




Dehydration of Alcohol & Williamson Synthesis Explained
Ether is a pleasant-smelling colourless volatile liquid that's highly flammable. It's used as an anaesthetic and as a solvent or intermediate in industrial processes. Ethers are highly flammable and used as polar solvents. When an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl groups, the compound is named ether. Ether vapours are employed as an anaesthetic because they produce unconsciousness when inhaled. Ethers are colourless, sweet-smelling, extremely volatile and flammable liquids.
Ethers
Ether are those compounds in which one oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl groups. The general of ethers is R-O-R’. on the basis of these R or alkyl groups, ether can be classified into two categories. If both R groups are the same, ether is called symmetrical ether and if both the R groups are different, ether is called asymmetrical ether.
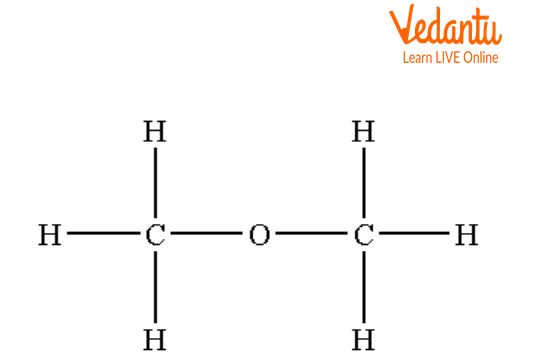
Structures of Dimethyl Ether
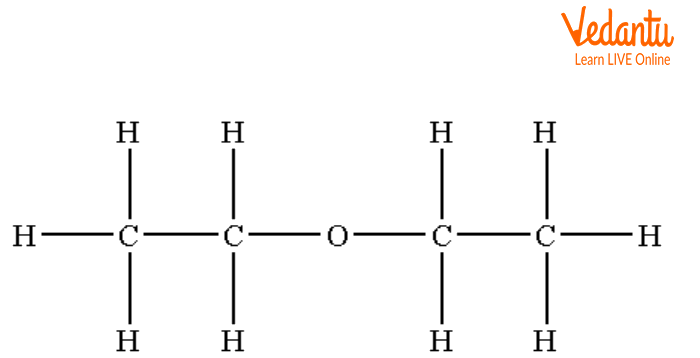
Diethyl Ether
Structures of Symmetrical Ether
The above structures are examples of symmetrical ether in which the same groups are attached on both sides of the oxygen atom.
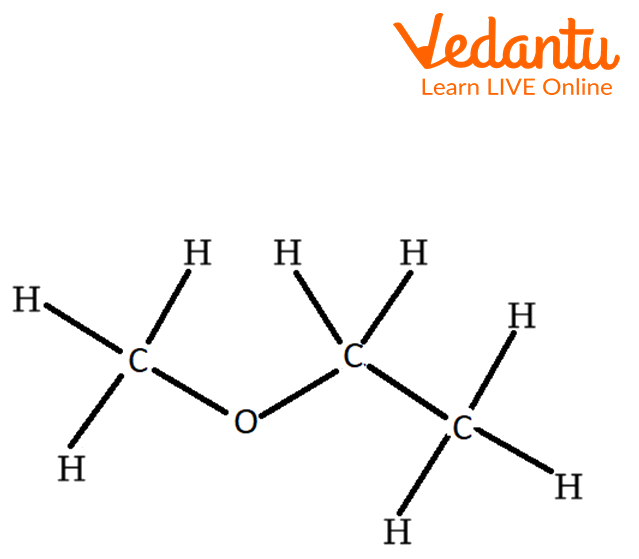
Structure of Unsymmetrical Ether
The above structure is an example of unsymmetrical ether. In which the different alkyl groups are attached to oxygen atoms.
An ether molecule features a net dipole moment due to the polarity of C-O bonds. The boiling point of ethers is like the alkanes but much lower than that of alcohols of comparable molecular mass despite the polarity of the C-O bond.
Alkyl Ethers
Alkyl ethers are commonly called ethers. In alkyl ethers, one oxygen atom is bonded with two alkyl groups. These alkyl groups are often the same or different. Alkyl groups are bonded to oxygen atoms by single bonds.
