
A car is moving on a circular path and takes a turn. If ${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$ be the reactions on the inner and outer wheels respectively, then
A. ${R_1} = {R_2}$
B. ${R_1} < {R_2}$
C. ${R_1} > {R_2}$
D. ${R_1} \geqslant {R_2}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we will first draw the rough diagram of wheels of the car and then indicate their normal reactions and then using concept of moment about the centre of gravity of the car we will determine the correct relation between normal reactions of the wheels.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, we have given that A car is moving on a circular path and takes a turn and in this ${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$ be the reactions on the inner and outer wheels, while turning the horizontal force required to make a turn is centripetal force f which is given by,
$f = \dfrac{{M{v^2}}}{r}$
where m is the mass, v is the velocity and r is the radius of the circular path.
Let us draw the free body diagram of wheels of the car where height of the wheel is h and distance between two wheels is $2a$ and G is the point of centre of gravity of the car as shown in the diagram
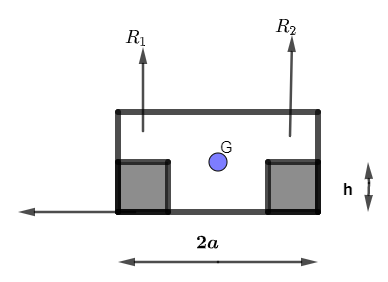
Now, if the car is turning towards left as shown in the diagram then on balancing vertical force we have,
${R_1} + {R_2} = Mg$
Now, taking the moments of vertical forces and horizontal forces about the point G, we get;
$Fh + {R_1}a = {R_2}a \\
\Rightarrow {R_2} = \dfrac{{Fh + {R_1}a}}{a} \\
\Rightarrow {R_2} = {R_1} + \dfrac{{Fh}}{a} \\ $
$\therefore {R_2} > {R_1}$
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: It should be remembered that, if the car was taking the turn towards right then these reactions will be exactly opposite as horizontal centripetal force will act towards right and always make the free body diagram to solve such questions.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, we have given that A car is moving on a circular path and takes a turn and in this ${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$ be the reactions on the inner and outer wheels, while turning the horizontal force required to make a turn is centripetal force f which is given by,
$f = \dfrac{{M{v^2}}}{r}$
where m is the mass, v is the velocity and r is the radius of the circular path.
Let us draw the free body diagram of wheels of the car where height of the wheel is h and distance between two wheels is $2a$ and G is the point of centre of gravity of the car as shown in the diagram

Now, if the car is turning towards left as shown in the diagram then on balancing vertical force we have,
${R_1} + {R_2} = Mg$
Now, taking the moments of vertical forces and horizontal forces about the point G, we get;
$Fh + {R_1}a = {R_2}a \\
\Rightarrow {R_2} = \dfrac{{Fh + {R_1}a}}{a} \\
\Rightarrow {R_2} = {R_1} + \dfrac{{Fh}}{a} \\ $
$\therefore {R_2} > {R_1}$
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: It should be remembered that, if the car was taking the turn towards right then these reactions will be exactly opposite as horizontal centripetal force will act towards right and always make the free body diagram to solve such questions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




