
A liquid is contaminated with non-volatile impurities. Suggest method of purification.
(A) Sedimentation
(B) Distillation
(C) Centrifugation
(D) Evaporation
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Purification means removal of unwanted impurities present in an organic compound. The general methods of purification are sublimation, crystallization, distillation and many more. Moreover, the process of extracting something from a substance is also known as purification.
Complete step by step answer:
The method of purification of the organic compound depends mainly on the nature of the compound and the impurities present.
One easy method to check the purity of an organic compound is to either melt or boil it, as organic compounds tend to have sharp melting and boiling points.
Further, distillation is the process used for separating a liquid with non-volatile impurities. It is a separation technique used to either increase the concentration of a particular component in the mixture or to obtain pure components from the mixture. The process is as shown:
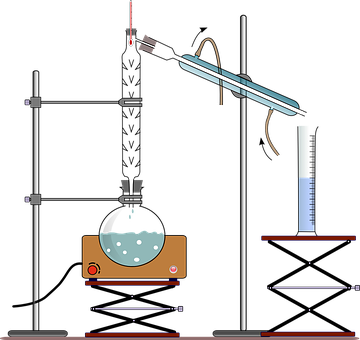
However, the distillation performed on a laboratory scale often uses batches of the liquid mixture whereas industrial distillation processes are generally continuous, requiring a constant composition of the mixture to be maintained.
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: Since a component in the mixture cannot have zero partial pressure, it is impossible to obtain a completely pure sample of a component from a mixture via distillation. Further, evaporation is a process of turning liquid to vapor. In case of sedimentation, the molecules or particles sediment downwards due to gravitational force and hence, centrifugation facilitates this process with centrifugal force by separating the particles into solid and liquid solvent.
Complete step by step answer:
The method of purification of the organic compound depends mainly on the nature of the compound and the impurities present.
One easy method to check the purity of an organic compound is to either melt or boil it, as organic compounds tend to have sharp melting and boiling points.
Further, distillation is the process used for separating a liquid with non-volatile impurities. It is a separation technique used to either increase the concentration of a particular component in the mixture or to obtain pure components from the mixture. The process is as shown:

However, the distillation performed on a laboratory scale often uses batches of the liquid mixture whereas industrial distillation processes are generally continuous, requiring a constant composition of the mixture to be maintained.
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: Since a component in the mixture cannot have zero partial pressure, it is impossible to obtain a completely pure sample of a component from a mixture via distillation. Further, evaporation is a process of turning liquid to vapor. In case of sedimentation, the molecules or particles sediment downwards due to gravitational force and hence, centrifugation facilitates this process with centrifugal force by separating the particles into solid and liquid solvent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




