An Overview of Important Questions Class 9 Science Chapter 14
Have you ever wondered how Earth provides us with everything we need to live—air, water, soil, and so much more? In Natural Resources Important Questions for Class 9 Science, you'll understand where these resources come from and why they are so precious. This chapter helps you explore the basics of our environment and explains important cycles like water, carbon, and nitrogen in a way that's easy to remember.
You might often feel a little confused about topics such as pollution, the greenhouse effect, or how natural resources are managed. These important questions have been designed by experts to clear up your doubts, help you practice different types of questions, and become more confident in Science. If you want to check the full syllabus or prepare for other chapters, you can find it naturally in the Class 9 Science Syllabus.
Make your exam prep smoother with Vedantu’s handy PDF of important questions for this chapter. Practice these questions to cover all key points and get familiar with the kinds of questions you might face. If you’re revising other chapters too, the Class 9 Science Important Questions can be a great help for you.
Important Questions For Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources - 2025-26
Study Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 – Natural Resources
1 Marks Questions
1. Which of the following does not contribute to the biotic components of the biosphere?
Producers
Consumers
Decomposers
Air
Ans: d) Air
2. Which of the following is the major source of minerals in the soil?
Parent rock from which soil is covered
Plants
Bacteria
Animals
Ans: a) Parent rock from which soil is covered.
3. Which of the following factors does not cause soil formation in nature?
Water
The Sun
Polythene bags
Wind
Ans: c) Polythene bags
4. The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrites and nitrates compounds can be occured by
The process of nitrogen fixation by the bacteria present in soil.
The process of carbon fixation by carbon fixing factors present in soil.
Any of the industries manufacturing nitrogenous compounds.
The plants used as cereal crops in the field.
Ans: a) The process of nitrogen fixation by the bacteria present in soil.
5. Write down two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere.
Ans: Ozone and Oxygen.
6. Write names of two compounds that contain both nitrogen and oxygen and are biologically important.
Ans: Proteins and urea are biologically important compounds that contain both nitrogen and oxygen.
7. Which of the given options is not fossil fuel?
Petrol
Diesel
Wood
Coal
Ans: c) Wood.
8. Carbon cycle does not have which of the following steps?
Respiration
Transpiration
Photosynthesis
Burning of fossils
Ans: b) Transpiration.
9. How much of the earth's surface is covered with water?
60%
50%
75%
85%
Ans: d) 85%
10. On barren rocks, lichens grow after the growth of which of the following organisms?
Mosses
Gymnosperms
Ferns
Algae
Ans: a) Mosses.
11. How will the earth’s temperature change, if there will be no atmosphere?
Earth’s temperature will decrease in that case.
Earth’s temperature will increase in that case.
Earth’s temperature will be unaffected in the absence of atmosphere.
Earth’s temperature will increase in daytime and will decrease at night.
Ans: d) Earth’s temperature will increase in daytime and will decrease at night.
12. Soil fertility decreases due to which of the following factors?
Crop rotation
Soil erosion
Afforestation
Strip cropping
Ans: b) Soil erosion.
13. Which of the following organisms cannot fix nitrogen in the atmosphere?
Nostoc
Rhizobium
E. Coli
Azotobacter
Ans: c) E. Coli
14. Which atmospheric gas absorbs the harmful UV radiations coming from the sun?
O2
CO2
NO2
O3
Ans: d) O3 (Ozone)
15. Ozone layer depletion is caused by _____.
CH4
CO2
CFC’s
CO
Ans: c) CFC’s
16. Which of the following statements is not correctly related to the ‘Water Pollution’?
Undesirable substances are added to the water bodies.
Undesirable substances are removed from the water bodies.
Pressure change in water sources.
Temperature change in water sources.
Ans: c) Pressure change in water sources.
17. The pattern of rainfall depends on which of the following factors?
Water table present underground
Number of natural water sources present in a zone
Population density of humans in an area
Prevailing season in an area.
Ans: b) Number of natural water sources present in a zone.
18. The air present on Venus and Mars has which of the following components?
CO2
O2
NO2
He
Ans: a) CO2
19. Which of the following gases is present in a high amount in the atmosphere?
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Nitrogen
Water
Ans: c) Nitrogen
20. From outside to inside, the sequence of regions of earth are ____.
Core, mantle, and crust
Core, crust, and mantle
Crust, mental, and core
Mantle, core, and crust
Ans: c) Crust, mental, and core.
21. _____ is the topmost layer of earth’s surface.
