
The equation of the line passing through the points \[{{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{3}}\widehat{k}\] and \[{{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{3}}\widehat{k}\].
A \[\left( {{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}+{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}+{{a}_{3}}\widehat{k} \right)+t\left( {{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}+{{b}_{2}}\widehat{j}+{{b}_{3}}\widehat{k} \right)\]
B \[\left( {{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}+{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}+{{a}_{3}}\widehat{k} \right)-t\left( {{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}+{{b}_{2}}\widehat{j}+{{b}_{3}}\widehat{k} \right)\]
C \[{{a}_{1}}\left( 1-t \right)\widehat{i}+{{a}_{2}}\left( 1-t \right)\widehat{j}+{{a}_{3}}\left( 1-t \right)\widehat{k}+\left( {{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}+{{b}_{2}}\widehat{j}+{{b}_{3}}\widehat{k} \right)t\]
D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are provided with the two points, \[\overrightarrow{a}={{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{3}}\widehat{k}\]and \[\overrightarrow{b}={{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{3}}\widehat{k}\]and we need to form an equation passing through these two points. For this, we need one point through which the line is passing and the direction ratio of the line. The direction ratio of line is given as \[\overrightarrow{b}\text{ }\text{ }\overrightarrow{a}\], where \[\overrightarrow{b}\]and \[\overrightarrow{a}\]both are the points through which the line is passing. The general equation of any line is \[\overrightarrow{r}\text{ }=\text{ }\overrightarrow{a}\text{ }+\text{ }t\text{ }\left( \overrightarrow{b}\text{ }\text{ }\overrightarrow{a} \right)\], where \[\overrightarrow{b}\text{ }\text{ }\overrightarrow{a}\]is the direction ratio of the line, r is position vector of arbitrary point through which line is passing, a is given point through which line is passing.
Complete step by step solution: The position vector for two given points through which a line is passing is given as
Let’s say \[\overrightarrow{a}\]is the position vector for point A whose positing in space is given as
\[\overrightarrow{a}={{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{3}}\widehat{k}\]
Let’s say \[\overrightarrow{b}\] is the position vector for point B whose position in space is given as
\[\overrightarrow{b}={{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{3}}\widehat{k}\]
The above points are given in the question through which a line is passing and to find the equation of that line assume an arbitrary point in between these points or away from these points let’s say P.
Let the position vector of point P is\[\overrightarrow{r}\]. And the relationship between the three position vectors is given as
\[\overrightarrow{AP}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\overrightarrow{AB}\], where t belongs to any real number
\[\overrightarrow{AP}\text{ }=\text{ }\overrightarrow{r}\text{ }\text{ }\overrightarrow{a}\] and \[\overrightarrow{AB}\text{ }=\text{ }\overrightarrow{b}\text{ }\text{ }\overrightarrow{a}\]
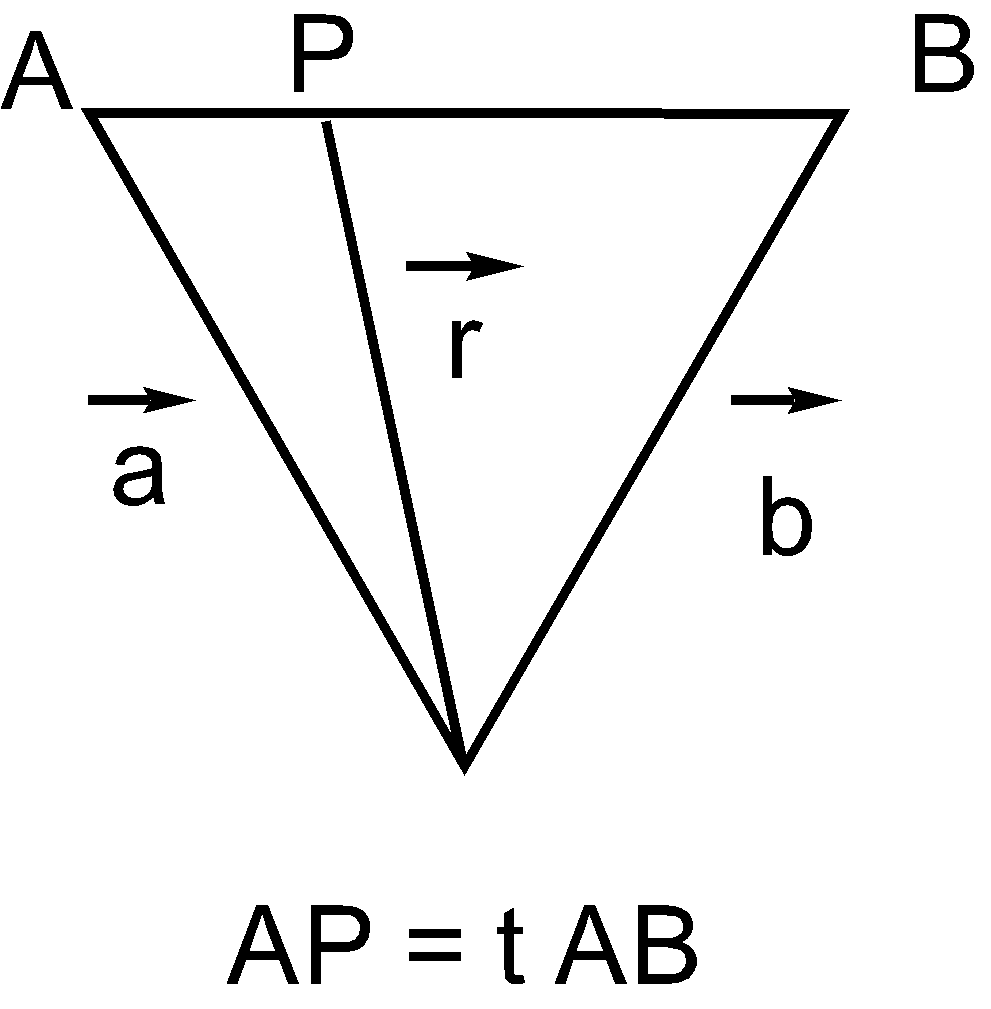
Now potting all the values of AB and AP in the first equation we will get the general equation of the line passing through two points such as
\[\overrightarrow{AP}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\overrightarrow{AB}\]
\[\widehat{r}\text{ }\text{ }\widehat{a}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\left( \widehat{b}\text{ }\text{ }\widehat{a} \right)\]
\[\overrightarrow{r}\text{ }=\text{ }\overrightarrow{a}\text{ }+\text{ }t\text{ }\left( \overrightarrow{b}\text{ }\text{ }\overrightarrow{a} \right)\]
Now putting all the values of a, and b position vectors we will get the equation of a line passing through the two points (A and B) such as
\[\widehat{r}\text{ }=\text{ }{{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{3}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }t\text{ }\left\{ \text{ }\left( {{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{b}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{b}_{3}}\widehat{k} \right)\text{ }\text{ }\left( {{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }a3\widehat{k} \right) \right\}\]
Modifying it we will get
\[\widehat{r}={{a}_{1}}\left( 1-t \right)\widehat{i}+{{a}_{2}}\left( 1-t \right)\widehat{j}+{{a}_{3}}\left( 1-t \right)\widehat{k}+\left( {{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}+{{b}_{2}}\widehat{j}+{{b}_{3}}\widehat{k} \right)t\]
Option ‘C’ is correct
Note: It is important to note that we can take an arbitrary point or arbitrary position vectors outside the two given points and in-between the two given points so that we can compare the assumed point concerning two given points so that we get an equation of the line passing through all the three points such as
\[\overrightarrow{AP}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\overrightarrow{AB}\]
\[\widehat{r}\text{ }\text{ }\widehat{a}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\left( \widehat{b}\text{ }\text{ }\widehat{a} \right)\]
Complete step by step solution: The position vector for two given points through which a line is passing is given as
Let’s say \[\overrightarrow{a}\]is the position vector for point A whose positing in space is given as
\[\overrightarrow{a}={{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{3}}\widehat{k}\]
Let’s say \[\overrightarrow{b}\] is the position vector for point B whose position in space is given as
\[\overrightarrow{b}={{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{3}}\widehat{k}\]
The above points are given in the question through which a line is passing and to find the equation of that line assume an arbitrary point in between these points or away from these points let’s say P.
Let the position vector of point P is\[\overrightarrow{r}\]. And the relationship between the three position vectors is given as
\[\overrightarrow{AP}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\overrightarrow{AB}\], where t belongs to any real number
\[\overrightarrow{AP}\text{ }=\text{ }\overrightarrow{r}\text{ }\text{ }\overrightarrow{a}\] and \[\overrightarrow{AB}\text{ }=\text{ }\overrightarrow{b}\text{ }\text{ }\overrightarrow{a}\]