The most prevalent use for alkyl ethers in organic synthesis is in the production of Grignard reagent and Grignard reaction, which may be a reaction that involves the addition of carbon-carbon bonds to the carbonyl group >C=O of aldehydes or ketones. The aprotic nature of alkyl ethers makes them ideal solvents for Grignard reactions.
Preparation of Diethyl Ether
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction in which ether is formed by the reaction of an organohalide and deprotonated alcohol or alkoxide. Typically, it involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl via an SN2 reaction.
The general reaction mechanism is as follows:
R-X + RO(−)Na(+) → R-O-R
The above reaction is the general reaction of preparation of ether in which alkyl halide reacts with alkoxide ions and forms an ether.
For example, reaction of sodium ethoxide with chloroethane to form diethyl ether and sodium chloride: The Williamson ether reaction follows an SN2 bimolecular nucleophilic substitution mechanism.
C2H5Cl + C2H5O-Na+ → C2H5 -O- C2H5
The above reaction shows the preparation of diethyl ether by Williamson synthesis.
Preparation of Ether by Acid Dehydration
Diethyl Ether (C2H5)2O is prepared by the dehydration of ethanol by using sulphuric acid. The chemical reaction is here:
2C2H5OH + 2H2SO4 → C2H5 -O- C2H5 + H2SO4 + H2O
Ethyl alcohol Diethyl ether
The above reaction is the preparation of diethyl ether by acid dehydration method in which alcohol reacts with sulphuric acid and forms diethyl ether.
Laboratory Preparation of Ether
In the laboratory, ether can be prepared by the acid dehydration of alcohol. Alcohol reacts with sulphuric acid to form alkyl hydrogen sulphate. This alkyl hydrogen sulphate further reacts with alcohol and forms ether.
For example, the preparation of diethyl ether.
At 110°C, the reaction of ethyl alcohol with sulphuric acid forms ethyl hydrogen sulphate and then at 140°C, ethyl hydrogen sulphate reacts with the second molecule of ethyl alcohol to form diethyl ether. The reaction is given below:
2C2H5OH + 2H2SO4 → C2H5 -O- SO3H + H2SO4 + H2O
Ethyl alcohol
C2H5 -O- SO3H + C2H5OH 4 → C2H5 -O- C2H5 + H2SO4
Diethyl ether
The above reaction shows the laboratory synthesis of diethyl ether. Alcohol reacts with sulphuric acid to form ether in two steps.
Preparation of Ether Polymers
The ether can be defined by the two alkyl groups attached to the oxygen atom. The ether can be used to manufacture soap, perfume and wax etc. Sodium laureth sulphate (CH3(CH2)10CH2(OCH2CH2)nOSO3Na) is a type of ether surfactant used in soaps. Preparation of ether soap (Sodium laureth sulphate) is done by ethoxylation of dodecyl alcohol which further is converted to a half ester of sulphuric acid and finally neutralised to form sodium salt.
Methods of Ether Preparation
Ethers are often prepared in the laboratory from alcohol and alkyl halides through Williamson synthesis. Both dehydration of alcohol and Williamson synthesis are popular methods of preparation of ethers. However, other ways of laboratory preparation include the following:
1. Passing alcohol vapours over Al2O3
CH3OH + Al2O3 → CH3 - O – CH3 + H2O
2. Heating alkyl halides with Silver Oxide
2R-X + Ag2O → R-O-R + 2AgX
3. The reaction of diazomethane with alcohol
CH3OH + CH3N2 → CH3 – O – CH3
Key Features
Ethers are used in the organic synthesis of various compounds.
Ethers are derivatives of hydrocarbons in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by an alkoxy or an aryloxy group.
Ethers show functional isomerism (with alcohols).
FAQs on Ether Preparation: Complete Guide for Students
1. What are the two primary methods for the preparation of ethers as per the Class 12 Chemistry syllabus for 2025-26?
The two main laboratory methods for preparing ethers are:
- Dehydration of Alcohols: This method involves heating alcohols with a protic acid like concentrated H₂SO₄ or H₃PO₄ under controlled temperature. It is mainly suitable for preparing symmetrical ethers from primary alcohols.
- Williamson Synthesis: This is a more versatile method where an alkyl halide reacts with a sodium alkoxide or sodium phenoxide. It is used to prepare both symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
2. How are ethers prepared by the dehydration of alcohols, and what is the mechanism involved?
Ethers are prepared by the acid-catalysed dehydration of primary alcohols at a specific temperature. For example, when excess ethanol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 413 K (140°C), it forms diethyl ether. The reaction follows an SN2 bimolecular substitution mechanism, where one protonated alcohol molecule is attacked by another alcohol molecule, leading to the elimination of a water molecule and the formation of an ether linkage (R-O-R).
3. Why is maintaining the correct temperature crucial when preparing ether from alcohol dehydration?
Temperature is a critical factor because it determines the reaction pathway. In the acid-catalysed dehydration of primary alcohols:
- At a lower temperature of 413 K, bimolecular substitution (SN2) is favoured, resulting in the formation of an ether.
- At a higher temperature of 443 K, intramolecular elimination (E2) becomes the dominant reaction, leading to the formation of an alkene instead of an ether.
Thus, precise temperature control is essential to maximise the yield of the desired ether and prevent the side-reaction of alkene formation.
4. What is the Williamson synthesis for preparing ethers?
The Williamson synthesis is a widely used laboratory method for preparing both symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. It involves an SN2 reaction between a sodium alkoxide (R-ONa) and a primary alkyl halide (R'-X). The alkoxide ion acts as a nucleophile, attacking the alkyl halide and displacing the halide ion to form an ether (R-O-R'). The general reaction is: R-ONa + R'-X → R-O-R' + NaX.
5. What is the major limitation of Williamson synthesis?
The major limitation of Williamson synthesis is that it works best when the alkyl halide is primary or methyl. If a secondary or, particularly, a tertiary alkyl halide is used, an elimination reaction occurs instead of substitution. This is because alkoxides are strong bases as well as strong nucleophiles. With a sterically hindered tertiary halide, the alkoxide acts as a base, abstracts a proton, and leads to the formation of an alkene, not an ether.
6. How can anisole (methoxybenzene) be prepared using Williamson synthesis?
Anisole can be prepared by reacting sodium phenoxide with a methyl halide (like methyl iodide or methyl bromide). First, phenol is treated with a strong base like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form the more nucleophilic sodium phenoxide. This phenoxide ion then attacks the methyl halide via an SN2 mechanism to form anisole. The reverse combination—reacting bromobenzene with sodium methoxide—is not feasible because aryl halides are unreactive towards nucleophilic substitution.
7. To prepare ethyl tert-butyl ether, which combination of reactants is correct in Williamson synthesis and why?
To prepare ethyl tert-butyl ether, the correct combination is reacting a primary alkyl halide (ethyl bromide) with a tertiary alkoxide (sodium tert-butoxide). This setup favours the SN2 substitution pathway because the attack is on an unhindered primary carbon.
The alternate combination—reacting a tertiary alkyl halide (tert-butyl bromide) with a primary alkoxide (sodium ethoxide)—would fail. The primary alkoxide would act as a strong base, and an E2 elimination reaction would occur on the tertiary halide, yielding 2-methylpropene as the major product instead of the desired ether.
8. What is the key difference in the types of ethers that can be prepared from alcohol dehydration versus Williamson synthesis?
The key difference lies in the scope of the ethers that can be formed:
- Dehydration of Alcohols: This method is generally suitable only for the preparation of simple, symmetrical ethers where both alkyl groups are identical (e.g., diethyl ether from ethanol). Attempting to make an unsymmetrical ether from a mixture of two different alcohols results in a mixture of three different ethers, which is difficult to separate.
- Williamson Synthesis: This method is much more versatile and is the preferred method for preparing unsymmetrical ethers (where R ≠ R'). By carefully choosing the primary alkyl halide and the alkoxide, a specific unsymmetrical ether can be synthesised with a high yield.