Troposphere
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
Ans: (d) Thermosphere
22. Which of the following processes convert O2 to CO2?
Photosynthesis
Breathing
Respiration
Both (a) and (b)
Ans: c) Respiration
23. Define the atmosphere and name the different regions of the atmosphere.
Ans: The atmosphere is the layer of air that surrounds the earth. Following are the different regions of the atmosphere:
(a) Troposphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere
(d) Thermosphere
25. The process of conversion of water vapor into water droplets is known as ____.
Condensation
Sublimation
Evaporation
Freezing
Ans: a) Condensation
26. The process of evaporation of plant water through its leaf surface is _____.
Condensation
Transpiration
Evaporation
Both a) and c)
Ans: b) Transpiration
27. What is the %age of O2 in the air?
21%
52%
78%
12.5%
Ans: a) 21%
28. What is the full form of CFC?
Carbon fluorine compounds
Carbon fluoro compound
Chloro fluoro carbons
Chlorine fluoro compound
Ans: c) Chloro fluoro carbons
29. From the given options, greenhouse gas is ____.
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Ozone
Both a) and b)
Ans: b) Carbon dioxide
30. On which layer of earth, is life possible?
Biosphere
Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
None of the above
Ans: a) Biosphere
31. Which of the following is the major component of the atmosphere of Mars?
Ozone
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
None of the above
Ans: c) Carbon dioxide
2 Marks Questions
1. During the water cycle, water is found in how many states?
Ans: Water is present in all three states of matter during the water cycle which are ice (solid form), water (liquid form), and water vapor (gaseous form).
2. Write any three human activities that can lead to an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the air.
Ans: Human activities that can increase the content of carbon dioxide in the air are given below:
Combustion of coal and oil
Burning wood
Deforestation (deforestation).
3. Define the greenhouse effect.
Ans: The phenomenon in which the temperature of the earth rises due to the trapping of harmful radiations by greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane that result in global warming is called the greenhouse effect.
5. Define soil erosion.
Ans: The process of wearing away topsoil that is rich in humus is known as soil erosion.
6. What role do the decomposers play in the biogeochemical cycle?
Ans: The decomposer breaks down rotten and dead organic matter into simpler forms and returns back the minerals to nutrient pools such as air, water, and soil.
7. Define the greenhouse effect. Write down the name of any one greenhouse gas.
Ans: The phenomenon of an increase in global temperature due to an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere is known as the greenhouse effect.
Carbon dioxide is one of the major greenhouse gases.
8. Mention some methods by which soil erosion can be prevented.
Ans: Methods to prevent soil erosion are given below:
Stop deforestation and plant more trees.
The borders of the crop fields should be planted with a few trees to mitigate the effects of strong winds on the fields.
Crop rotation i.e. growing different types of crops in the same field in a sequential manner should be applied to maintain soil fertility. The water retention capacity of the soil is also maintained in this way.
9. Write some causes of Water Pollution.
Ans: Water pollution can be caused by: -
a) Household waste such as detergent or sewage.
b) Agricultural wastes like fertilizers and pesticides are used for better crop production.
c) Calcium and magnesium compounds get dissolved in water and also act as pollutants in natural sediments.
d) Rivers, ponds, lakes, and other water bodies are used for bathing or washing purposes which results in water pollution as well as contaminate the water with a variety of bacteria and protozoa.
10. Mention the different types of natural resources with examples.
Ans: There are two types of natural resources which are given below:
a) Inexhaustible natural resources - There are some resources which are present in unlimited numbers in nature and are unlikely to be depleted by normal human activity like solar energy, air, water, etc.
b) Exhaustible Natural Resources - These resources exist in limited quantities in the natural world and may be depleted by human activities if not used in limits like coal, petroleum, and minerals.
11. Write some differences between renewable and non-renewable resources.
Ans: Some of the differences between renewable and nonrenewable resources are given below:
Renewable Resources | Non- renewable Resources | ||
1. | They will not get exhausted from nature. | 1. | They will get exhausted from nature if they are not used to the limit. |
2. | These can be used many times. | 2. | These should be used in limits and cannot be used again and again. |
12. Discuss how the rivers add minerals, taken from land to the seawater?
Ans: The river passes over land, absorbs the minerals present in the soil and adds them to the sea.
13. Draw a diagram representing the water cycle.
Ans: The following diagram represents the water cycle:
(Image will be uploaded soon)
14. Write down any two methods to restore the fertility of soil.
Ans: Soil fertility can be restored using the following methods:
(a) Alternately cultivate beans and other types of crops.
(b) Using manure and fertilizer.
15. Why does growing legumes increase soil fertility?
Ans: Legumes have nodules in their roots. There are nitrogen-fixing bacteria present in the nodules of these leguminous plants, which convert atmospheric nitrogen into soluble compounds. By adding these compounds to the soil, soil fertility increases.
16. Write any two reasons, mentioning over-exploitation of natural resources.
Ans: Over-exploitation of natural resources is caused by:
(a) Significant increase in population
(b) Advances in industry and technology are the major reasons for the increase in the use of resources.
(c) Rapid increase in urbanization.
17. Write down the constituents of soil.
Ans: Soil has the components given below:
(a) It contains soil particles like gravel, sand, silt and clay.
(b) It has humus which is formed by the decomposition of dead organisms and organic matter.
(c) Soil water
(d) Soil air
(e) Soil organisms like bacteria, earthworms, etc.
18. Define soil. How is it important for humans?
Ans: Soil is the top fertile layer of the earth called soil. It provides us -
(i) Soil provides food and feed.
(ii) It provides material for clothes.
(iii) It provides anchorage to plants.
(iv) It provides water and minerals in plants.
19. What is the importance of air?
Ans: Following are the importance of air:
a) Air provides oxygen gas for respiration in animals and plants.
b) Air provides CO2 for photosynthesis.
c) The atmosphere affects the climate by squeezing the sun's rays that reach the earth.
d) Air is a repository of some life-critical elements.
20. Write down the factors that affect soil fertility.
Ans: Soil fertility depends on
The presence of organic matter (humus) and nutrients.
Soil capacity to retain water and air.
21. Describe biological nitrogen fixation. Specify the name of the organism responsible for it.
Ans: The process by which nitrogen in the atmosphere is converted into a soluble and usable form by microorganisms is called nitrogen-fixation. Microorganisms responsible for nitrogen fixation include Rhizobium, Azotobacter, and Blue green algae.
22. Define biogeochemical cycle.
Ans: Biogeochemical cycle is the constant interaction between biotic and abiotic components of the biosphere that causes the exchange of matter and energy between them.
23. What are the reasons behind the possibility of life on the earth?
Ans: Life on earth is possible because:
(a) Earth temperatures are suitable for a variety of life forms.
(b) Oxygen is present in the air that is required by all living things.
24. What is the requirement of freshwater by terrestrial life forms?
Ans: Creatures that live on land need freshwater because their bodies cannot withstand saline water and also they cannot excrete the high amount of dissolved salt in seawater.
25. How is the climate-controlled by the atmosphere?
Ans: During the day, the atmosphere keeps the earth's average temperature constant and also prevents rapid temperature rise during the day. It also prevents heat from escaping into outer space, in this way, maintains a survivable climate on earth.
26. What is the process by which winds are created?
Ans: The air over land quickly heats up and begins to rise in the daytime. As it rises, it creates a zone of low pressure and the air moves from the sea towards the low pressure zone. The movement of this air from one area to another creates wind.
27. How does the sun help to break down the rocks into smaller pieces to form soil?
Ans: The sun heats and expands up the rock during the day. At night, this rock cools and shrinks. Because not all parts of the rock expand and contract at the same rate, as a result massive cracks form and then they break into smaller pieces.
28. What is the composition of air?
Ans: The air has following components:
Sr. No. | Name of gas | Percentage composition of gas by volume | Percentage composition of gas by mass |
1. | Nitrogen | 78.09 | 75.5 |
2. | Oxygen | 20.95 | 23.2 |
3. | Argon | 0.93 | 1.0 |
4. | Carbon dioxide | 0.031 | 0.046 |
5. | Neon | 0.002 | 0.0005 |
6. | Helium | Negligible | Negligible |
In addition to the gases, water vapors are also present in the air.
29. How does soil pollution occur?
Ans: Soil pollution occurs in the following ways:
Using high amounts of fertilizers and pesticides kill the microorganisms that help to recycle the nutrients from the soil.
Earthworms that created humus and fertilized the soil are also getting killed with increased use of pesticides.
Addition of harmful substances and removal of useful components also affect the soil fertility.
30. Describe the carbon cycle that occurs in nature.
Ans: Following are the processes involved in the carbon cycle:
(a) Plants convert the atmospheric carbon dioxide into organic compounds which then go to the animals when eaten by the animals.
(b) Plant organic compounds are also converted into petroleum and coal.
(c) Carbon dioxide is converted directly into carbonic acid or carbonates when present in water and then switched to the limestone.
(d) Organic compounds of animals change into carbon dioxide in the atmosphere by respiration and decomposition process.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Diagram Representing Carbon Cycle
1. Define smog and the process of its formation.
Ans: Smog - Smog is the combination of smoke and fog.
Formation of smog - Smog is formed when air pollution exists and a high level of smoke is formed in the atmosphere. This smoke gets mixed with the fog and forms smog.
2. What is the importance of water in life?
Ans: Water is important for life because:
All types of life processes occurring inside the cell take place in a water medium.
Transportation of various substances in the body occurs through the water.
Transportation of various substances in plants also occurs through the water.
3. How do living things cause the erosion of rocks?
Ans: Organisms such as lichens when growing on the surface of a rock, release certain chemical substances that cause crushing of the surface of the rock, breaking it down into fine particles.
4. What is the process of rain formation?
Ans: Water vapors are formed when water from the water bodies evaporates. These water vapors move up in the atmosphere and condense to form small water droplets. When a huge amount of water droplets are collected, it becomes a large water droplet and becomes heavy which results in the falling of rain.
