
A convex lens and convex mirror are placed co axially and separated by distance d. The focal length of both is \[20\,\,cm\] each. A point object is placed at a distance \[30\,\,cm\] from the lens as shown. Then the value of d so that image on the object itself is
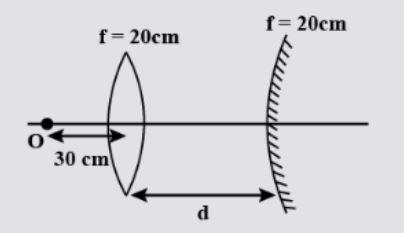
A) $10\,\,cm$
B) \[60\,\,cm\]
C) \[30\,\,cm\]
D) \[20\,\,cm\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:- The above problem can be solved using the formula derived from the object image and focal distance relationship formulas of the convex lens and the convex mirror of the same focal length. The formula for the focal length of the lens and the mirror is used.
Useful formula:
The distance of the value $d$;
\[\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{1}{f}\]
Where, the $d$ is the distance between the convex lens and convex mirror, $f$ is the focal length of the convex mirror.
Complete step by step solution:
The data given in the problem is;
Focal length of the convex lens is, ${f_1} = 20\,\,cm$.
Focal length of the convex mirror is, ${f_2} = 20\,\,cm$
Distance of the image placed from the image is, ${u_1} = 30\,\,cm$
At convex lens;
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{u_1}}}$
Substituting the value of focal length and the object distance from the lens
$
\dfrac{1}{{20}} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} + \dfrac{1}{{30}} \\
\dfrac{1}{{20}} - \dfrac{1}{{30}} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} \\
$
Where, ${d_i}$ denotes the distance of the image at convex lens.
\[\dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} = \dfrac{1}{{60}}\]
At convex mirror:
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{u_o}}}$
Substitutes the values of the focal length and the image distance;
$
\dfrac{1}{{20}} = \dfrac{1}{{60}} + \dfrac{1}{{{d_o}}} \\
\dfrac{1}{{20}} - \dfrac{1}{{60}} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_o}}} \\
$
Where, ${d_o}$ denotes the distance of the object at convex mirror.
\[\dfrac{1}{{{d_o}}} = \dfrac{1}{{30}}\]
The distance of the value $d$;
\[\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{1}{f}\]
That is
\[
\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{d_o}}} \\
\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{1}{{60}} + \dfrac{1}{{30}} \\
\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{{90}}{{1800}} \\
d = 20\,\,cm \\
\]
Therefore, the value of the $d$ is 20 cm.
Hence the option (D), \[d = 20\,\,cm\] is the correct answer.
Note: Image distance denotes that when the image is created then the distance between pole and image is known image distance. Focal length is the interval between pole and the principal focus of the mirror.
Useful formula:
The distance of the value $d$;
\[\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{1}{f}\]
Where, the $d$ is the distance between the convex lens and convex mirror, $f$ is the focal length of the convex mirror.
Complete step by step solution:
The data given in the problem is;
Focal length of the convex lens is, ${f_1} = 20\,\,cm$.
Focal length of the convex mirror is, ${f_2} = 20\,\,cm$
Distance of the image placed from the image is, ${u_1} = 30\,\,cm$
At convex lens;
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{u_1}}}$
Substituting the value of focal length and the object distance from the lens
$
\dfrac{1}{{20}} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} + \dfrac{1}{{30}} \\
\dfrac{1}{{20}} - \dfrac{1}{{30}} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} \\
$
Where, ${d_i}$ denotes the distance of the image at convex lens.
\[\dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} = \dfrac{1}{{60}}\]
At convex mirror:
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{u_o}}}$
Substitutes the values of the focal length and the image distance;
$
\dfrac{1}{{20}} = \dfrac{1}{{60}} + \dfrac{1}{{{d_o}}} \\
\dfrac{1}{{20}} - \dfrac{1}{{60}} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_o}}} \\
$
Where, ${d_o}$ denotes the distance of the object at convex mirror.
\[\dfrac{1}{{{d_o}}} = \dfrac{1}{{30}}\]
The distance of the value $d$;
\[\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{1}{f}\]
That is
\[
\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{d_o}}} \\
\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{1}{{60}} + \dfrac{1}{{30}} \\
\dfrac{1}{d} = \dfrac{{90}}{{1800}} \\
d = 20\,\,cm \\
\]
Therefore, the value of the $d$ is 20 cm.
Hence the option (D), \[d = 20\,\,cm\] is the correct answer.
Note: Image distance denotes that when the image is created then the distance between pole and image is known image distance. Focal length is the interval between pole and the principal focus of the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




