
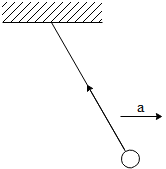
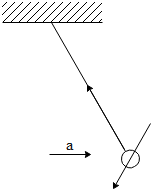
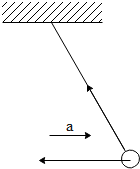
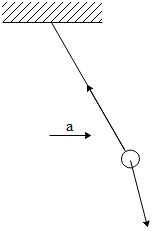
A simple pendulum is oscillating without damping. When the displacement of the bob is less than maximum, its acceleration vector $\vec a$ is correctly shown in:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)




Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint The simple pendulum is known to us as a pendulum which consists of a mass m hanging from a string which has a length of L and is fixed at a pivot point P. Whenever the pendulum is displaced to an initial angle and is released, the pendulum will swing back and forth with a periodic motion. Based on this concept we have to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer
We know that the bob has both radial as well as tangential acceleration when it is at a displacement less than its maximum displacement.
Let us draw the figure:
From the figure,
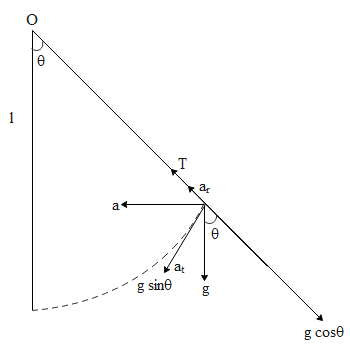
${a_t} = g\sin \theta$and,
${a_r} = \dfrac{T}{m} - g\cos \theta$
The resultant acceleration $\vec a = {\vec a_r} + {\vec a_t}$ points in the direction as shown in the figure
NoteDamping, as we know, is defined as the restraining of the vibratory motion, such as mechanical oscillations, noise or even alternating currents, by the dissipation of energy. IN case of waves, a damped wave is one whose amplitude of oscillation decreases with the time and ultimately goes to zero.
Complete step by step answer
We know that the bob has both radial as well as tangential acceleration when it is at a displacement less than its maximum displacement.
Let us draw the figure:
From the figure,

${a_t} = g\sin \theta$and,
${a_r} = \dfrac{T}{m} - g\cos \theta$
The resultant acceleration $\vec a = {\vec a_r} + {\vec a_t}$ points in the direction as shown in the figure
NoteDamping, as we know, is defined as the restraining of the vibratory motion, such as mechanical oscillations, noise or even alternating currents, by the dissipation of energy. IN case of waves, a damped wave is one whose amplitude of oscillation decreases with the time and ultimately goes to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




