
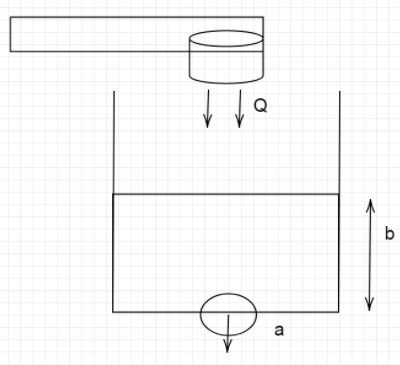
A cylindrical tank has a hole of $1{m^2}$ in its bottom. If the water is allowed to flow into the tank from a tube above it at the rate of $70c{m^3}/\sec $ then the maximum height up to which the water can rise in the tank is:
A) $2.5cm$
B) $5cm$
C) $10cm$
D) $0.25cm$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In the question, we need to calculate the maximum height attained by the liquid. It is evident that the height attained by the liquid must be maximum when the maximum volume of liquid flows through the hole.
Formula used:
$V = A\sqrt {2gh} $
where:
$V = $ Exit velocity
$A = $Area of the hole
$g = $Acceleration due to gravity
$h = $Height attained by the liquid.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question, we need an equation that relates to the speed of the fluid with the height attained by it.
We know, in fluid mechanics, Torricelli’s law relates the speed of the liquid exiting a hole with the height of the liquid. Torricelli’s law is applicable for ideal liquids.
In the question we have a similar scenario where we need to equate the rate at which the water flows through the hole to the rate at which water enters the tank:
Mathematically, the law can be written as:
$V = A\sqrt {2gh} $
where:
$V = $ Exit velocity
$A = $Area of the hole
$g = $Acceleration due to gravity
$h = $Height attained by the liquid.
Torricelli considered the liquid to be compressible, non-viscous, and have a laminar flow.
Now, we know for maximum height to be attained, the volume of water entering per second must equal the volume of water flowing out per second.
We can write:
The volume of water flowing in per second$ = 70c{m^3}/\sec $
Using Torricelli’s equation, the volume of water exiting $ = A\sqrt {2gh} $
Now, we obtain:
$\Rightarrow 70 = A\sqrt {2gh} $
We can write, area of the hole=$1{m^2} = 1 \times {10^4}c{m^2}$
Thus, putting the values, we arrive at:
$\Rightarrow 70 = 1 \times {10^4}\sqrt {2 \times 980 \times h} $
Therefore, on solving the equation, we get:
$\Rightarrow h = 25 \times {10^{ - 4}}cm$
This is our required solution.
Note: It is evident from the above equation of Torricelli’s equation, that the exit velocity is directly proportional to the height of the liquid obtained in the container. Thus, with an increase in height of the fluid within the container, the exit velocity also increases.
Formula used:
$V = A\sqrt {2gh} $
where:
$V = $ Exit velocity
$A = $Area of the hole
$g = $Acceleration due to gravity
$h = $Height attained by the liquid.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question, we need an equation that relates to the speed of the fluid with the height attained by it.
We know, in fluid mechanics, Torricelli’s law relates the speed of the liquid exiting a hole with the height of the liquid. Torricelli’s law is applicable for ideal liquids.
In the question we have a similar scenario where we need to equate the rate at which the water flows through the hole to the rate at which water enters the tank:
Mathematically, the law can be written as:
$V = A\sqrt {2gh} $
where:
$V = $ Exit velocity
$A = $Area of the hole
$g = $Acceleration due to gravity
$h = $Height attained by the liquid.
Torricelli considered the liquid to be compressible, non-viscous, and have a laminar flow.
Now, we know for maximum height to be attained, the volume of water entering per second must equal the volume of water flowing out per second.
We can write:
The volume of water flowing in per second$ = 70c{m^3}/\sec $
Using Torricelli’s equation, the volume of water exiting $ = A\sqrt {2gh} $
Now, we obtain:
$\Rightarrow 70 = A\sqrt {2gh} $
We can write, area of the hole=$1{m^2} = 1 \times {10^4}c{m^2}$
Thus, putting the values, we arrive at:
$\Rightarrow 70 = 1 \times {10^4}\sqrt {2 \times 980 \times h} $
Therefore, on solving the equation, we get:
$\Rightarrow h = 25 \times {10^{ - 4}}cm$
This is our required solution.
Note: It is evident from the above equation of Torricelli’s equation, that the exit velocity is directly proportional to the height of the liquid obtained in the container. Thus, with an increase in height of the fluid within the container, the exit velocity also increases.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




