
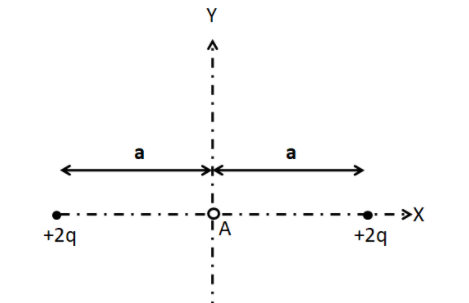
A point charge $ - q$ placed at the point A is
(A) In stable equilibrium along x-axis
(B) In unstable equilibrium along y-axis
(C) In stable equilibrium along y-axis
(D) In unstable equilibrium along x-axis
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To determine the nature of equilibrium along a particular direction, we need to displace the charge by a small displacement along that direction. If the net force acting on the charge is towards the equilibrium position, then the equilibrium is stable. But if the net force is away from the equilibrium position, then the equilibrium is unstable.
Complete step-by-step solution:
As can be seen in the given figure, the charge particle is symmetrically placed with respect to both of the charges of $ + 2q$. So the charge is in equilibrium at the point A. Now, for determining the nature of this equilibrium along the x and the y axis, we displace the charge through a small displacement along these directions separately.
For x direction:
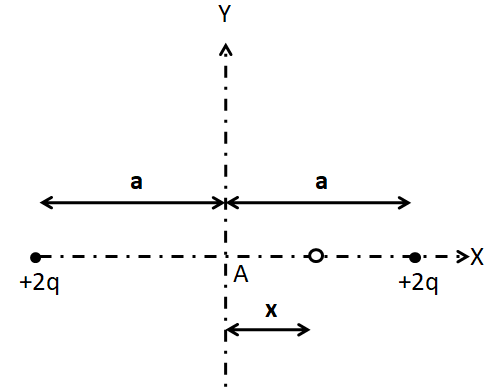
Let us displace the charge through a small displacement $x$ as shown in the below figure.
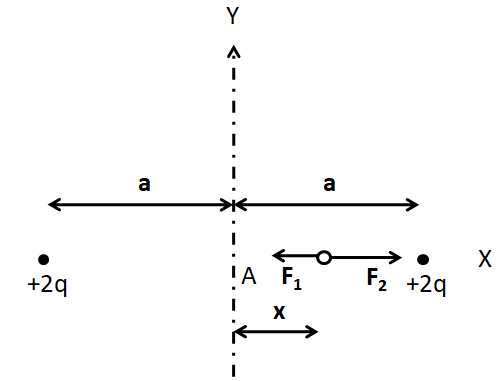
Since this charge is negative and both of the fixed charges are positive, so the charge will get attracted by the fixed charge. Let the force due to the left charge be \[{F_1}\] and that due to the right charge be ${F_2}$. So these can be shown in the figure below.
The distance of the charge from the left fixed charge is
${x_1} = a + x$
And the distance from the right fixed charge is
${x_2} = a - x$
Since the electrostatic force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, so \[{F_1}\] will be less than ${F_2}$.
Therefore, the net force on the charge will be towards the right, that is, away from the equilibrium position A.
So the charge is in unstable equilibrium along the x-axis.
Therefore, the option D is correct.
For y direction:
Let us displace the charge through a small displacement $y$ as shown in the below figure.
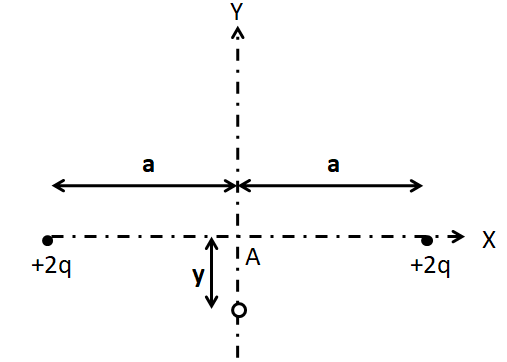
Since the charge is negative, it will get attracted by both of the fixed charges by forces of \[{F_1}\] and that due to the right charge be ${F_2}$ as shown in the figure below.
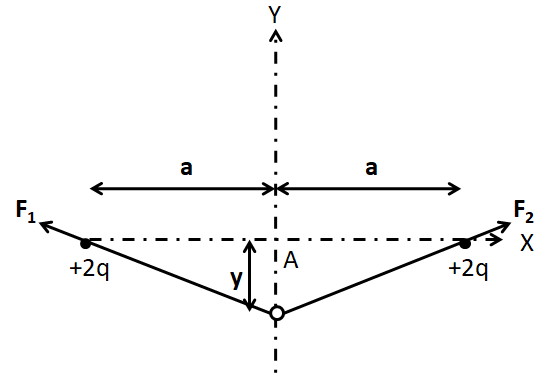
Since the charge is symmetric with respect to both the fixed charges, so \[{F_1}\] will be equal to ${F_2}$.
Therefore, the horizontal components of both the forces will get cancelled and the vertical components of the forces will get added up. Thus, the net force on the charged particle will be vertically downwards, that is, towards the equilibrium position.
So the charge is in stable equilibrium along the y-axis.
Therefore, the option C is also correct.
Hence, the correct options are C and D.
Note: There is no need to determine the magnitude of the net force after displacing the particle. We only need to find out the direction of the net force for determining the nature of equilibrium.
Complete step-by-step solution:
As can be seen in the given figure, the charge particle is symmetrically placed with respect to both of the charges of $ + 2q$. So the charge is in equilibrium at the point A. Now, for determining the nature of this equilibrium along the x and the y axis, we displace the charge through a small displacement along these directions separately.
For x direction:
Let us displace the charge through a small displacement $x$ as shown in the below figure.

Since this charge is negative and both of the fixed charges are positive, so the charge will get attracted by the fixed charge. Let the force due to the left charge be \[{F_1}\] and that due to the right charge be ${F_2}$. So these can be shown in the figure below.

The distance of the charge from the left fixed charge is
${x_1} = a + x$
And the distance from the right fixed charge is
${x_2} = a - x$
Since the electrostatic force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, so \[{F_1}\] will be less than ${F_2}$.
Therefore, the net force on the charge will be towards the right, that is, away from the equilibrium position A.
So the charge is in unstable equilibrium along the x-axis.
Therefore, the option D is correct.
For y direction:
Let us displace the charge through a small displacement $y$ as shown in the below figure.

Since the charge is negative, it will get attracted by both of the fixed charges by forces of \[{F_1}\] and that due to the right charge be ${F_2}$ as shown in the figure below.

Since the charge is symmetric with respect to both the fixed charges, so \[{F_1}\] will be equal to ${F_2}$.
Therefore, the horizontal components of both the forces will get cancelled and the vertical components of the forces will get added up. Thus, the net force on the charged particle will be vertically downwards, that is, towards the equilibrium position.
So the charge is in stable equilibrium along the y-axis.
Therefore, the option C is also correct.
Hence, the correct options are C and D.
Note: There is no need to determine the magnitude of the net force after displacing the particle. We only need to find out the direction of the net force for determining the nature of equilibrium.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




