
A cavity of radius $\dfrac{R}{2}$ is made inside a solid sphere of radius $R$. Find the gravitational force on a particle of mass $m$ at a distance $\dfrac{R}{2}$ from the center of sphere on the line joining both the centers of sphere and cavity (opposite to the center of cavity) if cavity is located at a distance $\dfrac{R}{2}$ from the center of sphere. Here, $g = \dfrac{{GM}}{{{R^2}}}$ , where $M$ is the mass of the sphere.
A) $\dfrac{{mg}}{2}$
B) $\dfrac{{3mg}}{8}$
C) $\dfrac{{mg}}{{16}}$
D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Find the gravitational field at mass $m$ due to full solid sphere and gravitational field at mass $m$ due to cavity. Then, by using the superposition principle for gravitational fields, find the net gravitational field.
Formula used:
Use the formula for gravitational field at the mass due to cavity $p$ –
$E = \dfrac{{p{a^3}}}{{3{\varepsilon _0}{r^2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
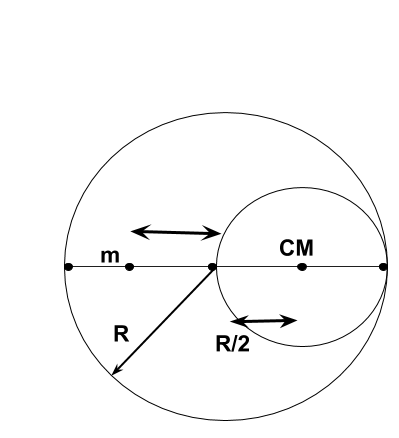
Let the cavity inside the solid sphere be $ - p$.
So, first of all, finding the gravitational field at mass $m$ due to full solid sphere –
${E_1} = \dfrac{{p\bar r}}{{3{\varepsilon _0}}}$
As given in the question that radius is equal to $\dfrac{R}{2}$
Therefore, putting the value of radius in the expression of gravitational field at mass $m$ due to full solid sphere –
$\therefore {E_1} = \dfrac{{pR}}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}} \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
So, now using the formula for gravitational field at the mass $m$ due to cavity $p$ -
$E = \dfrac{{p{a^3}}}{{3{\varepsilon _0}{r^2}}}$
So, putting the values in above formula –
$
\Rightarrow {E_2} = \dfrac{{\left( { - p} \right){{\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)}^3}}}{{3{\varepsilon _0}{R^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_2} = \dfrac{{\left( { - p} \right){R^3}}}{{24{\varepsilon _0}{R^2}}} \\
\therefore {E_2} = \dfrac{{\left( { - p} \right)R}}{{24{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
$
Now, using the superposition principle of gravitational field for finding the net gravitational field.
According to the superposition principle in the gravitational field, the net gravitational field at a point is the vector sum of the gravitational field at that point due to different sources.
Therefore, the net gravitational field:
$E = {E_1} + {E_2}$
Putting the values of ${E_1}$ and ${E_2}$ from the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$ respectively –
$
\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{{pR}}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}} - \dfrac{{pR}}{{24{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{{pR}}{{8{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
$
Now, finding the net force on the mass $m$ -
$\therefore F = mE$
Putting the value of $E$ -
$ \Rightarrow F = m \times \dfrac{{pR}}{{8{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Here, $p = \dfrac{M}{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)\pi {R^3}}}$ and ${\varepsilon _0} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi G}}$
Then, $F = \dfrac{{3mg}}{8}$
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: Negative mass concept is a technique used to find the gravitational field at a point. The body of the same mass is assumed when the part of mass is missing from the. That assumed part is made to be present on the opposite side of the point and the distance is the same with that of the original vacancy. Then, the net field is calculated by calculating the field due to the full body without vacancy and newly assumed mass.
Formula used:
Use the formula for gravitational field at the mass due to cavity $p$ –
$E = \dfrac{{p{a^3}}}{{3{\varepsilon _0}{r^2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:

Let the cavity inside the solid sphere be $ - p$.
So, first of all, finding the gravitational field at mass $m$ due to full solid sphere –
${E_1} = \dfrac{{p\bar r}}{{3{\varepsilon _0}}}$
As given in the question that radius is equal to $\dfrac{R}{2}$
Therefore, putting the value of radius in the expression of gravitational field at mass $m$ due to full solid sphere –
$\therefore {E_1} = \dfrac{{pR}}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}} \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
So, now using the formula for gravitational field at the mass $m$ due to cavity $p$ -
$E = \dfrac{{p{a^3}}}{{3{\varepsilon _0}{r^2}}}$
So, putting the values in above formula –
$
\Rightarrow {E_2} = \dfrac{{\left( { - p} \right){{\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)}^3}}}{{3{\varepsilon _0}{R^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_2} = \dfrac{{\left( { - p} \right){R^3}}}{{24{\varepsilon _0}{R^2}}} \\
\therefore {E_2} = \dfrac{{\left( { - p} \right)R}}{{24{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
$
Now, using the superposition principle of gravitational field for finding the net gravitational field.
According to the superposition principle in the gravitational field, the net gravitational field at a point is the vector sum of the gravitational field at that point due to different sources.
Therefore, the net gravitational field:
$E = {E_1} + {E_2}$
Putting the values of ${E_1}$ and ${E_2}$ from the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$ respectively –
$
\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{{pR}}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}} - \dfrac{{pR}}{{24{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{{pR}}{{8{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
$
Now, finding the net force on the mass $m$ -
$\therefore F = mE$
Putting the value of $E$ -
$ \Rightarrow F = m \times \dfrac{{pR}}{{8{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Here, $p = \dfrac{M}{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)\pi {R^3}}}$ and ${\varepsilon _0} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi G}}$
Then, $F = \dfrac{{3mg}}{8}$
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: Negative mass concept is a technique used to find the gravitational field at a point. The body of the same mass is assumed when the part of mass is missing from the. That assumed part is made to be present on the opposite side of the point and the distance is the same with that of the original vacancy. Then, the net field is calculated by calculating the field due to the full body without vacancy and newly assumed mass.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




