
A hydrocarbon X adds on one mole of hydrogen to give another hydrocarbon and decolorized bromine water. X reacts with\[KMn{O_4}\] in presence of acid to give two moles of the same carboxylic acid. The structure of X is
A. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
B. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{CH = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
C. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{CH = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
D. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CH = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The reaction of an alkene with bromine is an addition reaction. Alkene when reacted with bromine forms vicinal dihalides or 1,2-dihalides. Alkene on reaction with acidic potassium permanganate undergoes oxidation.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Here in this question, we are given a hydrocarbon X which adds on one mole of hydrogen to give another hydrocarbon and decolorized bromine water.
It then reacts with KMnO4 in presence of acid to give two moles of the same carboxylic acid.
We have to find out the compound.
A. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
This compound when added with bromine will give \[BrC{H_2}CHBr - C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\].
\[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3} + {\rm{ }}B{r_2} \to C{H_2}BrCHBr - C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\]
This compound on oxidation with acidified KMnO4 will give methanoic acid and butanoic acid.
The reaction will happen as follows:-

Image: Reaction with acidified potassium permanganate.
So, A is incorrect.
B. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{CH = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
This compound when added with bromine will give\[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2} - CHBrCHBrC{H_3}\].
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2} - CH = CHC{H_3} + {\rm{ }}B{r_2} \to C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2} - CHBrCHBrC{H_3}\]
This compound on oxidation with acidified KMnO4 will give butanoic acid and ethanoic acid.
The reaction will happen as follows:-
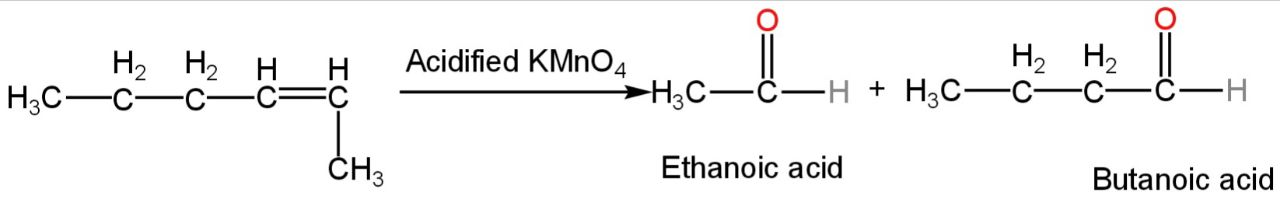
Image: Reaction with acidified potassium permanganate.
So, B is incorrect.
C. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{CH = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
This compound when added with bromine will give\[C{H_3}C{H_2}CHBrCHBrC{H_2}C{H_3}\].
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}CH = CHC{H_2}C{H_{3\;}} + {\rm{ }}B{r_2} \to C{H_3}C{H_2}CHBrCHBrC{H_2}C{H_3}\]
This compound on oxidation with acidified KMnO4 will give two moles of propanoic acid.
The reaction will happen as follows:-

Image: Reaction with acidified potassium permanganate.
Since this compound reacts with KMnO4 in presence of acid to give two moles of the same carboxylic acid.
So, C is correct.
D. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CH = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
This compound when added with bromine will give\[C{H_3}CHBrCHBrC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\].
\[C{H_3}CH = CHC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3} + B{r_2} \to C{H_3}CHBrCHBrC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\]
This compound on oxidation with acidified KMnO4 will give ethanoic acid and butanoic acid.
The reaction will happen as follows:-
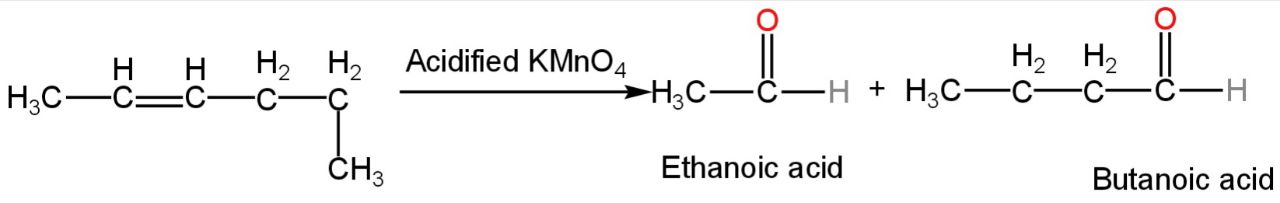
Image: Reaction with acidified potassium permanganate.
So, D is incorrect.
So, option C is correct.
Note: Out of the given options, the only option C is a symmetrical alkene. So, it will form two same carboxylic acids on oxidation. Acidified potassium permanganate is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises alkene by breaking down the carbon-carbon double bond and converting it into two carbon-oxygen double bonds i.e., \[C = O\].
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Here in this question, we are given a hydrocarbon X which adds on one mole of hydrogen to give another hydrocarbon and decolorized bromine water.
It then reacts with KMnO4 in presence of acid to give two moles of the same carboxylic acid.
We have to find out the compound.
A. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
This compound when added with bromine will give \[BrC{H_2}CHBr - C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\].
\[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3} + {\rm{ }}B{r_2} \to C{H_2}BrCHBr - C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\]
This compound on oxidation with acidified KMnO4 will give methanoic acid and butanoic acid.
The reaction will happen as follows:-

Image: Reaction with acidified potassium permanganate.
So, A is incorrect.
B. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{CH = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
This compound when added with bromine will give\[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2} - CHBrCHBrC{H_3}\].
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2} - CH = CHC{H_3} + {\rm{ }}B{r_2} \to C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2} - CHBrCHBrC{H_3}\]
This compound on oxidation with acidified KMnO4 will give butanoic acid and ethanoic acid.
The reaction will happen as follows:-

Image: Reaction with acidified potassium permanganate.
So, B is incorrect.
C. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{CH = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
This compound when added with bromine will give\[C{H_3}C{H_2}CHBrCHBrC{H_2}C{H_3}\].
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}CH = CHC{H_2}C{H_{3\;}} + {\rm{ }}B{r_2} \to C{H_3}C{H_2}CHBrCHBrC{H_2}C{H_3}\]
This compound on oxidation with acidified KMnO4 will give two moles of propanoic acid.
The reaction will happen as follows:-

Image: Reaction with acidified potassium permanganate.
Since this compound reacts with KMnO4 in presence of acid to give two moles of the same carboxylic acid.
So, C is correct.
D. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CH = CHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
This compound when added with bromine will give\[C{H_3}CHBrCHBrC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\].
\[C{H_3}CH = CHC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3} + B{r_2} \to C{H_3}CHBrCHBrC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\]
This compound on oxidation with acidified KMnO4 will give ethanoic acid and butanoic acid.
The reaction will happen as follows:-

Image: Reaction with acidified potassium permanganate.
So, D is incorrect.
So, option C is correct.
Note: Out of the given options, the only option C is a symmetrical alkene. So, it will form two same carboxylic acids on oxidation. Acidified potassium permanganate is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises alkene by breaking down the carbon-carbon double bond and converting it into two carbon-oxygen double bonds i.e., \[C = O\].
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




