
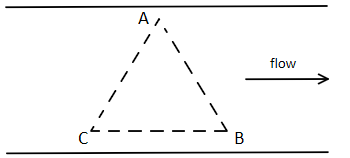
A, B and C are three rafts floating in a river such that they always form an equilateral triangle. A swimmer whose swimming speed is constant swims from A to B then B to C and finally from C to A along straight lines. Time taken by the swimmer is maximum in swimming:
A) From A to B
B) From B to C
C) From C to A
D) It is same in all parts
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: These problems are called river problems in one dimensional motion. In these problems we have to calculate the absolute velocity of the swimmer across all three edges with respect to absolute velocity of the river. As the swimmer has constant speed in swimming this will be taken as the velocity of the swimmer in still water.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s look at the diagram. Let’s assume the flow of water is along a positive x-axis.
Let $v$ be the velocity of the swimmer in still water, ${v_w}$ be the velocity of water flow and ${v_a}$ be the absolute velocity of the swimmer with respect to the flow of the river.
Thus the final velocity or absolute velocity of the swimmer will be the vector sum of its velocity in still water and the absolute velocity of the river.
Or \[\overrightarrow {{v_a}} = \overrightarrow v + \overrightarrow {{v_w}} \]
The magnitude of the resultant velocity vector is given by,
$ \Rightarrow {v_a} = {v^2} + {v_w}^2 + 2v{v_w}\cos \theta $
Where $\theta $ is the angle between the vectors.
From this we can conclude that the value of absolute velocity of the swimmer will be maximum for $\theta = 0^\circ $ and minimum for $\theta = 180^\circ $ .
Let’s now analyse the options.
If the swimmer now swims from A to B or along the axis CA, the angles between the velocity of the river and velocity of the swimmer will be $60^\circ $ .
But when the swimmer is travelling from B point to C point, the angle between the vectors will be $180^\circ $ , so the velocity will be minimum.
Thus the time taken by the swimmer will be maximum when he swims along BC.
The correct answer is (B), from B to C.
Note: We can also use vector resolving on these problems, but as it was a simpler problem, vector resolving was not necessary. If the triangle was inverted and the examiner asked about the shortest time interval the swimmer would take, the answer would have been from point C to point B, as the angle between the vectors of velocities of river and swimmer is $0^\circ $.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s look at the diagram. Let’s assume the flow of water is along a positive x-axis.
Let $v$ be the velocity of the swimmer in still water, ${v_w}$ be the velocity of water flow and ${v_a}$ be the absolute velocity of the swimmer with respect to the flow of the river.
Thus the final velocity or absolute velocity of the swimmer will be the vector sum of its velocity in still water and the absolute velocity of the river.
Or \[\overrightarrow {{v_a}} = \overrightarrow v + \overrightarrow {{v_w}} \]
The magnitude of the resultant velocity vector is given by,
$ \Rightarrow {v_a} = {v^2} + {v_w}^2 + 2v{v_w}\cos \theta $
Where $\theta $ is the angle between the vectors.
From this we can conclude that the value of absolute velocity of the swimmer will be maximum for $\theta = 0^\circ $ and minimum for $\theta = 180^\circ $ .
Let’s now analyse the options.
If the swimmer now swims from A to B or along the axis CA, the angles between the velocity of the river and velocity of the swimmer will be $60^\circ $ .
But when the swimmer is travelling from B point to C point, the angle between the vectors will be $180^\circ $ , so the velocity will be minimum.
Thus the time taken by the swimmer will be maximum when he swims along BC.
The correct answer is (B), from B to C.
Note: We can also use vector resolving on these problems, but as it was a simpler problem, vector resolving was not necessary. If the triangle was inverted and the examiner asked about the shortest time interval the swimmer would take, the answer would have been from point C to point B, as the angle between the vectors of velocities of river and swimmer is $0^\circ $.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




