
A cylindrical vessel partially filled with water is rotated about its vertical central axis, it's surface will
A. Rise equally
B. Rise from sides
C. Rise from the middle
D. Lowered equally
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:When a body is rotated about an axis then there is centripetal acceleration acting towards the center of the circular path described by the rotatory motion. The fluid pressure at the same horizontal level is equal.
Formula used:
\[P = \rho gh + \rho al\]
Where P is the fluid pressure at depth h from the surface of the water in an accelerated container with acceleration a and the distance from the center is $l$.
\[{a_c} = {\omega ^2}r\]
Here \[\omega \] is the angular speed with which the cylinder is rotated.
Complete step by step solution:
When a cylindrical vessel which is partially filled with water is rotated then the total pressure at the bottom of the container is due to fluid pressure, atmospheric pressure and the centripetal force acting per unit area.
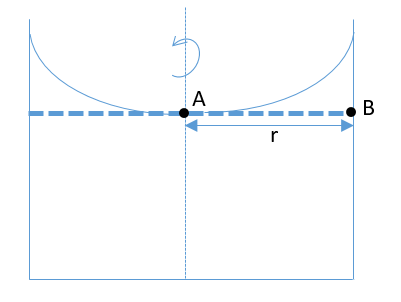
Image: A rotating cylinder with water
Taking two points on the same horizontal level. When the cylinder is rotated about its own axis then the centripetal force will act towards the center of the cylinder. The centripetal acceleration is given as,
\[{a_c} = {\omega ^2}r\]
Then the pressure at point A will be,
\[{P_A} = {P_0}\]
And the pressure at point B will be,
\[{P_B} = {P_0} - {\omega ^2}r\]
As both the points are on the same horizontal level, so the pressure at both the points at equilibrium must be the same. To balance the pressure, the water will rise above the horizontal level so that there is extra pressure due to fluid. And hence, the water surface will take a concave upward shape, i.e. the water will rise from the sides.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: When the cylinder is at rest then the surface of the water will be horizontal so that every point on the same horizontal level has the same pressure. Moreover, the measurement of the force per unit area on an item on the surface of a closed container or in the fluid is known as fluid pressure. This pressure is brought on by acceleration, gravity, or external forces in closed containers.
Formula used:
\[P = \rho gh + \rho al\]
Where P is the fluid pressure at depth h from the surface of the water in an accelerated container with acceleration a and the distance from the center is $l$.
\[{a_c} = {\omega ^2}r\]
Here \[\omega \] is the angular speed with which the cylinder is rotated.
Complete step by step solution:
When a cylindrical vessel which is partially filled with water is rotated then the total pressure at the bottom of the container is due to fluid pressure, atmospheric pressure and the centripetal force acting per unit area.

Image: A rotating cylinder with water
Taking two points on the same horizontal level. When the cylinder is rotated about its own axis then the centripetal force will act towards the center of the cylinder. The centripetal acceleration is given as,
\[{a_c} = {\omega ^2}r\]
Then the pressure at point A will be,
\[{P_A} = {P_0}\]
And the pressure at point B will be,
\[{P_B} = {P_0} - {\omega ^2}r\]
As both the points are on the same horizontal level, so the pressure at both the points at equilibrium must be the same. To balance the pressure, the water will rise above the horizontal level so that there is extra pressure due to fluid. And hence, the water surface will take a concave upward shape, i.e. the water will rise from the sides.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: When the cylinder is at rest then the surface of the water will be horizontal so that every point on the same horizontal level has the same pressure. Moreover, the measurement of the force per unit area on an item on the surface of a closed container or in the fluid is known as fluid pressure. This pressure is brought on by acceleration, gravity, or external forces in closed containers.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




