
A body is moved in a direction opposite to the direction of force acting on it. Work done is:
A. Against the force
B. Zero
C. Along the force
D. None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Work is a measurement of energy; it explains how much energy is consumed or released by a force over a distance. Work done can be either positive or negative, if the force has a component in the same direction as the displacement of the object, then the force is doing positive work. If the force has a component in the direction opposite to the displacement, the force does negative work.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that work is said to be done when force applied on an object shows the displacement in that object.
Mathematically we have,
\[W = \vec F.d\vec S = FdS\operatorname{Cos} \theta \]
Where,
$\vec F = $ Force applied.
$d\vec S = $ Displacement of an object.
$\theta = $ Angle between force applied and the displacement.
If the body is moved in a direction opposite to the force applied on it, then the work done is “Negative”.
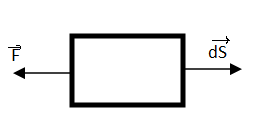
I.e., the displacement is in the direction opposite to the force applied then angle between the force and displacement will be 180.
Thus,
$W = FdS\operatorname{Cos} 180 = - FdS$;
$\because \operatorname{Cos} 180 = - 1$
Therefore, the work done is negative, i.e., against the direction of force.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:
$F\operatorname{Cos} \theta $ is the magnitude of the $\vec F$ in the direction of $d\vec S$. $\operatorname{Cos} \theta $ explains about the relative direction of the force and displacement. If the component of force along the direction of the displacement is opposite in direction to the displacement then the sign of displacement vector and force vector will be different. This is regardless of which was chosen as a positive direction.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that work is said to be done when force applied on an object shows the displacement in that object.
Mathematically we have,
\[W = \vec F.d\vec S = FdS\operatorname{Cos} \theta \]
Where,
$\vec F = $ Force applied.
$d\vec S = $ Displacement of an object.
$\theta = $ Angle between force applied and the displacement.
If the body is moved in a direction opposite to the force applied on it, then the work done is “Negative”.

I.e., the displacement is in the direction opposite to the force applied then angle between the force and displacement will be 180.
Thus,
$W = FdS\operatorname{Cos} 180 = - FdS$;
$\because \operatorname{Cos} 180 = - 1$
Therefore, the work done is negative, i.e., against the direction of force.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:
$F\operatorname{Cos} \theta $ is the magnitude of the $\vec F$ in the direction of $d\vec S$. $\operatorname{Cos} \theta $ explains about the relative direction of the force and displacement. If the component of force along the direction of the displacement is opposite in direction to the displacement then the sign of displacement vector and force vector will be different. This is regardless of which was chosen as a positive direction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




