
A small roller of diameter 20 cm has an axle of diameter 10 cm (see figure below on the left). It is on a horizontal floor and a meter scale is positioned horizontally on its axle with one edge of the scale on top of the axle (see figure on the right). The scale is now pushed slowly on the axle so that it moves without slipping on the axle, and the roller starts rolling without slipping. After the roller has moved 50 cm, the position of the scale will look like this (figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)
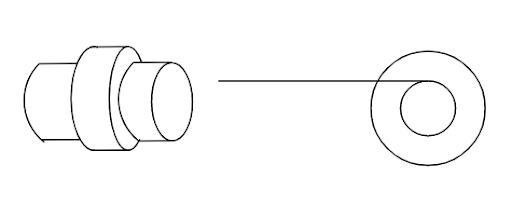
A. 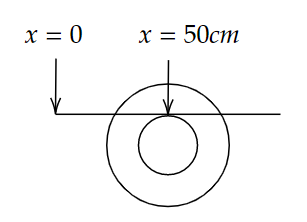
B. 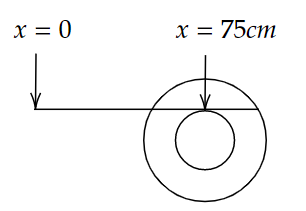
C. 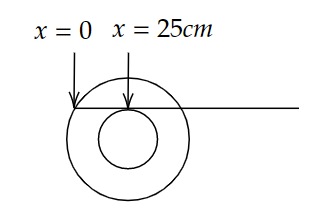
D. 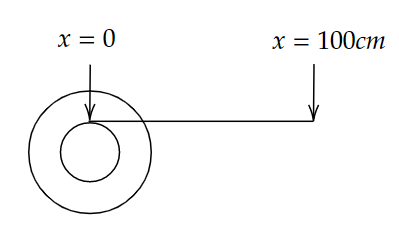
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Before we start addressing the problem, we need to know about the linear and angular velocity. The velocity at which the body moves in a linear motion is known as linear velocity. The velocity at which the body moves in a rotational motion is known as angular velocity.
Formula Used:
The formula for the relation between linear and angular velocity is,
\[v = r\omega \]
Where, v is linear velocity, r is radius and \[\omega \]is angular velocity.
Complete step by step solution:
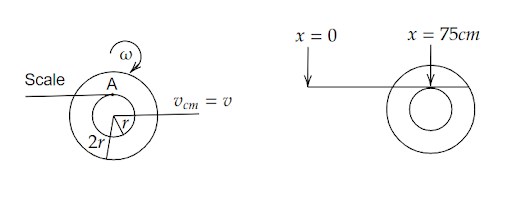
Consider a small roller placed on the horizontal floor of diameter 20 cm has an axle of a diameter of 10cm, a meter scale is positioned horizontally on its axle with one edge of the scale on top of the axle. Now the scale is pushed slowly on the axle so that it moves without slipping on the axle, and the roller starts rolling without slipping. After the roller has moved 50 cm, then we need to find how the position of the scale will look.
So, \[{d_1} = 10cm\], \[{r_1} = 5cm\], \[{d_2} = 20cm\]and \[{r_2} = 10cm\]
Now, \[\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{r_2}}} = \dfrac{5}{{10}}\]
\[\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{r_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
If the ratio of the radius of the axle to the roller is \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] then, the radius of the axle is r and the radius of the roller is 2r. As shown in figure, the velocity at the center is \[{v_{cm}} = v\]it is moving with an angular velocity \[\omega \]without slipping. Then,
\[v = r\omega \]
\[\omega = \dfrac{v}{r}\]
Since, \[r = 2r\](radius of roller)
\[\omega = \dfrac{v}{{2r}}\]
Now, we want to find the velocity at point A. Here, the axle will roll as well as move forward having both translational and rotational velocity that is,
\[v + \dfrac{v}{{2r}} \times r\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3v}}{2}\]
After some time the roller has moved 50 cm on the ground that is, \[v \times t = 50cm\]. Then, the distance will be,
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{3\left( {v \times t} \right)}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{3\left( {50} \right)}}{2}\]
\[ \therefore x = 75\,cm\]
Therefore, the position of the scale is 75 cm.
Hence, Option B is the correct answer
Note:Remember that, if a sphere of some radius r is rolling with some speed v, then it has both linear and angular velocity and the relation between these two is given by, \[v = r\omega \].
Formula Used:
The formula for the relation between linear and angular velocity is,
\[v = r\omega \]
Where, v is linear velocity, r is radius and \[\omega \]is angular velocity.
Complete step by step solution:

Consider a small roller placed on the horizontal floor of diameter 20 cm has an axle of a diameter of 10cm, a meter scale is positioned horizontally on its axle with one edge of the scale on top of the axle. Now the scale is pushed slowly on the axle so that it moves without slipping on the axle, and the roller starts rolling without slipping. After the roller has moved 50 cm, then we need to find how the position of the scale will look.
So, \[{d_1} = 10cm\], \[{r_1} = 5cm\], \[{d_2} = 20cm\]and \[{r_2} = 10cm\]
Now, \[\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{r_2}}} = \dfrac{5}{{10}}\]
\[\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{r_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
If the ratio of the radius of the axle to the roller is \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] then, the radius of the axle is r and the radius of the roller is 2r. As shown in figure, the velocity at the center is \[{v_{cm}} = v\]it is moving with an angular velocity \[\omega \]without slipping. Then,
\[v = r\omega \]
\[\omega = \dfrac{v}{r}\]
Since, \[r = 2r\](radius of roller)
\[\omega = \dfrac{v}{{2r}}\]
Now, we want to find the velocity at point A. Here, the axle will roll as well as move forward having both translational and rotational velocity that is,
\[v + \dfrac{v}{{2r}} \times r\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3v}}{2}\]
After some time the roller has moved 50 cm on the ground that is, \[v \times t = 50cm\]. Then, the distance will be,
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{3\left( {v \times t} \right)}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{3\left( {50} \right)}}{2}\]
\[ \therefore x = 75\,cm\]
Therefore, the position of the scale is 75 cm.
Hence, Option B is the correct answer
Note:Remember that, if a sphere of some radius r is rolling with some speed v, then it has both linear and angular velocity and the relation between these two is given by, \[v = r\omega \].
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




