
A pattern was observed without being able to view the source of the waves. The pattern is represented in the diagram.
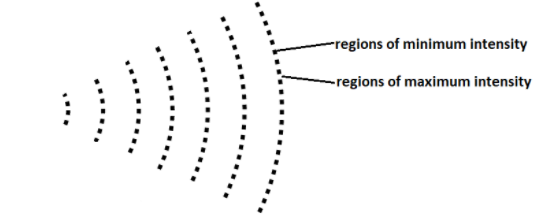
What can cause this pattern?
(A) Coherence only
(B) Diffraction and interference
(C) Diffraction only
(D) Interference only
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: When light waves from two (or one) coherent sources overlap with each other they create a pattern of bright and dark fringes. In interference, two coherent sources of light superpose over each other. While in diffraction the pattern is created due to bending of light due to edges of an object.
Complete step by step answer:
Looking at the terms used in the options we have:
Coherence: Two waves are said to be coherent when they have the same frequency and waveform the phase difference between remains constant. A coherent source of light can be created using a single, monochromatic source of light and passing it through two narrow slits situated at equal distance from the light source.
Interference: When light coming from two coherent sources, traveling in the same direction superposes over each other. The two waves are then added/ subtracted depending on their path difference. The places where the waves cancel out completely creates dark fringes whereas the places where the waves add up creates the bright fringes. There is no sharp boundary that separates the fringes so all the distances are measured with respect to the positions of the brightest and the darkest fringes. Interference creates a central bright fringe which has the largest intensity, followed by the darkest fringes on its either sides, after this as we increase the distance, the difference between intensities of the bright and dark fringes gets less prominent.
Diffraction: When a light wave coming from a single source encounters an obstacle or a hole, it bends around it, this phenomenon is known as diffraction. As the bent light now has a path difference, the waves superimpose over each other creating the addition and subtraction of the amplitudes, thus resulting in creation of fringes.
Thus it is clear that both, diffraction and interference can produce such pattern, the correct option is (B)
Note: Diffraction is different from interference as the central fringe produced is dark. Also, a diffraction pattern can have different shapes depending on the shape of hole and the object while the interference pattern (in YDSE) is hyperbolic in shape.
Complete step by step answer:
Looking at the terms used in the options we have:
Coherence: Two waves are said to be coherent when they have the same frequency and waveform the phase difference between remains constant. A coherent source of light can be created using a single, monochromatic source of light and passing it through two narrow slits situated at equal distance from the light source.
Interference: When light coming from two coherent sources, traveling in the same direction superposes over each other. The two waves are then added/ subtracted depending on their path difference. The places where the waves cancel out completely creates dark fringes whereas the places where the waves add up creates the bright fringes. There is no sharp boundary that separates the fringes so all the distances are measured with respect to the positions of the brightest and the darkest fringes. Interference creates a central bright fringe which has the largest intensity, followed by the darkest fringes on its either sides, after this as we increase the distance, the difference between intensities of the bright and dark fringes gets less prominent.
Diffraction: When a light wave coming from a single source encounters an obstacle or a hole, it bends around it, this phenomenon is known as diffraction. As the bent light now has a path difference, the waves superimpose over each other creating the addition and subtraction of the amplitudes, thus resulting in creation of fringes.
Thus it is clear that both, diffraction and interference can produce such pattern, the correct option is (B)
Note: Diffraction is different from interference as the central fringe produced is dark. Also, a diffraction pattern can have different shapes depending on the shape of hole and the object while the interference pattern (in YDSE) is hyperbolic in shape.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




