
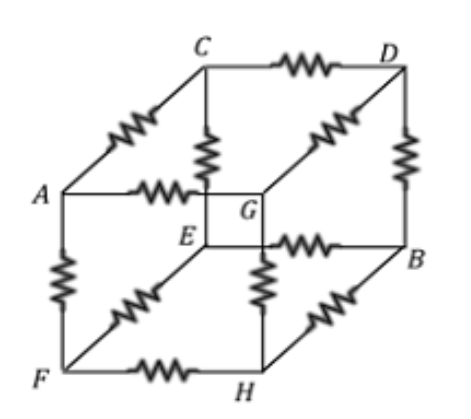
A cube made up of wire each of resistance R. Then find equivalent resistance across the diagonal.
a. $\dfrac{5}{6}R$
b. $\dfrac{3}{4}R$
c. $\dfrac{7}{12}R$
d. $R$
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: Here we have to find the equivalent resistance of the circuit in the shape of a cube. First of all, we have to simplify the circuit in order to find out the desired result. Here A and B is considered to be the ends or vertices which contain a diagonal.
Complete answer:
To find the equivalent resistance of the given circuit diagram in the shape of a cube. We have to simplify the cube in a $2$D sketch so that it is easily read or calculated.
Let us consider the diagonal to be AB.
So, we will formulate a sketch based on the $3$D structure of cube to a $2$D flat plane with A and B being the ends, as the question has asked to find out the resistance along a diagonal.
The sketch is formulated as:
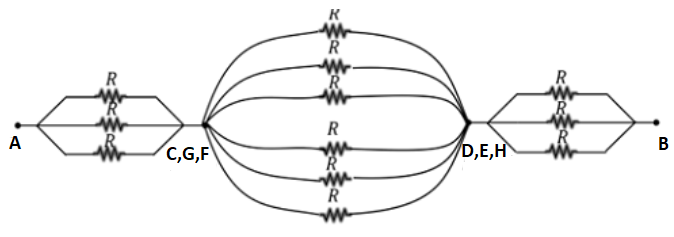
Due to symmetry, we have found out that the terminal C,G,F and D,E,H have the same potentials. So, can be regarded as the same point.
Now, the resistance around A and C,G,F are in parallel connection. Again, the resistance along B and D,E,H also the resistances along C,G,F and D,E,H are parallel. While all those three are in series connection.
So, the equivalent resistance is found as,
${{R}_{AB}}=\dfrac{R}{3}+\dfrac{R}{6}+\dfrac{R}{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{R}_{AB}}=\dfrac{5}{6}R$
The correct option is a. $\dfrac{5}{6}R$.
Note: It must be noted that we can figure out the equivalent resistance of anything in a $3$D format. So, our first aim must be to present it in the form of a $2$D sketch. And we must also remember that all the connections must be the same as that of a $3$D figure.
Complete answer:
To find the equivalent resistance of the given circuit diagram in the shape of a cube. We have to simplify the cube in a $2$D sketch so that it is easily read or calculated.
Let us consider the diagonal to be AB.
So, we will formulate a sketch based on the $3$D structure of cube to a $2$D flat plane with A and B being the ends, as the question has asked to find out the resistance along a diagonal.
The sketch is formulated as:

Due to symmetry, we have found out that the terminal C,G,F and D,E,H have the same potentials. So, can be regarded as the same point.
Now, the resistance around A and C,G,F are in parallel connection. Again, the resistance along B and D,E,H also the resistances along C,G,F and D,E,H are parallel. While all those three are in series connection.
So, the equivalent resistance is found as,
${{R}_{AB}}=\dfrac{R}{3}+\dfrac{R}{6}+\dfrac{R}{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{R}_{AB}}=\dfrac{5}{6}R$
The correct option is a. $\dfrac{5}{6}R$.
Note: It must be noted that we can figure out the equivalent resistance of anything in a $3$D format. So, our first aim must be to present it in the form of a $2$D sketch. And we must also remember that all the connections must be the same as that of a $3$D figure.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions