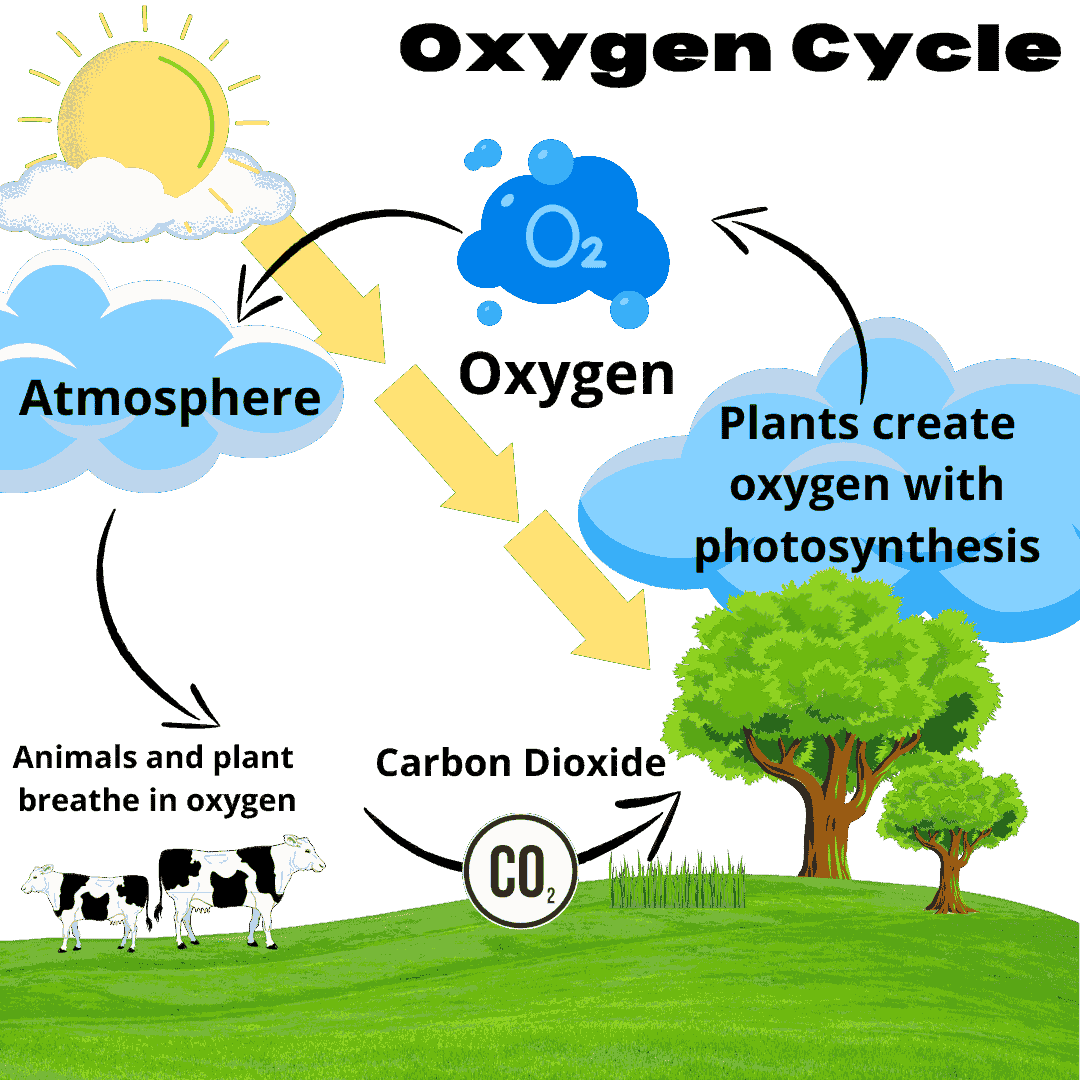
5. Explain the oxygen cycle that occurs in the atmosphere.
Ans: The following processes occur in the oxygen cycle:
Animals and humans take up the oxygen present in the air for respiration.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
They produce water and carbon dioxide as the byproduct of respiration and release them out of their body.
These byproducts are used by plants during photosynthesis.
Plants make organic compounds as well as release oxygen gas in air after using the byproducts of respiration (water and carbon dioxide) by animals.
Oxygen is restored in the atmosphere and glucose is used by plants and animals.
3 Marks Questions
1. How is the earth’s atmosphere different from that of Venus and Mars?
Ans: The air present on the earth is mainly a mixture of many gases like nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and carbon dioxide (0.03%). However, on planets such as Venus and Mars, it has been observed that carbon dioxide is the major component of their atmospheric air. It has been found that carbon dioxide is 95-97% in the atmosphere of Venus and Mars.
2. Why is the atmosphere considered a blanket?
Ans: Because air is a bad conductor of heat, the atmosphere that covers the earth is like a blanket. The atmosphere significantly stabilizes the earth's average temperature during the day and even throughout the year. The atmosphere prevents rapid temperature rises during the day and also it slows the rate at which heat goes out into space at night time.
3. How is the wind created?
Ans: Due to the heated land or water, the air present over their surface also gets heated up and rises. The air present over land gets rapidly heated up as compared to the air present over water because land gets heated faster than the water. Hence, the air on land heats up faster during daytime and begins to rise. When this air rises, a low-pressure region is created and the air above the sea moves to the low-pressure region. The wind is created due to the movement of air from one region to another.
4. What is the process of cloud formation?
Ans: A large amount of water evaporates and moves to the air when the water bodies get heated up during the day. Other biological activities also cause the movement of water in the atmosphere. Along with the water vapors, the air also gets heated up and rises. When the air rises, it expands and cools. The cooling causes condensation of the water vapors and converts them into droplets. This condensation of water is facilitated when some particles are able to act as the "nucleus" around which these droplets can form. In general, dust in the air and other suspended particles act as nuclei. Clouds are formed by this process.
5. Write down the human activities that are responsible for causing air pollution.
Ans: The given human activities can cause air pollution:
Combustion of fossil fuels such as coal or petroleum releases various nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides into the air.
Smoke and other suspended particles are released into the air due to burning of wood.
Usage of harmful chemicals like aerosols, CFCs, etc can cause air pollution.
6. What is the need for water for living organisms?
Ans: Living organisms require water to perform various life processes. All living things are made up of cells and all types of cellular processes take place in water medium. The chemical reactions take place in living cells between the compounds that are dissolved in water. Also transportation of various substances occurs from one part of the body to another in dissolved form. Therefore, to stay alive, living organisms require to maintain the water level in their bodies.
7. What are the freshwater sources in different places on earth?
Ans: Following are some freshwater sources found in different places on earth:
Ponds
Lakes
Rivers
Wells and Tubewells
Dams
Rainwater provides water to all of the above freshwater sources.
8. Do you know about activities that can pollute the freshwater sources?
Ans: We use fertilizers and pesticides in our farms. Their excess use can pollute these water sources. The sewage in our towns and cities and waste from factories and water used for cooling in a variety of operations in certain industries well are released into these water sources. Such activities pollute water bodies.
9. What is the process of soil formation?
Ans: Over a long period of time, like millions of years ago, the rocks present on earth were weathered by various physical, chemical and biological factors. This weathering resulted in the formation of soil particles. The factors responsible for weathering of rocks and formation of soil are given below:
The Sun: The heat radiation of the sun causes the expansion of rocks. These rocks cool down at night and contract, thus, forming cracks in the rocks.
Water: Water supports two methods by which soil formation takes place. First, water can enter cracks of rock formed due to uneven heating by the sun. And later on this water freezes and causes cracks to spread.
Wind: Strong winds rub against rocks and erode them down in a similar way to that of water.
Living organisms: Some living organisms release chemicals that cause crushing of the rocks. Lichens are such organisms that grow on the rocks and release some chemicals that convert the rocks into soil particles. Some other plants like mosses grow on rocks and create cracks in the rocks as their roots penetrate into the rocks.
10. By which methods soil erosion can be reduced or prevented?
Ans: By applying the following methods, soil erosion can be reduced or prevented:
Deforestation and overgrazing of animals should be reduced.
More trees should be planted to support afforestation or reforestation.
Agricultural methods should be improved.
11. What is the role of the atmosphere to make life possible on earth?
Ans: The atmosphere is essential for life in the following ways:
It protects the living organisms from harmful sun radiations by acting like a blanket that covers the earth’s surface and traps the harmful UV radiations from the sun. In this way, the atmosphere also maintains a constant temperature of the earth.
Carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and oxygen for respiration and combustion is provided by the atmosphere.
A sudden change in the earth’s temperature is prevented by the atmosphere.
12. What is the role of water to make life possible on earth?
Ans: Water is essential for all types of life forms because:
All living organisms comprise living cells and all types of cellular processes occur in water medium. All types of metabolic reactions occur in living organisms and in their cells take place between the substances that are dissolved in water.
Transportation of substances that occur in living organisms take place in dissolved form.
Water is required in digestion, excretion, and egestion-like body processes.
Water regulates the body temperature of organisms by sweating and evaporation.
13. How do living things depend on the soil? Are the organisms living in the water completely independent of the soil as a resource?
Ans: Plants require simple nutrients, such as certain elements to grow normally, and most of these elements are obtained from the soil. Plants use these elements to prepare their own food in the presence of the sun. Because all other living things depend on plants for their development and diet, we can say that organisms living in water are not completely independent of soil as a resource. Another reason is that the organic matter in the soil is dissolved in the water to provide nutrients for aquatic organisms.
14. There are weather reports on television and in newspapers. How predictable are these weather reports?
Ans: The weather forecast is based on information gathered from general patterns of temperature, humidity, wind and cloud changes.
15. There are many human activities that lead to increased air, water, and soil pollution. Do you think that isolating these activities in restricted and enclosed areas will help to reduce pollution?
Ans: Isolating many human activities that cause an increase in air, water, and soil pollution will help reduce water and soil pollution, but it is unlikely to affect the severity of air pollution, because gases can spread easily from the transmission area to other places nearby. We need to focus on the sustainable management of resources, rather than isolate them, and reduce or replace their consumption, such as using clean fuels such as CNG to replace fossil fuels.
16. Explain how forests affect the quality of air, water, and soil resources.
Ans: Effects of forests on air: Trees and plants in the forest can absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, thereby maintaining the level of these gases in the biosphere.
Effects of forests on water: Forests enable the water cycle in nature to form clouds and condense to cause rainfall.
Effects of forests on soil: The roots capture soil particles and prevent soil erosion. Dead trees and plants or parts of them enrich the soil with humus and organic matter, making it fertile.
17. Write down the biotic and abiotic factors that cause soil formation.
Ans: Some of the abiotic factors that cause soil formation are given below:
The Sun: The heat radiation of the sun causes the expansion of rocks. These rocks cool down at night and contract, thus, forming cracks in the rocks.
Water: Water supports two methods by which soil formation takes place. First, water can enter cracks of rock formed due to uneven heating by the sun. And later on this water freezes and causes cracks to spread.
Wind: Strong winds rub against rocks and erode them down in a similar way to that of water.
Biotic factors responsible for soil formation:
Some living organisms release chemicals that cause crushing of the rocks. Lichens are organisms that grow on the rocks and release some chemicals that convert the rocks into soil particles. Some other plants like mosses grow on rocks and create cracks in the rocks as their roots penetrate into the rocks.
18. Mention down some sources that cause air pollution.
Ans: The given sources can cause air pollution:
Air pollution can be caused by some natural processes like forest fires, smoking volcanoes, sandstorms, floating pollen particles, and organic degradation.
Consequences of some human activities like overpopulation, deforestation, urbanization and industrialization.
The burning of fossil fuels in automobiles, thermal power stations and industries cause air pollution.
19. Why is the Mathura refinery a problem for the Taj Mahal?
Ans: The Mathura refinery emits acidic gases such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide into the air. In the presence of moisture, sulfur dioxide is oxidized to sulfuric acid, and nitrogen dioxide is oxidized to nitric acid in the air. Acid reaches the surface and water bodies together with rain. Acid rain is rainwater that contains acid as a pollutant. This acid rain caused problems for Taj Mahal marble.
20. How does the atmosphere function as a protective blanket? Did you mention the harmful effects of ultraviolet light?
Ans: The atmosphere protects the earth as it absorbs most of the harmful radiation, such as ultraviolet radiation from the sun. The harmful radiation is absorbed by the upper atmosphere and reflected back to space. The sun's rays are reflected back to space by dust particles, water vapor, and clouds. Because of this, the earth receives the necessary heat and light from the sun, which helps control the weather and allows living things to survive. The harmful effects of UV radiation cause blindness and skin cancer.
21. Explain the reasons:
a) Step farming is very common in the mountains.
Ans: (a) On hilly slopes, step farming reduces the steepness of the slope, and thus controls soil erosion.
b) Fertile soil contains a lot of humus.
Ans: The decomposition of dead organic matter occurs in the topsoil. This monastery, built-in , converts organic materials into humus. Therefore, fertile soil has humus.
22. What are the hazards of air pollution?
Ans: The Harmful Effects of Air Pollution are:
Air pollution affects the respiratory tract of living things, causing bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, and lung cancer.
The burning of fossil fuels such as coal and patrols releases nitrogen oxides and sulfur, and causes acid rain.
Burning fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum will also increase particulate matter in the air. The presence of these pollutants in the air during the cold season can cause the formation of smog, which reduces visibility and causes road problems.
23. Most of the land is surrounded by the sea. Then why do we need to save water? Ans: Maintaining water conservation:
Due to population growth, water consumption is increasing substantially.
Due to increased water pollution.
The water level is falling due to the decrease in precipitation.
24. What is weathering? How does weathering happen?
Ans: The formation of soil due to the destruction of rocks is called weathering. is derived from
physical factors such as the sun (temperature), rain, wind, and frost.
Biological media-through the action of plants, animals and microorganisms.
25. Write down how to increase the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Ans: By following ways, the concentration of carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere:
Both plants and animals emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere through respiration.
When organic waste and carcasses are decomposed by decomposers.
Burning fossil fuels such as wood, coal, gasoline, natural gas and kerosene.
By volcanic eruptions.
The carbonate rock is weathered by soil microorganisms, plant roots and acid rain.
26. "Water is important." Give the reason for the statement.
Ans: The value of the water of life is explained in the following points:
It acts as a universal solvent.
Most of the activities in the body are carried out in the water.
The transfer of a substance from one part of the body to another in a dissolved form.
Dissolve waste and promote excretion from the body.
Aquatic organisms use oxygen dissolved in water.
27. How do forests affect our air, water, and soil?
Ans: Forests affect air, water, and soil in the following ways:
The forest acts as an air purifier. During photosynthesis, they consume carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
The forest also keeps the water level below ground level. The roots absorb water and raise the water level. Trees also contribute to cloud formation during evaporation and increase the humidity (water vapor) in the air. This water vapor will form more clouds, which will help when it rains.
Tree roots support the soil and prevent erosion, thereby maintaining soil fertility.
28. What is the greenhouse effect? How does this affect the earth’s atmosphere?
Ans: An increase in the concentration of watr vapor and other atmospheric gases (such as nitrous oxide methane) will prevent the release of solar radiation. This increases the temperature of the atmosphere above the earth's surface, making it warmer. This phenomenon is called the greenhouse effect. The warm atmosphere will melt snow from the polar and high mountains, which will raise sea levels and flood low-lying areas.
29. What are the hazards of water pollution?
Ans: The hazards of water pollution are as follows:
Polluted water can cause water-borne diseases such as dysentery, cholera and jaundice.
Pesticides such as DDT enter the water body with rainwater, and from there enter the food chain through producers and accumulate at various trophic levels. This is called biological surge , which seriously affects the body at the top of the food chain.
Eutrophication-Excessive growth of phytoplankton due to wastewater discharge will reduce the level of dissolved oxygen, thereby affecting aquatic organisms.
30. What is the biogeochemical cycle? What is the nutrient cycle in the atmosphere?
Ans: The nutrient cycle between the inanimate environment (soil, air, water) and living organisms is called the biogeochemical cycle.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Where i) shows the Ammonifaction process while ii) shows denitrification.
31. Explain how to reduce the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Ans: Ways to reduce the concentration of carbon dioxide-
a) Photosynthesis-Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and use it to synthesize food.
b) Fossils-Due to the pressure and temperature of the earth, dead plants and animals are converted into fossil fuels such as coal and oil.
c) The carbon dioxide contained in the water is combined with the carbonate and graphite in the rock.
32. How do fossil fuels produce air pollution?
Ans: The burning of fossil fuels has the following effects:
a) The burning of fossil fuels releases nitrogen oxides and sulfur. This can cause breathing problems and acid rain.
b) The burning of fossil fuels increases the amount of fine dust in the air, which can cause smog, reduced visibility and traffic accidents in winter.
c) When burned, it releases carbon dioxide, which absorbs solar energy and increases the temperature of the earth.
33. Write down what will happen if the water is contaminated.
Ans: When water is contaminated, the following events occur:
a) Undesirable substances that can cause cholera are added to water bodies.
b) It can remove required substances from water bodies and dissolve oxygen. , which is important for aquatic organisms and poses a danger to aquatic organisms.
c) When water is polluted, the temperature of the water will change, which will adversely affect the life forms in the water.
34. Write about the nitrogen cycle in nature?
Ans: The nitrogen cycle is divided into the following stages:
a) Nitrogen in the atmosphere is transformed into the protoplasm of green plants through nitrogen fixation.
b) Protoplast is converted to ammonia by ammoniating.
c) The ammonia is then converted to nitrite and then to nitrate.
d) The nitrogen in the atmosphere is then directly converted into nitrate through nitrification.
e) Nitrate is converted to nitrogen by denitrification.
35. What is the greenhouse effect? What happens if the amount of carbon dioxide in the air increases?
Ans: The phenomenon that various gases absorb heat in the air and cause the earth's temperature to rise is called the greenhouse effect. If the carbon dioxide content in the air rises, because carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, the greenhouse effect will increase and cause the earth’s atmospheric temperature to rise rapidly. That leads to the melting of glaciers and becoming a danger for various living organisms.
36. What is the role of ozone in the atmosphere? How is the ozone hole created?
Ans: The ozone layer absorbs harmful radiation from the sun and prevents it from reaching the surface of the earth, where it can harm living things. There are ozone layers, and an ozone hole has been discovered over Antarctica.
37. What is the role of the earth's soil in agriculture?
Ans: Under the ground, the loose surface of the earth's crust is present. Soil is the nutrient medium for all plants. It provides material support and nutrients for plant growth, as well as sufficient air and water.
38. What is the difference between the Earth's atmosphere and the atmospheres of Venus and Mars?
Ans: The earth's atmosphere contains oxygen, which is necessary for life to exist on the planet. It is required during breathing and respiration, two of life's most important events. Mars atmosphere has as its main constituent, and thus life on Earth is not possible.
39. What is air pollution and how does it cause acid rain?
Ans: The air is mixed with harmful substances, which changes the components of air to make it harmful, which is called air pollution. When fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum are burned, various nitrogen and sulfur oxides are formed, which are mixed with rainwater to form nitric acid and sulfuric acid, and then fall on the earth's surface in the form of acid rain. It is very dangerous because it can cause kinds of disturbances to living organisms and destroy buildings and monuments.
40. Why is carbon dioxide so vital to the survival of life on Earth? What are the two methods by which it is fixed on Earth?
Ans: Carbon dioxide aids in the heating of the earth's surface, which aids in the maintenance of a suitable temperature for life forms on Earth.It is also required for photosynthesis by plants.
It is fixed in two ways:
(a) green plants convert to glucose in the presence of sunlight.
(b) Marine animals make use of carbonates dissolved in seawater to make shells.
5 Marks Questions
1. What is the nitrogen cycle? Explain the different steps.
Ans: Steps of the Nitrogen cycle
1) Ammonification – The process of converting complex organic compounds such as proteins. Ammonification is the process of converting ammonia into ammonia.
2) Nitrification – Nitrification refers to the process of converting ammonia into nitrites and nitrates.
It occurs in two steps:
$\text{Ammonia} \underset{Nitrosomonas}{\longrightarrow} {\text{Nitrite}}$
$\text{Nitrite} \underset{Nitrobactor}{\longrightarrow} {\text{Nitrate}}$
3) Denitrification – The process of converting nitrite salts in soil and water to free nitrogen gas. This is done by bacteria pseudomonas.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
2. Draw a carbon cycle.
Ans:
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Download Important Questions of Natural Resources Class 9 PDF
Natural Resources Class 9 Important Questions Summary
Earth is the only planet on which life exists and its important resources are land, water, and air. And some of the other resources that earth includes are fossil fuels, sunlight, wind, and minerals. Biofactors which are referred to as living things in the ecosystem and air, water, soil, etc forms the non-living or abiotic components of the biosphere.
Topics covered in the natural resources Class 9 Important questions are - Natural resources, The Breath of Life: Air, Water: A Wonder Liquid, Mineral Riches in the Soil, Biogeochemical Cycles, Ozone Layer.
Air and Air Pollution - The atmosphere is surrounded by a layer of gases. Some of the gases are 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases by volume. The main role of the atmosphere is to keep the temperature steady. It also slows down the escape of the temperature of heat to outer space and it also prevents the sudden rise of temperature during the day.
Ozone Layer - It is a thin layer of the earth's atmosphere. The main function of the ozone layer is to provide a shield over the earth's stratosphere and absorb the greatest amount of the sun's ultraviolet rays. The ozone layer comprises a high concentration of ozone when compared to other parts of the atmosphere. When the amount of ozone is reduced in the stratosphere is known as ozone depletion. Which results in greater UV radiations reaching the earth’s surface. The main reason for ozone depletion is the greenhouse effect and CFCs.
Water: A Natural Resource - Water is the main component of our life in day-to-day activities. It forms two-thirds of our body and helps to keep our body temperature normal. It is also used for various purposes like agricultural, domestic, industrial, etc. earth has only three percent of freshwater, and the rest 97 percent of water resides in the ocean. When any impurities are mixed with water, this is caused by the discharge of pollutants directly or indirectly to freshwater without proper treatment. The main causes of water pollution are urbanization, industries, agriculture, religious and social practices.
Soil - It is the uppermost layer of the earth's surface. The formation of soil takes place by continuous weathering and it depends on the parent material, time, climate, and organisms. Soil is a mixture of organic matter and its basic components are minerals, inorganic matter, water, and air. The various types of soil are clay, loam, silt, sand, etc.
Conclusion
After going through all Class 9 Science Chapter 14 important questions, provides fully solved solutions to all questions. These important questions will help the student to save their time during exam preparation and those answers are designed in such a way that it improves the confidence of the student by solving them. If a student goes through all-important questions of natural resources class 9, he can easily score good marks in the board examinations.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 9
CBSE Class 9 Study Materials |
Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 |
FAQs on Important Questions For Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources - 2025-26
1. What are the most important topics in Class 9 Science Chapter 14 for the 2025-26 exam?
For the Class 9 Science exam session 2025-26, the most frequently asked and high-weightage topics from Chapter 14, Natural Resources, are:
- The different biogeochemical cycles (Water, Nitrogen, Carbon, Oxygen).
- The causes and effects of air pollution and water pollution.
- The concept of the greenhouse effect and its impact on global warming.
- The formation and importance of the ozone layer, along with the causes of its depletion.
- The process of soil formation and the factors leading to soil erosion.
2. Explain the key biogeochemical cycles that are important from an examination perspective.
The key biogeochemical cycles in Chapter 14 that are often tested in 3-mark or 5-mark questions are:
- The Water Cycle: This includes the processes of evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and the collection of water.
- The Nitrogen Cycle: This covers essential stages like nitrogen fixation, nitrification, ammonification, and denitrification.
- The Carbon Cycle: This details the movement of carbon through photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion of fossil fuels.
- The Oxygen Cycle: This explains how oxygen is cycled through respiration and photosynthesis, maintaining its balance in the atmosphere.
3. Differentiate between renewable and non-renewable resources, as this is a frequently asked 2-mark question.
This is a fundamental and important question.
- Renewable resources are those that can be replenished naturally over a short period. Examples from the chapter include air, water, and solar energy.
- Non-renewable resources are those that exist in finite quantities and take millions of years to form, making them exhaustible with use. Key examples include coal and petroleum.
4. How does the greenhouse effect work, and why is it an important question for exams?
The greenhouse effect is a crucial topic. It is a natural process where certain atmospheric gases, like carbon dioxide (CO₂), trap heat from the sun, which keeps the Earth's surface warm enough for life. It becomes an important exam question because human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, have drastically increased the concentration of these gases. This enhancement of the natural effect leads to global warming. A complete answer should explain both the natural phenomenon and the human-induced problem.
5. Why is the ozone layer considered vital for life, and what important questions are related to its depletion?
The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, is vital because it absorbs the majority of the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Without this shield, life on Earth would be exposed to radiation that causes skin cancer, cataracts, and damages entire ecosystems. Important exam questions often focus on:
- The chemicals responsible for its depletion, especially chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
- The location of the 'ozone hole'.
- The impact of UV radiation on living organisms.
6. From an exam point of view, why is soil considered a complex mixture and a valuable resource?
Soil is an important topic because it is not a simple substance but a complex mixture, and its formation is an extremely slow process. Exam questions often require you to explain that soil is formed by:
- The physical, chemical, and biological weathering of rocks over thousands of years.
- The addition of humus (decaying organic matter), which is crucial for soil fertility.
- The presence of various living organisms like bacteria, fungi, and earthworms.
7. How are air pollution and water pollution interconnected? Provide an example like acid rain from Chapter 14.
This is a common Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) question. Air and water pollution are directly linked. For example, burning fossil fuels releases oxides of sulphur and nitrogen into the atmosphere (air pollution). These gases then dissolve in water droplets in the clouds to form sulphuric acid and nitric acid. When this falls as acid rain (water pollution), it damages buildings, harms aquatic life, and acidifies the soil, demonstrating a clear link between the two environmental issues.
8. How should a student prepare for the value-based or application-based questions from the 'Natural Resources' chapter?
To tackle application-based questions from this chapter, focus on the real-world impact of the concepts. Instead of just defining a problem, think about its consequences and solutions. For instance:
- Analyse how deforestation not only impacts the carbon cycle but also leads to soil erosion and loss of biodiversity.
- Think about practical steps to conserve water at home or in your community.
- Relate the concept of biogeochemical cycles to farming practices, such as the use of fertilisers in the nitrogen cycle.














 Watch Video
Watch Video















