
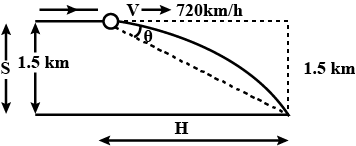
A fighter plane is flying horizontally at an altitude of 1.5 km with speed of 720 km/h. What angle of sight (w.r.t horizontal) when the target is seen, should the pilot drop the bomb in order to attack the target?
A) ${23^o}4'$
B) ${43^o}4'$
C) ${33^o}4'$
D) ${53^o}4'$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In these types of questions we follow the approach of Parabolic motion with the equation of motion in 2-D. We are going to break the motion in the x and y axis and then apply the equation of motion separately in horizontal and vertical motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Given is Vertical distance = S = 1.5 km
Speed=V=720km/h
The concept that we are to solve the question is as follows:
As clearly mentioned, the bomb will drop from the fighter plane so, when it leaves the plane at that instant its velocity becomes equal to the fighter jet. Hence, we can say at that instant the bomb will have only horizontal velocity and no vertical velocity.
As the time goes on it gains both horizontal and vertical velocity because of the presence of gravitational pull of acceleration \[g\] but remember there is no acceleration in horizontal direction.
So concept is clear now and we will proceed to the solution-
Using formula of semi parabolic,
Time of flight
Let us discuss how get the formula of time of fight:
So, let consider the motion in vertical axis that is y-axis
Applying 3rd equation of motion
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Where u is the initial velocity in vertical direction, t is the time taken and h is the height.
$u = 0$
So, $h = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
$
= t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{a}} {\text{ where a = g}} \\
{\text{Then H = horizontal distance = }}vt = 720 \times \sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 1500}}{{9.8}}} = 3.5km \\
{\text{So }}\tan \theta = \dfrac{{1.5}}{{3.5}} = 0.428 \\
\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}0.428 = {23.17^o} \\
$
(tan$\theta $=$\dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}}$)
Hence the closest answer is ${23^o}4'$
So option (A) is correct
Note: The main point to remember here is units as most of the student converts km/h into m/s but forget to convert the final units into km/h due which fluctuation in answer occurs. secondly always remember the trigonometric formulas it will help you in the whole course. Also when it is said ‘drops’ in the question we assume the bomb is dropped with zero force and zero velocity in the y-direction.
Complete step by step answer:
Given is Vertical distance = S = 1.5 km
Speed=V=720km/h
The concept that we are to solve the question is as follows:
As clearly mentioned, the bomb will drop from the fighter plane so, when it leaves the plane at that instant its velocity becomes equal to the fighter jet. Hence, we can say at that instant the bomb will have only horizontal velocity and no vertical velocity.
As the time goes on it gains both horizontal and vertical velocity because of the presence of gravitational pull of acceleration \[g\] but remember there is no acceleration in horizontal direction.
So concept is clear now and we will proceed to the solution-

Using formula of semi parabolic,
Time of flight
Let us discuss how get the formula of time of fight:
So, let consider the motion in vertical axis that is y-axis
Applying 3rd equation of motion
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Where u is the initial velocity in vertical direction, t is the time taken and h is the height.
$u = 0$
So, $h = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
$
= t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{a}} {\text{ where a = g}} \\
{\text{Then H = horizontal distance = }}vt = 720 \times \sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 1500}}{{9.8}}} = 3.5km \\
{\text{So }}\tan \theta = \dfrac{{1.5}}{{3.5}} = 0.428 \\
\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}0.428 = {23.17^o} \\
$
(tan$\theta $=$\dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}}$)
Hence the closest answer is ${23^o}4'$
So option (A) is correct
Note: The main point to remember here is units as most of the student converts km/h into m/s but forget to convert the final units into km/h due which fluctuation in answer occurs. secondly always remember the trigonometric formulas it will help you in the whole course. Also when it is said ‘drops’ in the question we assume the bomb is dropped with zero force and zero velocity in the y-direction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




