
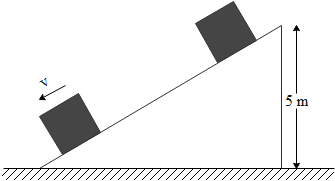
A block slides down the frictionless ramp shown in figure. Use the law of conservation of energy to find its speed when it gets to the bottom. $\left(g=10 \mathrm{m} \mathrm{s}^{-2}\right)$,
(A) $20 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}$
(B) $10 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}$
(C) $30 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}$
(D) $60 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. Keeping this in mind, we can solve the given question.
Complete step by step answer
We know from the data given in the question that,
The height $\mathrm{h}=5 \mathrm{m}$
The gravitational acceleration $\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{ms}^{-2}$
Using conservation of energy, we get that,
$\mathrm{mgh}=0.5 \times \mathrm{mv}^{2}$
Cancelling mass from either side of the equation, we get
$10 \times 5=0.5 \times \mathrm{v}^{2}$
$\mathrm{v}=\sqrt{100}=10 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}$
Therefore, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: We must effectively be able to draw free body diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams.
Complete step by step answer
We know from the data given in the question that,
The height $\mathrm{h}=5 \mathrm{m}$
The gravitational acceleration $\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{ms}^{-2}$
Using conservation of energy, we get that,
$\mathrm{mgh}=0.5 \times \mathrm{mv}^{2}$
Cancelling mass from either side of the equation, we get
$10 \times 5=0.5 \times \mathrm{v}^{2}$
$\mathrm{v}=\sqrt{100}=10 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}$
Therefore, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: We must effectively be able to draw free body diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




