
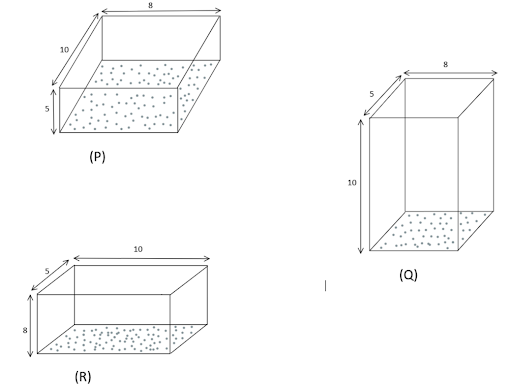
A rectangular block of size $10cm \times 8cm \times 5cm$ is kept in three different positions P, Q and R in turns as shown in the figure. In case, the shaded area is rigidly fixed and a definite force F is applied tangentially to the opposite face to deform the block. The displacement to the upper face will be ?
A. Same in all three faces
B. Maximum in P position
C. Maximum in Q position
D. Maximum in R position
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:In the case, when a problem is based on the mechanical properties of a solid, we know that the Modulus of Rigidity plays a significant role in establishing a relationship between shear stress and shear strain hence, apply the formula of modulus of rigidity in the given problem in order to provide an accurate solution.
Formula used:
The formula of Modulus of Rigidity is,
$\text{Modulus of Rigidity}(\eta ) = \dfrac{\text{Shear Stress}({\sigma _s})}{\text{Shear Strain}(\theta )}$
The formula of shear stress is,
$\text{Shear Stress}({\sigma _s}) = \dfrac{\text{Force}}{\text{Area}}$
The formula of shear strain is,
$\text{Shear Strain}( \theta ) = \dfrac{{\Delta x}}{l}$
Complete step by step solution:
We know that $\text{Modulus of Rigidity}(\eta ) = \dfrac{\text{Shear Stress}({\sigma _s})}{\text{Shear Strain}(\theta )}$ … (1)
But $\text{Shear Stress}({\sigma _s}) = \dfrac{\text{Force}}{\text{Area}} = \dfrac{F}{A}$ and $\text{Shear Strain}(\theta ) = \dfrac{{\Delta x}}{l}$
From eq. (1), we get
$ \Rightarrow \eta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{F}{A}}}{{\dfrac{{\Delta x}}{l}}} = \dfrac{{F.l}}{{A.\Delta x}}$
Or, it can also be written as: -
$ \Rightarrow \Delta x = \dfrac{F}{\eta }.\dfrac{l}{A}$
Now if F and $\eta $ are constant, then $\Delta x$ varies with $\dfrac{l}{A}$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta x = \left( k \right)\dfrac{l}{A}$.......$\left( {Let,k = \dfrac{F}{\eta }} \right)$
Let us consider all the three cases given one by one: -
At position P, $\Delta x = \left( k \right)\dfrac{5}{{10 \times 8}} = \dfrac{{5k}}{{80}}$
At position Q, $\Delta x = \left( k \right)\dfrac{{10}}{{5 \times 8}} = \dfrac{{10k}}{{40}}$
At position R, $\Delta x = \left( k \right)\dfrac{8}{{10 \times 5}} = \dfrac{{8k}}{{50}}$
Clearly, it can be seen that the displacement to the upper face will be maximum in Q position rather than P and R. Thus, the displacement to the upper face will be maximum in Q position.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Since this is a problem related to stress-strain analysis in mechanics hence, given conditions are analyzed very carefully, and quantities that are required to find the maximum displacement, such as shear modulus must be identified on a prior basis as it gives a better understanding of the problem.
Formula used:
The formula of Modulus of Rigidity is,
$\text{Modulus of Rigidity}(\eta ) = \dfrac{\text{Shear Stress}({\sigma _s})}{\text{Shear Strain}(\theta )}$
The formula of shear stress is,
$\text{Shear Stress}({\sigma _s}) = \dfrac{\text{Force}}{\text{Area}}$
The formula of shear strain is,
$\text{Shear Strain}( \theta ) = \dfrac{{\Delta x}}{l}$
Complete step by step solution:
We know that $\text{Modulus of Rigidity}(\eta ) = \dfrac{\text{Shear Stress}({\sigma _s})}{\text{Shear Strain}(\theta )}$ … (1)
But $\text{Shear Stress}({\sigma _s}) = \dfrac{\text{Force}}{\text{Area}} = \dfrac{F}{A}$ and $\text{Shear Strain}(\theta ) = \dfrac{{\Delta x}}{l}$
From eq. (1), we get
$ \Rightarrow \eta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{F}{A}}}{{\dfrac{{\Delta x}}{l}}} = \dfrac{{F.l}}{{A.\Delta x}}$
Or, it can also be written as: -
$ \Rightarrow \Delta x = \dfrac{F}{\eta }.\dfrac{l}{A}$
Now if F and $\eta $ are constant, then $\Delta x$ varies with $\dfrac{l}{A}$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta x = \left( k \right)\dfrac{l}{A}$.......$\left( {Let,k = \dfrac{F}{\eta }} \right)$
Let us consider all the three cases given one by one: -
At position P, $\Delta x = \left( k \right)\dfrac{5}{{10 \times 8}} = \dfrac{{5k}}{{80}}$
At position Q, $\Delta x = \left( k \right)\dfrac{{10}}{{5 \times 8}} = \dfrac{{10k}}{{40}}$
At position R, $\Delta x = \left( k \right)\dfrac{8}{{10 \times 5}} = \dfrac{{8k}}{{50}}$
Clearly, it can be seen that the displacement to the upper face will be maximum in Q position rather than P and R. Thus, the displacement to the upper face will be maximum in Q position.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Since this is a problem related to stress-strain analysis in mechanics hence, given conditions are analyzed very carefully, and quantities that are required to find the maximum displacement, such as shear modulus must be identified on a prior basis as it gives a better understanding of the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




