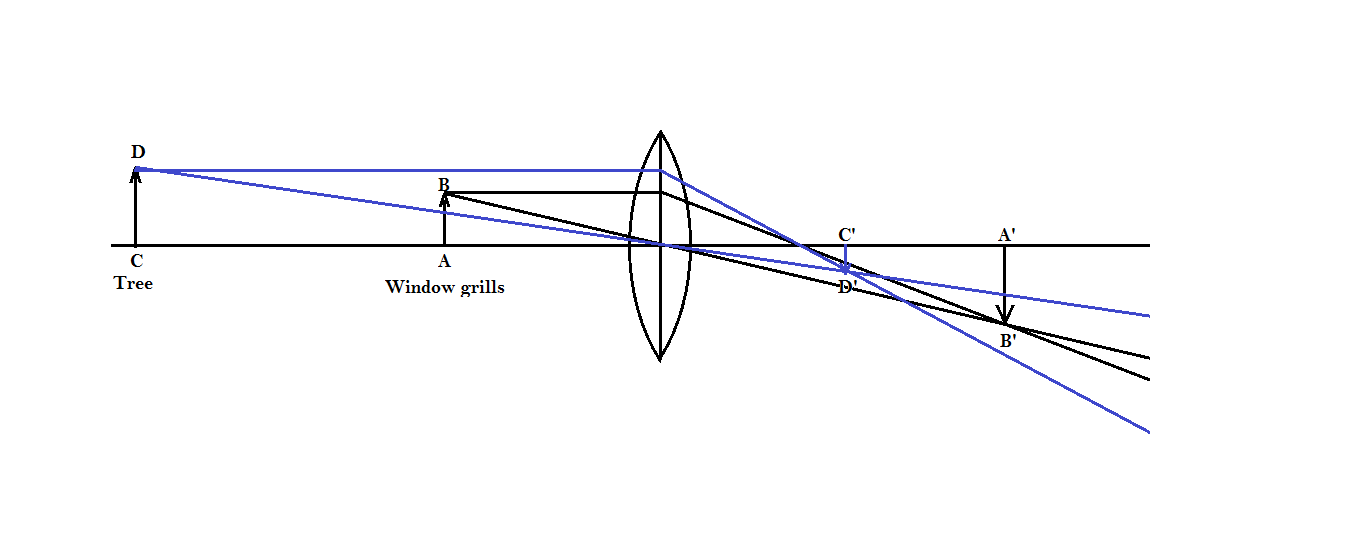 In the ray diagram window grills, AB is closer to the lens in comparison to the tree CD. Since the student is getting a clear image of the window grill therefore the screen kept by the student will be at the same distance as the distance of the image of the window grills A’B’.
In the ray diagram window grills, AB is closer to the lens in comparison to the tree CD. Since the student is getting a clear image of the window grill therefore the screen kept by the student will be at the same distance as the distance of the image of the window grills A’B’.
Step 2: From the above diagram it is also clear that when the student was getting a clear image of the window grills then the image of the tree which is far away from the grills was being formed between the screen and the lens. The screen is fixed. If we can only move the lens then it is pretty clear that the lens should be moved towards the screen to get a clear image of the tree. Then only the image C’D’ can be found clearly on the screen.
Hence the correct option is Option A.
Note: The lens cannot be moved away from the screen if we want a clear image of the tree. Because the distance of the image from the lens of an object depends on the distance of the object from the lens. In the case of the converging lens the far the object is kept nearer the image is formed. If we took the lens away from the screen then the image of the tree will go away from the screen.
Complete solution:
Step 1: First let us understand how a converging lens forms the image and how the position of the object affects the position of the image. Consider the following diagram.
 In the ray diagram window grills, AB is closer to the lens in comparison to the tree CD. Since the student is getting a clear image of the window grill therefore the screen kept by the student will be at the same distance as the distance of the image of the window grills A’B’.
In the ray diagram window grills, AB is closer to the lens in comparison to the tree CD. Since the student is getting a clear image of the window grill therefore the screen kept by the student will be at the same distance as the distance of the image of the window grills A’B’.Step 2: From the above diagram it is also clear that when the student was getting a clear image of the window grills then the image of the tree which is far away from the grills was being formed between the screen and the lens. The screen is fixed. If we can only move the lens then it is pretty clear that the lens should be moved towards the screen to get a clear image of the tree. Then only the image C’D’ can be found clearly on the screen.
Hence the correct option is Option A.
Note: The lens cannot be moved away from the screen if we want a clear image of the tree. Because the distance of the image from the lens of an object depends on the distance of the object from the lens. In the case of the converging lens the far the object is kept nearer the image is formed. If we took the lens away from the screen then the image of the tree will go away from the screen.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions




