
A straight line is equally inclined to all the three axes. Then the angle made by y-axes is
$
{\text{A}}{\text{.}}{\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right) \\
{\text{B}}{\text{.}}{\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right) \\
{\text{C}}{\text{.}}{\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right) \\
{\text{D}}{\text{.}}\dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint : Use the concept of direction cosines i.e. make the sum of squares of all the direction cosines as equal to one.
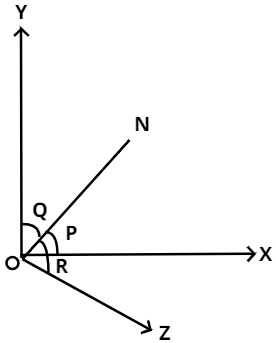
This the diagram of the line equally inclined to all the three axes.
From the Figure we come to know that ON is the line which is equally inclined to all the three axes.
Here we will use the concept of direction cosines $l,m,n$.
From the figure we know
$
l = \cos p{\text{ }}......{\text{(}}i{\text{)}} \\
m = \cos q\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,......(ii) \\
n = \cos r\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,......(iii) \\
\\
$
We also know ${l^2} + {m^2} + {n^2} = 1\,\,\,\,\,\,......(iv)$
From the question we come to know $p = q = r = \theta (say)\,\,\,\,\,\,......(v)$
From ${\text{(}}i{\text{),(}}ii{\text{),(}}iii{\text{),(}}iv{\text{)\& (}}v{\text{)}}$We do
${\cos ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$
$ \to 3{\cos ^2}\theta = 1$
Therefore,
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Then ,
$\theta = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)$
Hence the correct option is B.
Note :- In these types of questions we will always use the concept of cosines . That is the sum of squares of all the direction cosines is one. By using this we can get the answer easily . Drawing figures will make your concept more clear.

This the diagram of the line equally inclined to all the three axes.
From the Figure we come to know that ON is the line which is equally inclined to all the three axes.
Here we will use the concept of direction cosines $l,m,n$.
From the figure we know
$
l = \cos p{\text{ }}......{\text{(}}i{\text{)}} \\
m = \cos q\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,......(ii) \\
n = \cos r\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,......(iii) \\
\\
$
We also know ${l^2} + {m^2} + {n^2} = 1\,\,\,\,\,\,......(iv)$
From the question we come to know $p = q = r = \theta (say)\,\,\,\,\,\,......(v)$
From ${\text{(}}i{\text{),(}}ii{\text{),(}}iii{\text{),(}}iv{\text{)\& (}}v{\text{)}}$We do
${\cos ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$
$ \to 3{\cos ^2}\theta = 1$
Therefore,
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Then ,
$\theta = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)$
Hence the correct option is B.
Note :- In these types of questions we will always use the concept of cosines . That is the sum of squares of all the direction cosines is one. By using this we can get the answer easily . Drawing figures will make your concept more clear.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

JEE Main Syllabus 2026: Download Detailed Subject-wise PDF

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Keys & Solutions

If y xxx cdots infty then find dfracdydx A yxy 1 B class 12 maths JEE_Main




