
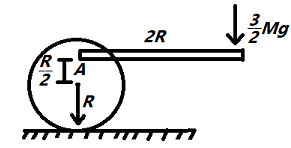
A disc of mass M and radius R is placed on a rough horizontal surface. A light rod of length 2R is fixed to the disc at point A as shown in the figure and force $\dfrac{3}{2}Mg$ is applied at the other end of the rod. Find the minimum value of coefficient of friction (upto one decimal place) between disc and horizontal surface, so that disc starts to roll without slipping.
A. $0.2$
B. $0.4$
C. $0.6$
D. $0.8$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Here in this question, we have to find the minimum value of friction by which the disk starts to roll without slipping. For which we must know that, Create an inclination plane out of one of the materials, then place a body made of the other material on it to determine the minimum coefficient of static friction between the two. Up until the body begins to slide, steepen the incline. The coefficient of friction is the angle's tangent.
Formula Used:
Frictional force,
$f \leqslant \mu N$
${\sigma _{net}} = I\alpha $
Complete step by step solution:
As we know that, the normal reaction value would be equal to,
$N = \dfrac{3}{2}Mg + Mg$
By taking solution, we get the value of N as,
$N = \dfrac{5}{2}Mg$
Now, we get the value of N from the above equation, after which putting the value of N in the Formula of Frictional force we get the value as,
$f \leqslant \dfrac{5}{2}\mu Mg$
For horizontal planes the value of friction will be $f = ma$.
As we mentioned the horizontal plane equation,
${\sigma _{net}} = I\alpha $
The net value from the diagram is,
$\dfrac{3}{2}Mg \times 2R - f \times R = \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{2}\alpha $
As we used all formula in the above equation such as the moment of inertia, after which now we put the value of frictional force in the above equation for horizontal plane,
$\dfrac{3}{2}Mg \times 2R - Ma \times R = \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{2} \times \dfrac{\alpha }{R}$
By solving the whole above equation, we get the value of acceleration as,
$a = 2g$
Now, we get the value of acceleration after putting the value of acceleration in frictional formula we get the value as,
$f = 2Mg$
Since, we also know that the relation from the limiting value of the frictional force as,
$f \leqslant \dfrac{5}{2}\mu Mg$ and $f = 2Mg$
As from the above equation we get the conclusion that,
$f = 2Mg \leqslant \dfrac{5}{2}\mu Mg$
Here, from this condition we get that the value of $\mu $ will be,
$\mu \geqslant \dfrac{4}{5} \geqslant 0.8$
As from the above conclusion we get the coefficient of friction should be greater than $0.8$. Therefore, the correct answer is $0.8$.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note: The quantity of friction between two surfaces is known as the coefficient of friction. Less force is required for sliding when the coefficient of friction is low. A greater score indicates that more force is necessary. As the force is increased, the object begins to move, and the force that opposes the movement of the object is referred to as frictional force or friction. Because there is no significant bodily movement, static friction has the lowest friction rating.
Formula Used:
Frictional force,
$f \leqslant \mu N$
${\sigma _{net}} = I\alpha $
Complete step by step solution:
As we know that, the normal reaction value would be equal to,
$N = \dfrac{3}{2}Mg + Mg$
By taking solution, we get the value of N as,
$N = \dfrac{5}{2}Mg$
Now, we get the value of N from the above equation, after which putting the value of N in the Formula of Frictional force we get the value as,
$f \leqslant \dfrac{5}{2}\mu Mg$
For horizontal planes the value of friction will be $f = ma$.
As we mentioned the horizontal plane equation,
${\sigma _{net}} = I\alpha $
The net value from the diagram is,
$\dfrac{3}{2}Mg \times 2R - f \times R = \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{2}\alpha $
As we used all formula in the above equation such as the moment of inertia, after which now we put the value of frictional force in the above equation for horizontal plane,
$\dfrac{3}{2}Mg \times 2R - Ma \times R = \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{2} \times \dfrac{\alpha }{R}$
By solving the whole above equation, we get the value of acceleration as,
$a = 2g$
Now, we get the value of acceleration after putting the value of acceleration in frictional formula we get the value as,
$f = 2Mg$
Since, we also know that the relation from the limiting value of the frictional force as,
$f \leqslant \dfrac{5}{2}\mu Mg$ and $f = 2Mg$
As from the above equation we get the conclusion that,
$f = 2Mg \leqslant \dfrac{5}{2}\mu Mg$
Here, from this condition we get that the value of $\mu $ will be,
$\mu \geqslant \dfrac{4}{5} \geqslant 0.8$
As from the above conclusion we get the coefficient of friction should be greater than $0.8$. Therefore, the correct answer is $0.8$.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note: The quantity of friction between two surfaces is known as the coefficient of friction. Less force is required for sliding when the coefficient of friction is low. A greater score indicates that more force is necessary. As the force is increased, the object begins to move, and the force that opposes the movement of the object is referred to as frictional force or friction. Because there is no significant bodily movement, static friction has the lowest friction rating.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




