
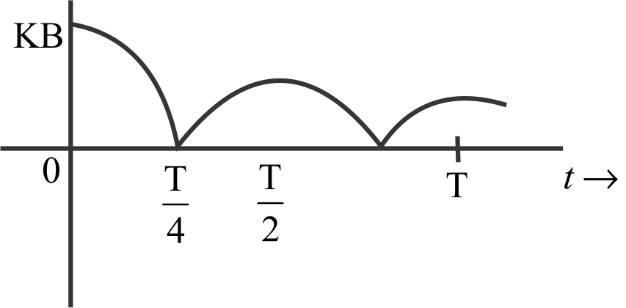
A particle is executing simple harmonic motion with a time period $T$. At the time $t = 0$, it is at its position of equilibrium. The kinetic energy-time graph of the particle will look like:
$\left( a \right)$
$\left( b \right)$
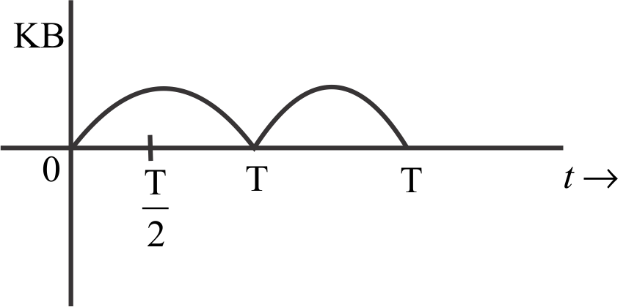
$\left( c \right)$

$\left( d \right)$
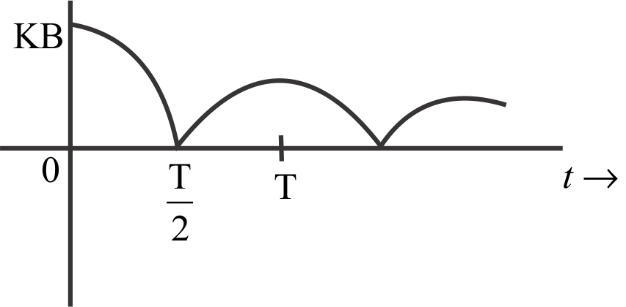
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We have been given a particle having a simple harmonic motion about its equilibrium position. And we know whenever a particle performs the simple harmonic motion, it varies with time. And velocity at the mean position will be maximum. By using all this information we can answer this question.
Complete Step By Step Solution:
After executing the simple harmonic motion, the position of the particle will be
So it can be represented as -
$x = A\sin \omega t$
Now the velocity function can be represented by,
Velocity function is $v = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$
Since,
$v = A\omega \cos \omega t$
Kinetic energy, K.E. will be written as
$K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
On substituting the values of the velocity, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{A^2}{\omega ^2}{\cos ^2}\omega t$
From this, we can say that the kinetic energy will be directly proportional to the ${\cos ^2}\omega t$
Mathematically, it can be written as
$ \Rightarrow K.E \propto {\cos ^2}\omega t$
But at $t = \dfrac{T}{4}$
The value of the angle will be
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\omega \dfrac{r}{4}} \right) = 0$
Therefore by putting the values, we get the kinetic energy will be equal to zero.
Mathematically, it can be written as
$ \Rightarrow K.E = 0$
Now we will check at $t = \dfrac{T}{2}$
The value of the angle will be
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\omega \dfrac{r}{2}} \right) = - 1$
Therefore by putting the values, we get the kinetic energy will be positive and hence kinetic energy will be maximum.
Now we will check it$t = T$, we get
The value of the angle will be
$\cos \left( {\omega T} \right) = 1$
Therefore by putting the values, we get the kinetic energy will be positive and hence kinetic energy will be maximum
So from all the equations we had got the options $A$ to match all the criteria.
Note: When harmonic motion occurs harmonic functions are the waveforms of the motions that result. In other cases, for example, various musical instruments, when the player stimulates the instrument in a certain way, multiple wavelengths of response are being stimulated at the same time. In that case, the waveform produced will be a combination of different frequencies.
Complete Step By Step Solution:
After executing the simple harmonic motion, the position of the particle will be
So it can be represented as -
$x = A\sin \omega t$
Now the velocity function can be represented by,
Velocity function is $v = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$
Since,
$v = A\omega \cos \omega t$
Kinetic energy, K.E. will be written as
$K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
On substituting the values of the velocity, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{A^2}{\omega ^2}{\cos ^2}\omega t$
From this, we can say that the kinetic energy will be directly proportional to the ${\cos ^2}\omega t$
Mathematically, it can be written as
$ \Rightarrow K.E \propto {\cos ^2}\omega t$
But at $t = \dfrac{T}{4}$
The value of the angle will be
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\omega \dfrac{r}{4}} \right) = 0$
Therefore by putting the values, we get the kinetic energy will be equal to zero.
Mathematically, it can be written as
$ \Rightarrow K.E = 0$
Now we will check at $t = \dfrac{T}{2}$
The value of the angle will be
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\omega \dfrac{r}{2}} \right) = - 1$
Therefore by putting the values, we get the kinetic energy will be positive and hence kinetic energy will be maximum.
Now we will check it$t = T$, we get
The value of the angle will be
$\cos \left( {\omega T} \right) = 1$
Therefore by putting the values, we get the kinetic energy will be positive and hence kinetic energy will be maximum
So from all the equations we had got the options $A$ to match all the criteria.
Note: When harmonic motion occurs harmonic functions are the waveforms of the motions that result. In other cases, for example, various musical instruments, when the player stimulates the instrument in a certain way, multiple wavelengths of response are being stimulated at the same time. In that case, the waveform produced will be a combination of different frequencies.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




