
A massless rod having length $2l$ has equal point masses attached to its two ends shown in figure. The rod is rotating about its axis passing through its centre and making angle $\alpha $ with the axis. The magnitude change of momentum of rod, i.e., $(\left| {\dfrac{{dL}}{{dt}}} \right|)$ equals?
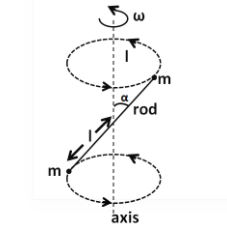
(A) \[2{m^3}{\omega ^3}\sin {\theta}\cos {\theta} \]
(B) \[m{l^2}{\omega ^2}\sin 2{\theta}\]
(C) \[m{v^2}\sin 2{\theta}\]
(D) \[{m^{1/2}}{l^{1/2}}\omega \sin {\theta }\cos {\theta}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to find out the expression of the torque exerted on both the point masses, due to which they are rotating. The net torque on the system will be equal to the sum of the two torques on the two particles.
Formula used: The formula used to solve this question is given by
$\tau = {r_P}F$, here $\tau $ is the torque exerted on a particle due to a force of $F$, which is applied at a perpendicular distance of ${r_p}$ from the particle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that the rate of change of momentum of a system is equal to the net external torque acting on the system.
So for finding out the rate of change of momentum of the rod, we have to find out the net external torque on the rod.
As can be seen on the figure, the torque on the given rod is due to the rotation of the two point masses which are attached to it.
We label the points on the given figure as shown in the figure below.
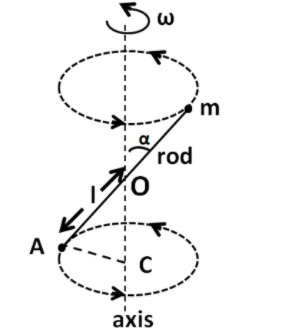
Here C is the centre of the lower circle. Now, we have
$\angle AOC = \alpha $ (Vertically opposite angles)
In the triangle OAC we have
$\sin \alpha = \dfrac{{AC}}{{OA}}$
$ \Rightarrow AC = OA\sin \alpha $
From the figure, $OA = l$. Therefore we have
$AC = l\sin \alpha $
So the radius of the lower circle is equal to $l\sin \alpha $.
As the point mass $m$ is rotating in the lower circle, so the centripetal force towards the centre can be given by
$F = m{\omega ^2}l\sin \alpha $ ………...(1)
Now, for finding the torque exerted by this mass on the rod, we have to consider the torque about the centre of the rod, O. We know that the magnitude of the torque is given by
${\tau _1} = {r_P}F$...........(2)
From the above figure, we have
${r_p} = OC$
$ \Rightarrow {r_p} = l\cos \alpha $..................(3)
Putting (1) and (3) in (2) we get
${\tau _1} = m{\omega ^2}l\sin \alpha \times l\cos \alpha $
$ \Rightarrow {\tau _1} = m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha $................(4)
Similarly the torque exerted by the other point mass on the rod is
${\tau _2} = m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha $ ………...(5)
As these torques are in the same direction, so the net torque on the rod is given by
$\tau = {\tau _1} + {\tau _2}$
Putting (4) and (5) in the above equation, we finally get
$\tau = m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha + m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha $
$ \Rightarrow \tau = 2m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha $
We know that $\sin 2{\theta } = 2\sin {\theta}\cos {\theta }$. Therefore we have
$\tau = m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin 2\alpha $
Thus, the magnitude of the rate of change of momentum of the rod is equal to $m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin 2\alpha $.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: There also exists another formula for the torque, which is equal to the moment of inertia and the angular acceleration. But that formula is not applicable here because the rod is massless, which means that its moment of inertia will be zero.
Formula used: The formula used to solve this question is given by
$\tau = {r_P}F$, here $\tau $ is the torque exerted on a particle due to a force of $F$, which is applied at a perpendicular distance of ${r_p}$ from the particle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that the rate of change of momentum of a system is equal to the net external torque acting on the system.
So for finding out the rate of change of momentum of the rod, we have to find out the net external torque on the rod.
As can be seen on the figure, the torque on the given rod is due to the rotation of the two point masses which are attached to it.
We label the points on the given figure as shown in the figure below.

Here C is the centre of the lower circle. Now, we have
$\angle AOC = \alpha $ (Vertically opposite angles)
In the triangle OAC we have
$\sin \alpha = \dfrac{{AC}}{{OA}}$
$ \Rightarrow AC = OA\sin \alpha $
From the figure, $OA = l$. Therefore we have
$AC = l\sin \alpha $
So the radius of the lower circle is equal to $l\sin \alpha $.
As the point mass $m$ is rotating in the lower circle, so the centripetal force towards the centre can be given by
$F = m{\omega ^2}l\sin \alpha $ ………...(1)
Now, for finding the torque exerted by this mass on the rod, we have to consider the torque about the centre of the rod, O. We know that the magnitude of the torque is given by
${\tau _1} = {r_P}F$...........(2)
From the above figure, we have
${r_p} = OC$
$ \Rightarrow {r_p} = l\cos \alpha $..................(3)
Putting (1) and (3) in (2) we get
${\tau _1} = m{\omega ^2}l\sin \alpha \times l\cos \alpha $
$ \Rightarrow {\tau _1} = m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha $................(4)
Similarly the torque exerted by the other point mass on the rod is
${\tau _2} = m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha $ ………...(5)
As these torques are in the same direction, so the net torque on the rod is given by
$\tau = {\tau _1} + {\tau _2}$
Putting (4) and (5) in the above equation, we finally get
$\tau = m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha + m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha $
$ \Rightarrow \tau = 2m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin \alpha \cos \alpha $
We know that $\sin 2{\theta } = 2\sin {\theta}\cos {\theta }$. Therefore we have
$\tau = m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin 2\alpha $
Thus, the magnitude of the rate of change of momentum of the rod is equal to $m{\omega ^2}{l^2}\sin 2\alpha $.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: There also exists another formula for the torque, which is equal to the moment of inertia and the angular acceleration. But that formula is not applicable here because the rod is massless, which means that its moment of inertia will be zero.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