Now potting all the values of AB and AP in the first equation we will get the general equation of the line passing through two points such as
\[\overrightarrow{AP}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\overrightarrow{AB}\]
\[\widehat{r}\text{ }\text{ }\widehat{a}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\left( \widehat{b}\text{ }\text{ }\widehat{a} \right)\]
\[\overrightarrow{r}\text{ }=\text{ }\overrightarrow{a}\text{ }+\text{ }t\text{ }\left( \overrightarrow{b}\text{ }\text{ }\overrightarrow{a} \right)\]
Now putting all the values of a, and b position vectors we will get the equation of a line passing through the two points (A and B) such as
\[\widehat{r}\text{ }=\text{ }{{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{3}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }t\text{ }\left\{ \text{ }\left( {{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{b}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }{{b}_{3}}\widehat{k} \right)\text{ }\text{ }\left( {{a}_{1}}\widehat{i}\text{ }+\text{ }{{a}_{2}}\widehat{j}\text{ }+\text{ }a3\widehat{k} \right) \right\}\]
Modifying it we will get
\[\widehat{r}={{a}_{1}}\left( 1-t \right)\widehat{i}+{{a}_{2}}\left( 1-t \right)\widehat{j}+{{a}_{3}}\left( 1-t \right)\widehat{k}+\left( {{b}_{1}}\widehat{i}+{{b}_{2}}\widehat{j}+{{b}_{3}}\widehat{k} \right)t\]
Option ‘C’ is correct
Note: It is important to note that we can take an arbitrary point or arbitrary position vectors outside the two given points and in-between the two given points so that we can compare the assumed point concerning two given points so that we get an equation of the line passing through all the three points such as
\[\overrightarrow{AP}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\overrightarrow{AB}\]
\[\widehat{r}\text{ }\text{ }\widehat{a}\text{ }=\text{ }t\text{ }\left( \widehat{b}\text{ }\text{ }\widehat{a} \right)\]
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Advanced 2026 Revision Notes for Chemistry Energetics - Free PDF Download

JEE Advanced 2021 Chemistry Question Paper 1 with Solutions

JEE Advanced 2022 Physics Question Paper 2 with Solutions

JEE Advanced 2022 Chemistry Question Paper 2 with Solutions

JEE Advanced 2021 Chemistry Question Paper 2 with Solutions

JEE Advanced 2022 Maths Question Paper 2 with Solutions

Trending doubts
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Difference Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions Explained

IIT CSE Cutoff: Category‐Wise Opening and Closing Ranks

IIT Fees Structure 2025

Top IIT Colleges in India 2025

Other Pages
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter




