
A bomb of mass $16\,kg$ at rest explodes into two pieces of mass $4\,kg$ and $12\,kg$. The velocity of the $12\,kg$ mass is $4\,\,m/s$. The kinetic energy of the other mass is:
(A) $96J$
(B) $144J$
(C) $288J$
(D) $192J$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: You can easily solve the question if you try to recall that there is no external force in the system provided in the question, thus, the Center of Mass will not move even a little bit even though both of the masses into which the original mass exploded into, will move with their own respective velocities, the Center of Mass will always stay stationery.
Complete step by step answer
We will try to solve the question by approaching the solution exactly as described in the hint section of the solution to the question.
We already know that no external force was applied in the system that is mentioned in the question, thus the Center of Mass will have no motion, thus no velocity and no kinetic energy and acceleration.
Let us draw what is happening in the question mentioned above:
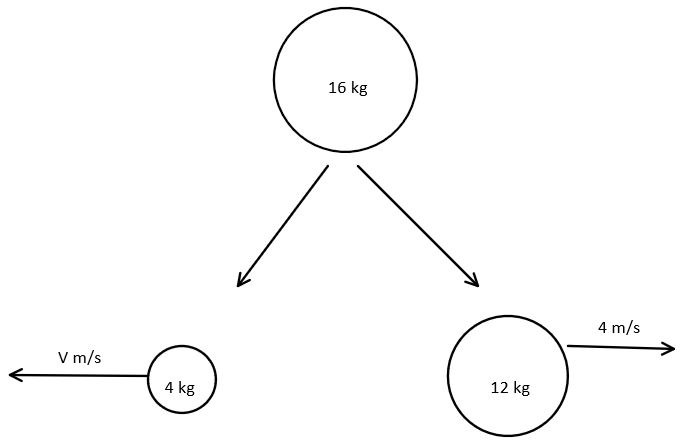
We can see that the bigger mass exploded into two pieces, one of their velocity is given to use in the question.
Since there is no external force applied, we know that the mass of $4\,kg$ will move in the opposite direction to that of the $12{\kern 1pt} kg$. Not just this, the velocity will be such that the velocity of their Center of Mass stays stationery. This can be represented mathematically as:
${v_{com}} = \dfrac{{m{v_1} + M{v_2}}}{{m + M}}$
Where, ${v_{com}}$ is the velocity of center of mass, which is $0$
$m$ is the smaller mass of $4\,kg$
${v_1}$ is the velocity of the smaller mass
$M$ is the bigger mass of $12\,kg$
${v_2}$ is the velocity of the bigger mass, which is given to us by the question as $4\,m/s$
Putting in the values in the formula:
$
0\, = \,\dfrac{{4{v_1} + 12 \times 4}}{{4 + 12}} \\
4{v_1}\, = \, - 48 \\
{v_1}\, = \, - 12\,m/s \\
$
The negative sign represents that the velocity of the smaller mass is exactly in the opposite direction of the velocity of the bigger mass.
Now that we have found out the velocity of smaller mass, all that is left to do is to find its kinetic energy using the formula of kinetic energy:
$KE\, = \,\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Now, let’s substitute the values:
$
KE = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 \times {12^2} \\
KE = \,288\,J \\
$
Here, we got the value of Kinetic Energy which is the same as option (C).
Hence, the correct answer is the option (C).
Note: Many students forget the fact that no external force is applied hence Center of Mass will remain stationery and won’t move. Even after that, many students will try to equate the Kinetic energies of both masses thinking they will have no net Kinetic energy, which is a completely wrong and false approach to the question.
Complete step by step answer
We will try to solve the question by approaching the solution exactly as described in the hint section of the solution to the question.
We already know that no external force was applied in the system that is mentioned in the question, thus the Center of Mass will have no motion, thus no velocity and no kinetic energy and acceleration.
Let us draw what is happening in the question mentioned above:

We can see that the bigger mass exploded into two pieces, one of their velocity is given to use in the question.
Since there is no external force applied, we know that the mass of $4\,kg$ will move in the opposite direction to that of the $12{\kern 1pt} kg$. Not just this, the velocity will be such that the velocity of their Center of Mass stays stationery. This can be represented mathematically as:
${v_{com}} = \dfrac{{m{v_1} + M{v_2}}}{{m + M}}$
Where, ${v_{com}}$ is the velocity of center of mass, which is $0$
$m$ is the smaller mass of $4\,kg$
${v_1}$ is the velocity of the smaller mass
$M$ is the bigger mass of $12\,kg$
${v_2}$ is the velocity of the bigger mass, which is given to us by the question as $4\,m/s$
Putting in the values in the formula:
$
0\, = \,\dfrac{{4{v_1} + 12 \times 4}}{{4 + 12}} \\
4{v_1}\, = \, - 48 \\
{v_1}\, = \, - 12\,m/s \\
$
The negative sign represents that the velocity of the smaller mass is exactly in the opposite direction of the velocity of the bigger mass.
Now that we have found out the velocity of smaller mass, all that is left to do is to find its kinetic energy using the formula of kinetic energy:
$KE\, = \,\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Now, let’s substitute the values:
$
KE = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 \times {12^2} \\
KE = \,288\,J \\
$
Here, we got the value of Kinetic Energy which is the same as option (C).
Hence, the correct answer is the option (C).
Note: Many students forget the fact that no external force is applied hence Center of Mass will remain stationery and won’t move. Even after that, many students will try to equate the Kinetic energies of both masses thinking they will have no net Kinetic energy, which is a completely wrong and false approach to the question.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




