The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Extra Questions and Answers Free PDF Download
Important Questions For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life - 2025-26
FAQs on Important Questions For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life - 2025-26
1. What are the most important topics in CBSE Class 9 Science, Chapter 5 (The Fundamental Unit of Life) for the 2025-26 exams?
For the 2025-26 session, students should focus on these high-weightage topics from Chapter 5:
- The discovery of the cell and Cell Theory.
- The structural differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
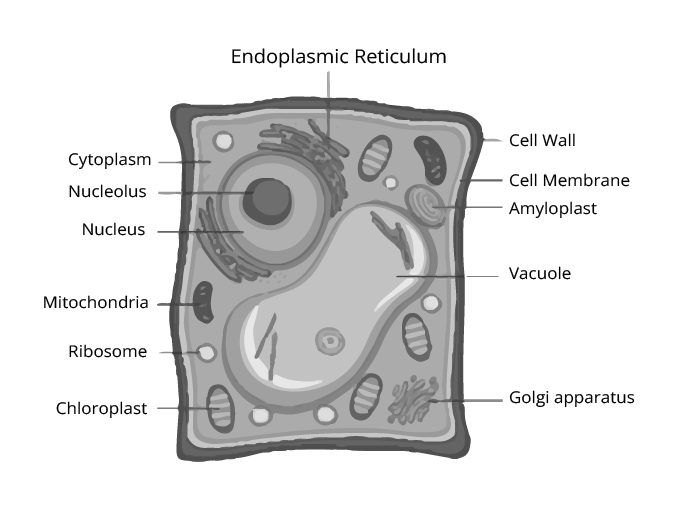
- Functions and structures of key cell organelles like the Nucleus, Mitochondria, Plastids, and Endoplasmic Reticulum.
- The processes of osmosis and diffusion across the plasma membrane.
- The stages and significance of Mitosis and Meiosis (Cell Division).
These topics frequently form the basis for 3-mark and 5-mark questions.
2. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
The cell is called the structural unit because all living organisms are composed of one or more cells. It is called the functional unit because all essential life processes, such as respiration, digestion, and excretion, occur at the cellular level. Each cell can perform these basic functions independently, making it the fundamental building block of life.
3. What are the key differences between a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell?
The primary differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that are important for exams are:
- Nucleus: Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined, membrane-bound nucleus, while prokaryotic cells have an undefined nuclear region called a nucleoid, which lacks a nuclear membrane.
- Organelles: Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and Golgi apparatus. These are absent in prokaryotic cells.
- Chromosomes: Eukaryotic cells typically have more than one chromosome, whereas prokaryotic cells usually have a single, circular chromosome.
- Examples: Plants and animals are eukaryotes; bacteria are prokaryotes.
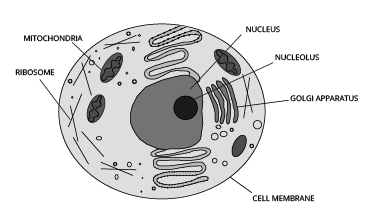
4. Which diagrams are important to practise from Chapter 5 for the Class 9 Science exam?
For scoring well in exams, it is crucial to practise drawing and labelling the following diagrams from 'The Fundamental Unit of Life':
- A detailed diagram of a plant cell.
- A detailed diagram of an animal cell.
- The structure of a eukaryotic nucleus.
- The structure of Mitochondria.
Ensure you can correctly label all the organelles as this is often a source of easy marks.
5. What would happen to the life of a cell if its plasma membrane ruptures?
If the plasma membrane of a cell ruptures, the cell would die. The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Its rupture would lead to an uncontrolled exchange with the external environment, causing the essential cytoplasmic contents to leak out and harmful substances to enter, thereby disrupting all cellular functions.
6. Why are lysosomes known as 'suicide bags' of the cell?
Lysosomes are called 'suicide bags' because they contain powerful digestive enzymes. When a cell gets damaged, old, or diseased, the lysosomes may burst. The release of these enzymes into the cytoplasm digests the cell's own organelles and components, leading to the death of the cell. This process of self-digestion is known as autolysis and is a protective mechanism for the organism.
7. Explain why a plant cell can withstand greater changes in the surrounding medium than an animal cell.
A plant cell can tolerate greater changes in the external medium due to the presence of a rigid cell wall outside its plasma membrane. This cell wall is fully permeable and provides structural strength and support. In a hypotonic solution (dilute medium), an animal cell would swell and burst due to excessive water intake (osmosis). However, a plant cell will only swell up to a certain point, as the rigid cell wall exerts a counter-pressure, preventing it from bursting.
8. What are the expected types of questions from the 'Cell Division' topic for the 2025-26 exam?
From the 'Cell Division' section, you can expect questions worth 3 to 5 marks. Important question types include:
- Differentiating between Mitosis and Meiosis based on the number of daughter cells produced and the change in chromosome number.
- Explaining the significance of mitosis for growth and repair in organisms.
- Explaining the importance of meiosis in the formation of gametes for sexual reproduction.
- A HOTS (High Order Thinking Skills) question might ask about the consequences if meiosis did not reduce the chromosome number by half.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video