
When a player hits a football, it moves along the curved path and falls on the ground. What is the work done by the force of gravity on the football?
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Zero
D) not defined
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In order to obtain the work done by the force of gravity on the football when the player kicks the particular football we have to find the angle formed between the direction of the football and the force of gravity.
Formula used:
The work done by the force of gravity on any particular particle or body is given by the following mathematical expression:
$W = F \times D\cos \theta $
Here D represents the distance and $\theta $ represents the angle between the two forces.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to solve this problem we have to first have a good idea of the path followed or travelled by the football when the player kicks the football. This can be represented using the diagram given below:
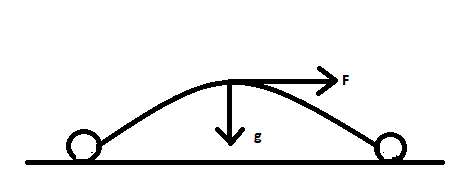
From the diagram we can clearly see that the two forces are perpendicular to each other. Thus, the angle made between the force with which the player kicks the football and the force of gravity is equal to ${90^ \circ }$. Now substituting this value of the angle between the two forces or $\theta$ in the above mathematical expression, we get:
$W = FD\cos {90^ \circ }$
Now, we know that the accurate value of $\cos {90^ \circ }$ is equal to 0. Thus, we have:
$ \Rightarrow W = F \times D \times 0 = 0$
Thus, we find that the work done by the force of gravity on the football when it is travelling in a curved path is equal to 0. Thus we can say that the force of gravity has no effect on the work done on the football. Or the force of gravity does not work on the football when the player kicks it.
Thus, we find that (C) is the correct answer to this problem.
Note: The force of gravity does maximum work when the two forces are opposite to each other. For example when a ball is thrown vertically upwards the force of gravity pulls the ball towards the earth. Thus, in this case maximum work is done by the force of gravity on the ball.
Formula used:
The work done by the force of gravity on any particular particle or body is given by the following mathematical expression:
$W = F \times D\cos \theta $
Here D represents the distance and $\theta $ represents the angle between the two forces.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to solve this problem we have to first have a good idea of the path followed or travelled by the football when the player kicks the football. This can be represented using the diagram given below:

From the diagram we can clearly see that the two forces are perpendicular to each other. Thus, the angle made between the force with which the player kicks the football and the force of gravity is equal to ${90^ \circ }$. Now substituting this value of the angle between the two forces or $\theta$ in the above mathematical expression, we get:
$W = FD\cos {90^ \circ }$
Now, we know that the accurate value of $\cos {90^ \circ }$ is equal to 0. Thus, we have:
$ \Rightarrow W = F \times D \times 0 = 0$
Thus, we find that the work done by the force of gravity on the football when it is travelling in a curved path is equal to 0. Thus we can say that the force of gravity has no effect on the work done on the football. Or the force of gravity does not work on the football when the player kicks it.
Thus, we find that (C) is the correct answer to this problem.
Note: The force of gravity does maximum work when the two forces are opposite to each other. For example when a ball is thrown vertically upwards the force of gravity pulls the ball towards the earth. Thus, in this case maximum work is done by the force of gravity on the ball.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




