
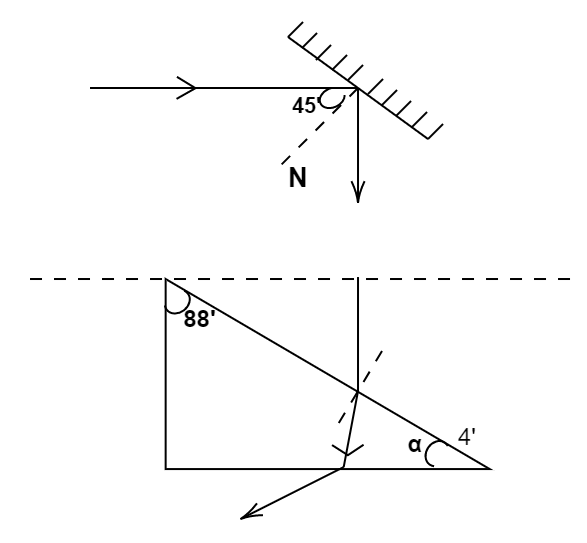
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of incidence ${45^ \circ }$ as shown in fig. After reflection, the ray passes through a prism of the refractive index $1.5$ whose apex angle is ${4^ \circ }$ . If the mirror is rotated by $X$ degrees then the total deviation of the ray becomes ${90^ \circ }$ . Find X?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint When a ray of light travels through a glass prism, it undergoes refraction and gets deviated from its original path. The deviation made by a small angled prism is always ${2^ \circ }$ . Furthermore, it is specified when the mirror is rotated by X degrees then the total deviation of the ray becomes ${90^ \circ }$. Substitute these values to the basic formula and solve for the answer.
Complete step-by-step solution
When a light ray enters through a glass prism, the emergent ray is not parallel to the incident ray after refraction. Relatively, the emergent ray diverges from its original direction by a certain angle, known as the angle of deviation.
In the case of a prism the deviation, ${\delta _m}$ of the emergent ray is given by:
$\mu = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}}}{{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}}$
If the angle of the prism $A$ is small,
${\delta _m}$ is also small. So the equation becomes:
${\delta _m} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)A$
As a result, the deviation made via a small angled prism is always, given by
${\delta _1} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\alpha = \left( {1.5 - 1} \right){4^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow {\delta _1} = {2^ \circ }$
Deviation caused by the mirror will be:
${\delta _2} = {180^ \circ } - 2i$
${\delta _2} = {180^ \circ } - 2 \times {45^ \circ }$
${\delta _2} = {90^ \circ }$
Hence, the net deviation made by the system will be;
${\delta _1} + {\delta _2} = {2^ \circ } + {90^ \circ }$
$\therefore {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} = {92^ \circ }$
The total deviation is more than ${90^ \circ }$ .
If the angle of incidence on the mirror is larger than its associated deviation will be reduced. Let $X$ be the angle of rotation of mirror in clockwise direction done to raise the angle of incidence, so deviation made by the mirror=
${180^ \circ } + 2\left( {{{45}^ \circ } + X} \right) = {90^ \circ } - 2X$
Hence, the total deviation produced=
${90^ \circ } - 2X + {2^ \circ } = {92^ \circ } - 2X$
However, it is detailed the mirror be rotated by $X$ degrees then the total deviation of the ray becomes ${90^ \circ }$ ,
${92^ \circ } - 2X = {90^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow X = {1^ \circ }$
Therefore, the mirror is rotated by ${1^ \circ }$ then the total deviation of the ray becomes ${90^ \circ }$ .
Note Draw a well-labeled diagram of the given reflection and refraction scenario for a better understanding of the given question as visual clues will help. Formulas and universal facts like the deviation produced by a small angled prism are always ${2^ \circ }$, must be learned by the students.
Complete step-by-step solution
When a light ray enters through a glass prism, the emergent ray is not parallel to the incident ray after refraction. Relatively, the emergent ray diverges from its original direction by a certain angle, known as the angle of deviation.
In the case of a prism the deviation, ${\delta _m}$ of the emergent ray is given by:
$\mu = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}}}{{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}}$
If the angle of the prism $A$ is small,
${\delta _m}$ is also small. So the equation becomes:
${\delta _m} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)A$
As a result, the deviation made via a small angled prism is always, given by
${\delta _1} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\alpha = \left( {1.5 - 1} \right){4^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow {\delta _1} = {2^ \circ }$
Deviation caused by the mirror will be:
${\delta _2} = {180^ \circ } - 2i$
${\delta _2} = {180^ \circ } - 2 \times {45^ \circ }$
${\delta _2} = {90^ \circ }$
Hence, the net deviation made by the system will be;
${\delta _1} + {\delta _2} = {2^ \circ } + {90^ \circ }$
$\therefore {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} = {92^ \circ }$
The total deviation is more than ${90^ \circ }$ .
If the angle of incidence on the mirror is larger than its associated deviation will be reduced. Let $X$ be the angle of rotation of mirror in clockwise direction done to raise the angle of incidence, so deviation made by the mirror=
${180^ \circ } + 2\left( {{{45}^ \circ } + X} \right) = {90^ \circ } - 2X$
Hence, the total deviation produced=
${90^ \circ } - 2X + {2^ \circ } = {92^ \circ } - 2X$
However, it is detailed the mirror be rotated by $X$ degrees then the total deviation of the ray becomes ${90^ \circ }$ ,
${92^ \circ } - 2X = {90^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow X = {1^ \circ }$
Therefore, the mirror is rotated by ${1^ \circ }$ then the total deviation of the ray becomes ${90^ \circ }$ .
Note Draw a well-labeled diagram of the given reflection and refraction scenario for a better understanding of the given question as visual clues will help. Formulas and universal facts like the deviation produced by a small angled prism are always ${2^ \circ }$, must be learned by the students.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




