
A force of 5N, making an angle \[\theta \] with the horizontal, acting on an object displaces it by 0.4m along the horizontal direction. If the object gains kinetic energy of 1J, then calculate the horizontal component of the force.
A. 1.5N
B. 2.5N
C. 3.5N
D. 4.5N
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:Before going to solve this question we need to understand the work-energy theorem. The work-energy theorem states that work done on an object is equal to the change in the kinetic energy.
Formula Used:
To find the work done the formula is,
\[W = \overrightarrow F \cdot \overrightarrow S \]
Where, \[\overrightarrow F \] is force applied and \[\overrightarrow S \] is displacement.
Complete step by step solution:
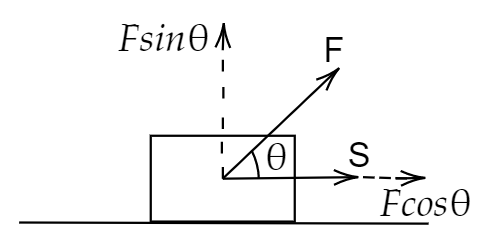
Image: Force acting on an object.
Consider an object which is getting displaced in the horizontal direction \[S = 0.4m\]. With respect to this horizontal direction a force of 5N is acting at some angle, by this, the object is gaining 1 J of kinetic energy. Let us find the horizontal component of force. In order to do that, the F is resolved into two components that are along the horizontal direction as \[F\cos \theta \] and vertical component as \[F\sin \theta \].
According to work-energy theorem we have,
Work done = gain in the kinetic energy
\[W = 1J\]
And also by the definition of work done we have,
\[W = \overrightarrow F \cdot \overrightarrow S \]
\[W = FS\cos \theta \]
Substitute the values of W and S we get,
\[1 = F\cos \theta \left( {0.4} \right)\]
\[F\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{0.4}}\]
\[ \therefore F\cos \theta = 2.5N\]
Therefore, the horizontal component of force is 2.5N.
Hence, option B is the correct answer.
Note:The force that is exerted on a body consists of two components one is the horizontal component and other is vertical component. Here we are using the horizontal component of force where a force is applied in a direction parallel to the horizon.
Formula Used:
To find the work done the formula is,
\[W = \overrightarrow F \cdot \overrightarrow S \]
Where, \[\overrightarrow F \] is force applied and \[\overrightarrow S \] is displacement.
Complete step by step solution:

Image: Force acting on an object.
Consider an object which is getting displaced in the horizontal direction \[S = 0.4m\]. With respect to this horizontal direction a force of 5N is acting at some angle, by this, the object is gaining 1 J of kinetic energy. Let us find the horizontal component of force. In order to do that, the F is resolved into two components that are along the horizontal direction as \[F\cos \theta \] and vertical component as \[F\sin \theta \].
According to work-energy theorem we have,
Work done = gain in the kinetic energy
\[W = 1J\]
And also by the definition of work done we have,
\[W = \overrightarrow F \cdot \overrightarrow S \]
\[W = FS\cos \theta \]
Substitute the values of W and S we get,
\[1 = F\cos \theta \left( {0.4} \right)\]
\[F\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{0.4}}\]
\[ \therefore F\cos \theta = 2.5N\]
Therefore, the horizontal component of force is 2.5N.
Hence, option B is the correct answer.
Note:The force that is exerted on a body consists of two components one is the horizontal component and other is vertical component. Here we are using the horizontal component of force where a force is applied in a direction parallel to the horizon.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




