
A block of ice at \[ - {10^0}C\]is slowly heated and converted to steam at \[{100^0}C\]. Which of the following curves represent the phenomenon qualitatively?
A. 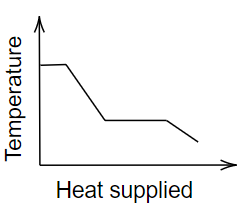
B. 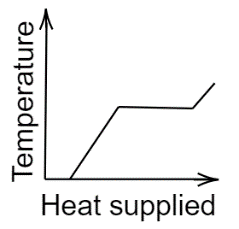
C. 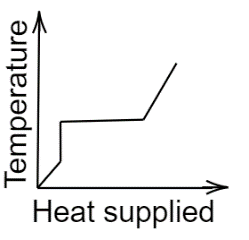
D. None of the above
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Before going to answer this question, let’s know about the latent heat. It is defined as the heat required to change the state of the matter without a change in temperature, that is, in latent heat the temperature remains constant and the energy transfer occurs in order to change the state of a substance.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a solid ice cube initially at \[ - {10^0}C\]. When we start heating it gradually, it gains some energy, and the ice converts to its liquid form at \[{0^0}C\]. Here the latent heat of fusion comes into existence, and upon further addition of energy, it changes its state to its gaseous form as steam at\[{100^0}C\]. After that temperature remains constant using latent heat of vaporization.
Now, let’s see which graph shows this condition. Consider the first graph, in which the initial temperature remains constant, again decreases, and later on, it remains constant for a while and finally decreases.
In the second graph, initially, the temperature remains constant, increases, and stabilizes for some time, and finally, it increases.Now, coming to the third graph here also temperature initially increases non-linearly, stabilizes for a while, and again increases linearly.
Therefore, as we discussed above, initially the temperature should start at \[ - {10^0}C\] and reaches \[{0^0}C\] to become a liquid, and then stabilizes, later reaching \[{100^0}C\] at which point it starts converting into steam. This should be depicted in the graph. But all the three graphs are not showing this condition.
Hence, Option D is the correct answer.
Note: The Latent heat of fusion is defined as the amount of heat required to change a substance from a solid to a liquid state and the Latent heat of vaporization is defined as the amount of heat required to change a state from liquid to gaseous state. Here both the phenomena take place.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a solid ice cube initially at \[ - {10^0}C\]. When we start heating it gradually, it gains some energy, and the ice converts to its liquid form at \[{0^0}C\]. Here the latent heat of fusion comes into existence, and upon further addition of energy, it changes its state to its gaseous form as steam at\[{100^0}C\]. After that temperature remains constant using latent heat of vaporization.
Now, let’s see which graph shows this condition. Consider the first graph, in which the initial temperature remains constant, again decreases, and later on, it remains constant for a while and finally decreases.
In the second graph, initially, the temperature remains constant, increases, and stabilizes for some time, and finally, it increases.Now, coming to the third graph here also temperature initially increases non-linearly, stabilizes for a while, and again increases linearly.
Therefore, as we discussed above, initially the temperature should start at \[ - {10^0}C\] and reaches \[{0^0}C\] to become a liquid, and then stabilizes, later reaching \[{100^0}C\] at which point it starts converting into steam. This should be depicted in the graph. But all the three graphs are not showing this condition.
Hence, Option D is the correct answer.
Note: The Latent heat of fusion is defined as the amount of heat required to change a substance from a solid to a liquid state and the Latent heat of vaporization is defined as the amount of heat required to change a state from liquid to gaseous state. Here both the phenomena take place.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




