
A circle is drawn to cut a chord of length 2a units X-axis and to touch the Y-axis. Find the locus of the center of the circle.
A.${x^2} + {y^2} = {a^2}$
B. ${x^2} - {y^2} = {a^2}$
C.$x + y = {a^2}$
D.${x^2} - {y^2} = 4{a^2}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: First draw a rough diagram to understand the given facts. Then suppose the coordinate of the center and apply Pythagoras theorem in the right-angle triangle of the diagram to obtain the required locus.
Formula Used:
Pythagoras theorem of right-angle triangle is,
${h^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$ , where h is the hypotenuse, a is the height and b is the base.
Complete step by step solution:
The diagram of the given problem is,
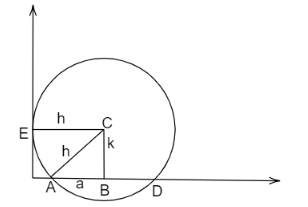
Image: Circle
Suppose that the coordinate of the circle is $C(h,k)$ .
We know that $AB = \dfrac{1}{2}AD$
Given that, $AD = 2a$ , therefore, $AB = a$ .
And, CE and CA are the radius of the circle, so the lengths are equal and equal to h.
Now, apply Pythagoras theorem in the right-angle triangle ABC,
${h^2} = {k^2} + {a^2}$
${h^2} - {k^2} = {a^2}$
Hence, the locus is,
${x^2} - {y^2} = {a^2}$
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: The circle touches the y-axis, it means the abscissa of the center is the radius of the circle. The perpendicular from the center on a chord of a circle bisects the chord. Now apply Pythagorean theorem to find the locus of the center.
Formula Used:
Pythagoras theorem of right-angle triangle is,
${h^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$ , where h is the hypotenuse, a is the height and b is the base.
Complete step by step solution:
The diagram of the given problem is,

Image: Circle
Suppose that the coordinate of the circle is $C(h,k)$ .
We know that $AB = \dfrac{1}{2}AD$
Given that, $AD = 2a$ , therefore, $AB = a$ .
And, CE and CA are the radius of the circle, so the lengths are equal and equal to h.
Now, apply Pythagoras theorem in the right-angle triangle ABC,
${h^2} = {k^2} + {a^2}$
${h^2} - {k^2} = {a^2}$
Hence, the locus is,
${x^2} - {y^2} = {a^2}$
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: The circle touches the y-axis, it means the abscissa of the center is the radius of the circle. The perpendicular from the center on a chord of a circle bisects the chord. Now apply Pythagorean theorem to find the locus of the center.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole




