
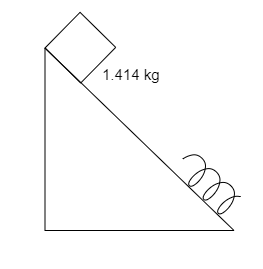
A block of mass $\sqrt 2 \,kg$ is released from the top of an inclined and smooth surface as shown in figure. If thee spring constant of spring is $100\,N{m^{ - 1}}$ and block comes to rest after compressing the spring by $1\,m$, then the distance travelled by the block before it comes to rest is:
(A) $1\,m$
(B) $1.25\,m$
(C) $2.5\,m$
(D) $5\,m$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint The distance travelled by the block before it comes to rest can be determined by using the statement that the work done by the block will be equal to the potential energy stored by the spring, by equating the two formulas, then the distance is determined.
Useful formula:
The work done by the block will be equal to the potential energy stored by the spring is given by,
$mg\sin \theta \times s = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$
Where, $m$ is the mass of the block, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity, $\theta $ is the angle of the inclination, $s$ is the distance travelled by the block, $k$ is the spring constant and $x$ is the compression of the spring.
Complete step by step answer
Given that,
The mass of the block is given as, $m = \sqrt 2 \,kg$,
The spring constant is given as, $k = 100\,N{m^{ - 1}}$,
The compression of the spring is given as, $x = 1\,m$.
Now,
The work done by the block will be equal to the potential energy stored by the spring is given by,
$\Rightarrow$ $mg\sin \theta \times s = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\,...................\left( 1 \right)$
By substituting the mass of the block, acceleration due to gravity, the angle of the inclination, spring constant and the compression of the spring in the above equation (1), then the above equation (1) is written as,
$\Rightarrow$ $\sqrt 2 \times 10 \times \sin {45^ \circ } \times s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 100 \times {1^2}$
From the trigonometry, the value of the $\sin {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$, then the above equation is written as,
$\sqrt 2 \times 10 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 100 \times {1^2}$
By cancelling the same terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow$ $10 \times s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 100 \times {1^2}$
By rearranging the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow$ $s = \dfrac{{1 \times 100 \times {1^2}}}{{2 \times 10}}$
By multiplying the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$s = \dfrac{{100}}{{20}}$
By dividing the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow$ $s = 5\,m$
Hence, the option (D) is the correct answer.
Note Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. The energy can be transferred from one form of the energy to the other form of the energy. Here, the potential energy of the block is converted to the spring energy, because the block from the definite height will have the potential energy and then the block compresses the spring.
Useful formula:
The work done by the block will be equal to the potential energy stored by the spring is given by,
$mg\sin \theta \times s = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$
Where, $m$ is the mass of the block, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity, $\theta $ is the angle of the inclination, $s$ is the distance travelled by the block, $k$ is the spring constant and $x$ is the compression of the spring.
Complete step by step answer
Given that,
The mass of the block is given as, $m = \sqrt 2 \,kg$,
The spring constant is given as, $k = 100\,N{m^{ - 1}}$,
The compression of the spring is given as, $x = 1\,m$.
Now,
The work done by the block will be equal to the potential energy stored by the spring is given by,
$\Rightarrow$ $mg\sin \theta \times s = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\,...................\left( 1 \right)$
By substituting the mass of the block, acceleration due to gravity, the angle of the inclination, spring constant and the compression of the spring in the above equation (1), then the above equation (1) is written as,
$\Rightarrow$ $\sqrt 2 \times 10 \times \sin {45^ \circ } \times s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 100 \times {1^2}$
From the trigonometry, the value of the $\sin {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$, then the above equation is written as,
$\sqrt 2 \times 10 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 100 \times {1^2}$
By cancelling the same terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow$ $10 \times s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 100 \times {1^2}$
By rearranging the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow$ $s = \dfrac{{1 \times 100 \times {1^2}}}{{2 \times 10}}$
By multiplying the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$s = \dfrac{{100}}{{20}}$
By dividing the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow$ $s = 5\,m$
Hence, the option (D) is the correct answer.
Note Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. The energy can be transferred from one form of the energy to the other form of the energy. Here, the potential energy of the block is converted to the spring energy, because the block from the definite height will have the potential energy and then the block compresses the spring.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




