
A gas formed by the action of alcoholic KOH on ethyl iodide decolourises alkaline \[{\rm{KMn}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\] . The gas is:
A. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}\]
B. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}\]
C. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
D. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The dehydrohalogenation reaction is the reaction of an alkyl halide in which the removal of a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom takes place in presence of the action of alcoholic KOH. The obtained product in the reaction is an alkene.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let’s understand the dehydrohalogenation reaction of ethyl iodide by the action of potassium hydroxide which is alcoholic in nature. In this reaction, a molecule of hydrogen iodide is removed from the compound, and an alkene forms. The reaction is as follows:
\[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}} - {\rm{I}} + \,{\rm{Alc}}{\rm{.}}\,{\rm{KOH}} \to {{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}\]
So, the formation of ethene takes place in the above reaction.
Now, we will understand the decolorization of \[{\rm{KMn}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]. We know that pink colour of potassium permanganate (\[{\rm{KMn}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]) disappears when it undergoes a reaction with unsaturated compounds (alkene and alkyne). This reaction is termed Baeyer’s reaction. And Baeyer’s reagent is cold, acidified, and dilute potassium permanganate. And in this reaction, the formation of 1,2-diol occurs. The chemical reaction is shown below:
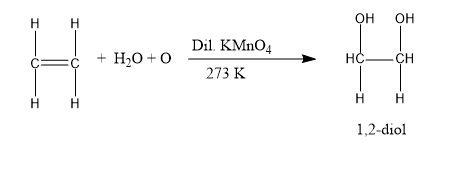
Image: Baeyer’s test
So, the gas produced in the dehydrohalogenation reaction of ethyl iodide, that is, ethene (\[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}\]) can decolorize the potassium permanganate.
Therefore, option D is right.
Note: It is to be noted that only the acidic nature of potassium permanganate gives the test of unsaturation. If the medium is alkaline, the reaction will change. In such conditions, the purple coloured permanganate (VII) changes to green coloured manganate (VII) ions first and then changes to manganese (IV) oxide which is of dark brown colour.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let’s understand the dehydrohalogenation reaction of ethyl iodide by the action of potassium hydroxide which is alcoholic in nature. In this reaction, a molecule of hydrogen iodide is removed from the compound, and an alkene forms. The reaction is as follows:
\[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}} - {\rm{I}} + \,{\rm{Alc}}{\rm{.}}\,{\rm{KOH}} \to {{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}\]
So, the formation of ethene takes place in the above reaction.
Now, we will understand the decolorization of \[{\rm{KMn}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]. We know that pink colour of potassium permanganate (\[{\rm{KMn}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]) disappears when it undergoes a reaction with unsaturated compounds (alkene and alkyne). This reaction is termed Baeyer’s reaction. And Baeyer’s reagent is cold, acidified, and dilute potassium permanganate. And in this reaction, the formation of 1,2-diol occurs. The chemical reaction is shown below:

Image: Baeyer’s test
So, the gas produced in the dehydrohalogenation reaction of ethyl iodide, that is, ethene (\[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}\]) can decolorize the potassium permanganate.
Therefore, option D is right.
Note: It is to be noted that only the acidic nature of potassium permanganate gives the test of unsaturation. If the medium is alkaline, the reaction will change. In such conditions, the purple coloured permanganate (VII) changes to green coloured manganate (VII) ions first and then changes to manganese (IV) oxide which is of dark brown colour.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




