
A ring is hung on a nail. It can oscillate, without slipping or sliding
(i) in its plane with a time period $T_1$ and,
(ii) back and forth in a direction perpendicular to its plane, with a period $T_2$.
The ratio $\dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}}$will be:
A. $\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
B. $\dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{3}$
C. $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
D. $\dfrac{2}{3}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:The ring is used as a physical pendulum to determine its time period. The ring's centre of mass and moment of inertia are computed and compared to the appropriate equation for this physical pendulum.
Formula Used:
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{Mg{l_{cm}}}}} $
Complete answer:
First case:
The first scenario, where the ring is suspended at a location on its rim and oscillates so that the centre travels in its own plane, can be represented by the diagram below.
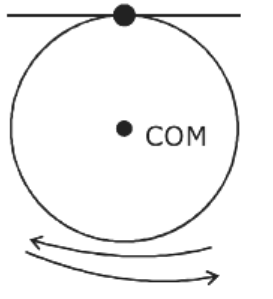
For a physical pendulum, time period is given by,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{Mg{l_{cm}}}}} $
Where,
I is the moment of inertia of the pendulum about the axis of its support,
M is the mass of the pendulum
g is the acceleration due to gravity
${l_{cm}}$ is the distance of the centre of mass of the pendulum from the point of support.
Moment of inertia is the property of a body that prevents it from resisting angular acceleration. It is calculated by multiplying each particle's mass times the square of its distance from the axis of rotation.
Since a ring is suspended from its rim in the first scenario, its centre of mass is in the centre, making the radius of the ring $R$ the distance between the centre of mass and the support,
$ \Rightarrow {l_{cm}} = R$
The moment of inertia of a ring about its diameter is given by
${I_1} = M{R^2}$
We require the moment of inertia about its tangent, because this is where it is attached to the support.
By the parallel axis theorem. The distance between the axis of diameter and the axis of support is $R$
Therefore,
${I_1} = M{R^2} + M{R^2} = 2M{R^2}$
Substituting all of these values in the equation for time period we get,
${T_1} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{Mg{l_{cm}}}}} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{2M{R^2}}}{{MgR}}} $
${T_1} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{2R}}{g}} $
For second case
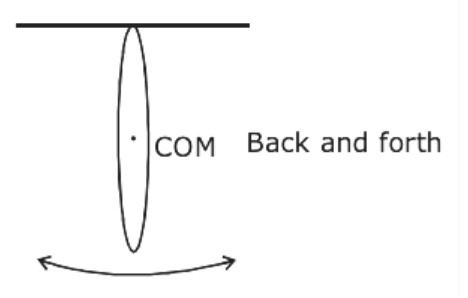
${I_2} = \dfrac{3}{2}M{R^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {T_2} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_2}}}{{Mg{l_{cm}}}}} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{2}M{R^2}}}{{MgR}}} $
${T_2} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{3R}}{{2g}}} $
Taking the ratio we get, $\dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{4}{3}} = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Therefore, correct option is (C).
Note:A physical pendulum can be any size or shape, and it can have a distinct centre of mass and moment of inertia. There are two sorts of pendulums: simple and physical. Moment of inertia calculations for both scenarios should be done carefully because they depend on orientation. We are able to apply the axis theorem for simple calculations.
Formula Used:
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{Mg{l_{cm}}}}} $
Complete answer:
First case:
The first scenario, where the ring is suspended at a location on its rim and oscillates so that the centre travels in its own plane, can be represented by the diagram below.

For a physical pendulum, time period is given by,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{Mg{l_{cm}}}}} $
Where,
I is the moment of inertia of the pendulum about the axis of its support,
M is the mass of the pendulum
g is the acceleration due to gravity
${l_{cm}}$ is the distance of the centre of mass of the pendulum from the point of support.
Moment of inertia is the property of a body that prevents it from resisting angular acceleration. It is calculated by multiplying each particle's mass times the square of its distance from the axis of rotation.
Since a ring is suspended from its rim in the first scenario, its centre of mass is in the centre, making the radius of the ring $R$ the distance between the centre of mass and the support,
$ \Rightarrow {l_{cm}} = R$
The moment of inertia of a ring about its diameter is given by
${I_1} = M{R^2}$
We require the moment of inertia about its tangent, because this is where it is attached to the support.
By the parallel axis theorem. The distance between the axis of diameter and the axis of support is $R$
Therefore,
${I_1} = M{R^2} + M{R^2} = 2M{R^2}$
Substituting all of these values in the equation for time period we get,
${T_1} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{Mg{l_{cm}}}}} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{2M{R^2}}}{{MgR}}} $
${T_1} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{2R}}{g}} $
For second case

${I_2} = \dfrac{3}{2}M{R^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {T_2} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_2}}}{{Mg{l_{cm}}}}} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{2}M{R^2}}}{{MgR}}} $
${T_2} = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{3R}}{{2g}}} $
Taking the ratio we get, $\dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{4}{3}} = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Therefore, correct option is (C).
Note:A physical pendulum can be any size or shape, and it can have a distinct centre of mass and moment of inertia. There are two sorts of pendulums: simple and physical. Moment of inertia calculations for both scenarios should be done carefully because they depend on orientation. We are able to apply the axis theorem for simple calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




