
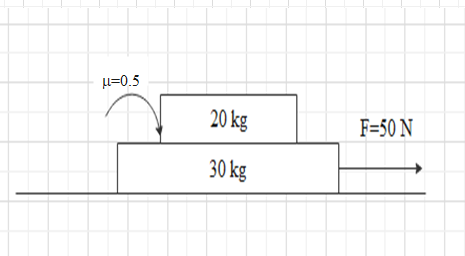
A small block of mass $20\,kg$ rests on a bigger block of mass $30\,kg$ , which lies on a smooth horizontal plane. Initially the whole system is at rest. The coefficient of friction between the block is 0.5. The horizontal force $F = 50\,N$ is applied on the lower block.
(a) Find the work done by frictional force on the upper block and on the lower block when $t = 2\,s$ .
(b) Is the magnitude of work done by the frictional force on upper and lower blocks the same?
(c) Is the work done by the frictional force on the upper block converted to heat or mechanical energy or both?
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint:Work done can be calculated as the product of force and displacement. The displacement for 2 second can be found using the second equation of motion. The force of friction acting on the upper block and lower block will be equal and opposite. By analyzing the magnitude of work done by frictional force on the upper and lower block we can find the answer of part b. if there is no sliding between the blocks then work done will be converted into mechanical energy.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the mass of the upper block is ${m_1} = 20\,kg$
Mass of the lower block is ${m_2} = 30\,kg$
it is said that initially the whole system is at rest, therefore initial velocity $u = 0$
The coefficient of friction between the block is given as $\mu = 0.5$
Horizontal force applied is $F = 50\,N$.
(a) we need to find the work done by frictional force on the upper block and on the lower block for a time $t = 2\,s$ .
Let us assume that the upper block and lower block move together.
We know that force is a product of mass and acceleration.
Thus, force in this case can be written as $F = ma$
Here mass will be the total mass that is $m = {m_1} + {m_2}$
From this we can find acceleration.
$a = \dfrac{F}{m}$
$a = \dfrac{{50}}{{50}} = 1\,m/{s^2}$
Now let's find the distance covered in 2 seconds.
For this we can use a second equation of motion
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where u is the initial velocity t is the time taken a is acceleration.
On substituting the given values we get
$s = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1 \times {2^2} = 2\,m$
The upper block moves forward with the help of static friction that is acting on it.
The frictional force on the upper block is
${F_r} = ma$
mass of upper block is $20\,kg$ thus we get,
${F_r} = 20 \times 1 = 20\,N$
the maximum value of frictional force of limiting friction is given by the formula
${F_{\max }} = \mu N$
Where $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction and N is a normal reaction force. In this case the normal reaction is balanced by the weight $m\,g$ .
Thus we can write limiting friction as
${F_{\max }} = \mu mg$
Let us substitute the values in this equation.
${F_{\max }} = 0.5 \times 20 \times 10$
$\therefore {F_{\max }} = 100\,N$
Since the given force is less than this there will not be any sliding between the upper and lower blocks.
Now we can calculate the work done. We know that work done is a product of force and displacement in the direction of force.
We got the distance as $2\,m$ and the frictional force as $20\,N$ .
So, work done on upper block is
${W_u} = 20 \times 2 = 40\,J$
The frictional force acting on both the blocks will be the same but direction will be opposite.
So, for the lower block we can take the value of force to be negative.
The magnitude will be the same.
Thus, work done on the lower block is
${W_L} = - 20 \times 2 = - 40\,J$
(b) Since the magnitude of the work done on both blocks are the same the answer to part B is yes.
(c) There is no relative sliding between the two blocks so there will be no heat energy produced. The frictional force is actually making the upper block move. So we can say that the frictional force is being converted into mechanical energy.
Note: Remember that the limiting value of the friction is the maximum value. Motion will occur only if the given force can overcome this value. If the force provided is larger than this then sliding will occur in that case the work done by friction will be converted to heat energy also.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the mass of the upper block is ${m_1} = 20\,kg$
Mass of the lower block is ${m_2} = 30\,kg$
it is said that initially the whole system is at rest, therefore initial velocity $u = 0$
The coefficient of friction between the block is given as $\mu = 0.5$
Horizontal force applied is $F = 50\,N$.
(a) we need to find the work done by frictional force on the upper block and on the lower block for a time $t = 2\,s$ .
Let us assume that the upper block and lower block move together.
We know that force is a product of mass and acceleration.
Thus, force in this case can be written as $F = ma$
Here mass will be the total mass that is $m = {m_1} + {m_2}$
From this we can find acceleration.
$a = \dfrac{F}{m}$
$a = \dfrac{{50}}{{50}} = 1\,m/{s^2}$
Now let's find the distance covered in 2 seconds.
For this we can use a second equation of motion
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where u is the initial velocity t is the time taken a is acceleration.
On substituting the given values we get
$s = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1 \times {2^2} = 2\,m$
The upper block moves forward with the help of static friction that is acting on it.
The frictional force on the upper block is
${F_r} = ma$
mass of upper block is $20\,kg$ thus we get,
${F_r} = 20 \times 1 = 20\,N$
the maximum value of frictional force of limiting friction is given by the formula
${F_{\max }} = \mu N$
Where $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction and N is a normal reaction force. In this case the normal reaction is balanced by the weight $m\,g$ .
Thus we can write limiting friction as
${F_{\max }} = \mu mg$
Let us substitute the values in this equation.
${F_{\max }} = 0.5 \times 20 \times 10$
$\therefore {F_{\max }} = 100\,N$
Since the given force is less than this there will not be any sliding between the upper and lower blocks.
Now we can calculate the work done. We know that work done is a product of force and displacement in the direction of force.
We got the distance as $2\,m$ and the frictional force as $20\,N$ .
So, work done on upper block is
${W_u} = 20 \times 2 = 40\,J$
The frictional force acting on both the blocks will be the same but direction will be opposite.
So, for the lower block we can take the value of force to be negative.
The magnitude will be the same.
Thus, work done on the lower block is
${W_L} = - 20 \times 2 = - 40\,J$
(b) Since the magnitude of the work done on both blocks are the same the answer to part B is yes.
(c) There is no relative sliding between the two blocks so there will be no heat energy produced. The frictional force is actually making the upper block move. So we can say that the frictional force is being converted into mechanical energy.
Note: Remember that the limiting value of the friction is the maximum value. Motion will occur only if the given force can overcome this value. If the force provided is larger than this then sliding will occur in that case the work done by friction will be converted to heat energy also.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 - Units And Measurements - 2025-26

Important Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Units and Measurement - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26




