
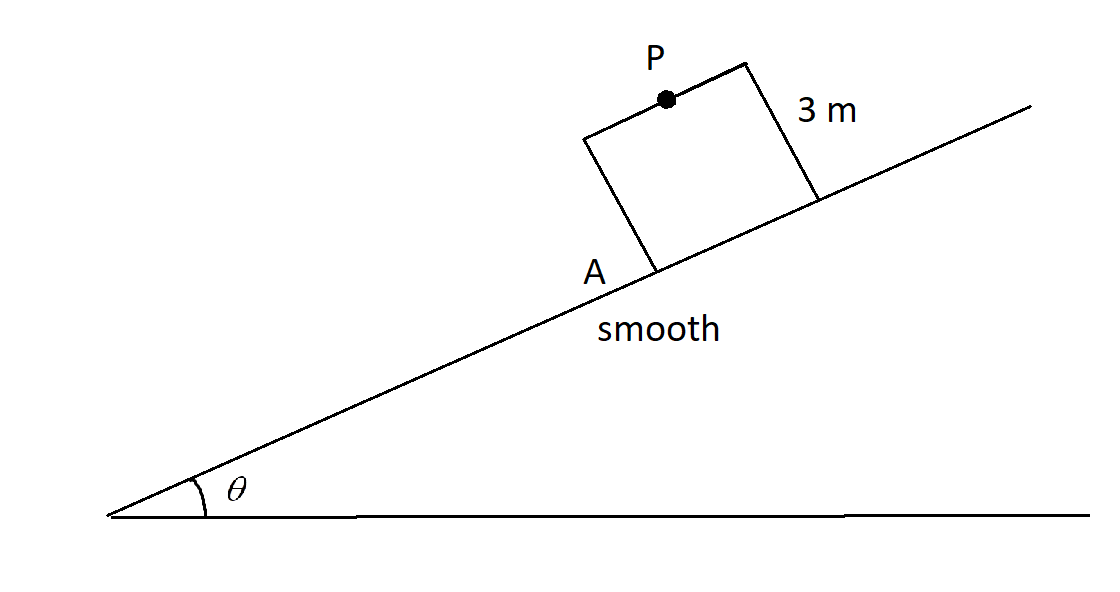
A cuboidal car of height 3 m is slipping on a smooth inclined plane. A bolt released from the roof of car from the centre of roof (P) then distance from centre of roof where bolt hits the floor with respect to car is:
A) 5 m
B) 4 m
C) 3 m
D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In this case, the bolt and car both, are in motion. Hence, in order to understand the motion of the bolt, we have to consider the motion in relation to the car since the car is also, moving down the inclined plane.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a cuboidal car placed at a height of 3m from the ground on an inclined plane.
 P is the point where the bolt is present and from where, the bolt is released to the ground.
P is the point where the bolt is present and from where, the bolt is released to the ground.
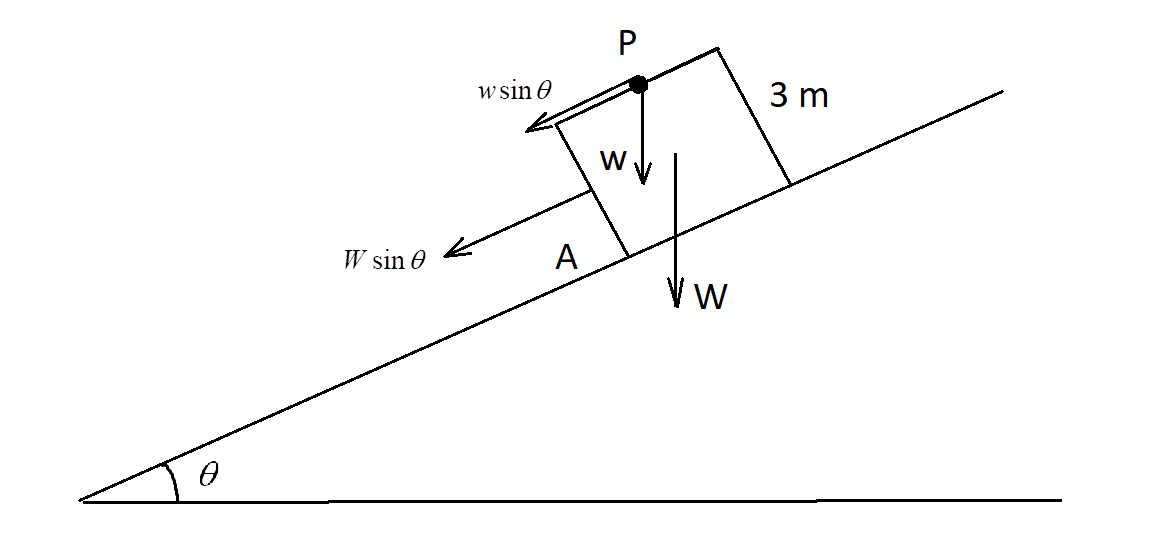
Here we see that there is a weight exerted by the bolt which leads to its acceleration.
Weight exerted by the bolt, $w = mg$
The component of acceleration of the bolt with respect to the car is –
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{w\sin \theta }}{m} = g\sin \theta $
Weight exerted by the car, $W = Mg$
Acceleration of the car down the inclined plane is equal to –
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{W\sin \theta }}{M} = g\sin \theta $
Thus, we see here that the values of acceleration of the bolt with respect to the car and the acceleration of the car down the inclined plane is equal to $g\sin \theta $.
So, if we take the frame of reference inside the car, the bolt appears to have no motion since both the bolt and the car have the same values of acceleration.
This means that the bolt falls to the ground at the same instant as that of the car.
Given that the car touches the ground after sliding down a height of 3m, it can be said that the bolt also takes the same distance of 3m to touch the ground.
Hence, the distance from the roof where the bolt hits the ground is equal to 3 m.
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: The frame of reference concept which is explained in brief here, is the same reason that we fall as if the objects outside the car/train are moving backwards while riding inside the car/train since our relative motion with respect to the car/train is zero.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a cuboidal car placed at a height of 3m from the ground on an inclined plane.
 P is the point where the bolt is present and from where, the bolt is released to the ground.
P is the point where the bolt is present and from where, the bolt is released to the ground.Here we see that there is a weight exerted by the bolt which leads to its acceleration.
Weight exerted by the bolt, $w = mg$
The component of acceleration of the bolt with respect to the car is –
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{w\sin \theta }}{m} = g\sin \theta $
Weight exerted by the car, $W = Mg$
Acceleration of the car down the inclined plane is equal to –
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{W\sin \theta }}{M} = g\sin \theta $
Thus, we see here that the values of acceleration of the bolt with respect to the car and the acceleration of the car down the inclined plane is equal to $g\sin \theta $.
So, if we take the frame of reference inside the car, the bolt appears to have no motion since both the bolt and the car have the same values of acceleration.
This means that the bolt falls to the ground at the same instant as that of the car.
Given that the car touches the ground after sliding down a height of 3m, it can be said that the bolt also takes the same distance of 3m to touch the ground.
Hence, the distance from the roof where the bolt hits the ground is equal to 3 m.
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: The frame of reference concept which is explained in brief here, is the same reason that we fall as if the objects outside the car/train are moving backwards while riding inside the car/train since our relative motion with respect to the car/train is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Law of Motion (2025-26)

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




