




An Overview of Class 12 Chemistry To Prepare Colloidal Solution Of Arsenious Sulphide Experiment
Colloidal solutions are heterogeneous solutions containing an insoluble dispersed phase. The solvent medium here is a dispersion medium in which solute particles are suspended. There are various types of colloidal solutions, examples-sols, emulsions, foam, and aerosols. Sols are a common type of colloid wherein the solute is solid, and the solvent is liquid. Sols are of two types, lyophobic, which is solvent-repelling and lyophilic, which is solvent-attracting. Lyophobic sols and lyophilic sols are differentiated based on the nature of the interaction between the solute and solvent particles. Common lyophobic sols are arsenious sulphide, aluminium hydroxide, ferric hydroxide etc
Table of Contents
Aim
Apparatus Required
Theory
Observation
Result
Aim
To prepare a colloidal solution of arsenious sulphide As2S3
Apparatus required
Conical flask
Beaker
Glass-rod
Funnel
Filter paper
Burner
Wire-gauze
Tripod Stand
Stand with clamp
Distilled water
Glass tube
Theory
Arsenious sulphide forms a lyophobic colloidal solution. Arsenious sulphide sol is prepared through hydrolysis of arsenious oxide As2O3 in boiling distilled water. H2S gas is passed through the above arsenious oxide solution, giving the final arsenious sulphide. In this colloidal sol, each colloidal particle is surrounded by HS- ions, formed from the dissociation of H2S gas. A layer of H+ ions again surrounds this sulphide ion layer.
Procedure
Take a clean conical flask and clean it by the steaming-out process.
Add 0.2g of arsenious oxide solid into the above flask and then pour 100 ml of Distilled water.
Boil this solution for approximately 10 mins.
Using a fluted filter paper, filter out the above contents and collect the filtrate in another beaker.
Pass a slow current of H2S gas into an Arsenious oxide solution until a stable yellow-coloured solution is not obtained.
Remove the excess H2S gas by boiling the sol slowly.
Filter the bright yellow-coloured filtrate in a dry conical flask using a fluted-filter paper and cork it.
Arsenious sulphide sol is prepared.
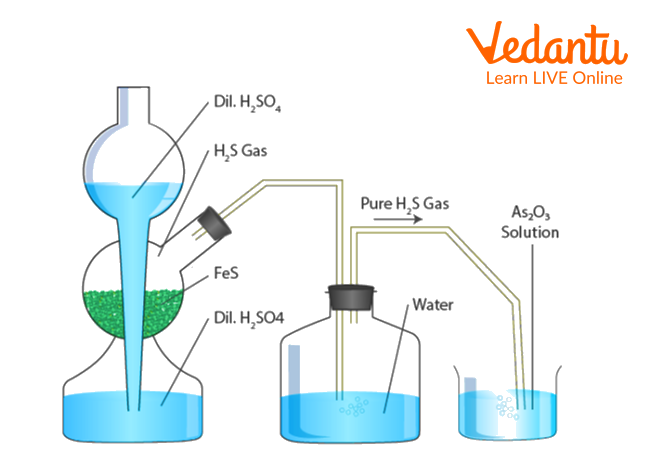
Preparation of As2S3 solution
Observations
The hydrolysis of the arsenious oxide process was followed by the passing of H2S in the arsenious oxide solution, which led to the formation of a yellow-coloured solution. With every step of passing H2S gas in the solution, the intensity of the yellow colour increased until there was no change in the intensity of the yellow-coloured form.
Result
A lyophobic colloidal sol of arsenious sulphide was prepared by the process of hydrolysis of arsenious oxide with distilled water followed by passage of H2S gas from the above solution.
Precautions
Use properly cleaned apparatus for the experiment.
Be careful while working with H2S gas.
Arsenious oxide is highly poisonous, hence use protective gear while working with it.
Do not eat or drink anything while performing this experiment.
Clean your hands properly after the experiment is completed.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What are the properties of arsenious sulphide?
Ans: Following are properties of arsenious sulphide
It is an inorganic compound.
Its chemical formula is As2S3.
It is a dark yellow solid compound.
It is insoluble in water.
It is found in two mineral forms- orpiment and realgar.
2. How is Arsenious sulphide sol prepared?
Ans: Arsenious sulphide is a lyophobic sol; hence, it contains a solid dispersed phase-arsenious oxide and a liquid dispersion medium-water. To form arsenious sulphide, sol-hydrolysis of arsenious oxide is done with boiling water, followed by the passing of hydrogen sulphide gas in the above solution. After which, the entire solution is filtered, and yellow-coloured arsenious sulphide sol is obtained.
3. Why is clean and washed lab apparatus required for this experiment?
Ans: The apparatus used for the above experiment has to be cleaned properly because the preparation of such inorganic compounds is highly sensitive, and even the minute presence of impurities or contamination will hinder the formation of arsenious sulphide, and a pure As2O3 solution will not be prepared. The steaming-out process is used to clean the apparatus to remove all impurities.
4. What is responsible for the stability of arsenious sulphide sol?
Ans: Lyophobic sols such as arsenious sulphide, aluminium hydroxide, and ferric hydroxide are stabilised due to the charge present on the surfaces of the colloidal particles. They are easy to coagulate if these charges on the surfaces are disturbed or neutralised.
Viva Questions
1. What is the reason for the yellow-coloured solution of As2O3?
Ans: The yellow colour of As2O3 solution when hydrogen sulphide gas is passed is due to the formation of arsenious sulphide solution.
2. The colloidal solution of silver is prepared by which process?
Ans: A colloidal solution of silver is prepared by Bredig’s method.
3. Which apparatus is used for the generation of H2S?
Ans: Kipp’s apparatus is used for the generation of H2S.
4. What is an alternative way of preparation of H2S gas?
Ans: Another way to obtain H2S gas via Kipp’s apparatus is by using zinc flakes with glass marbles and pouring dil. HCl into this mixture.
5. How to bring coagulation of arsenious sulphide?
Ans: Coagulation of 100ml of arsenious sulphide can be brought about by using a 5ml of 1M NaCl solution.
6. What is an associated colloid?
Ans: Associated colloids are colloids which, at lower concentrations, behave as strong electrolytes, but at higher concentrations behave as colloids due to aggregation of particles.
7. Name the mineral forms of arsenious sulphide.
Ans: Orpiment and Realgar are the two mineral forms of arsenious sulphide.
8. What are lyophobic sols?
Ans: Sols wherein the solid dispersed phase has a low affinity with the liquid dispersion medium are known as lyophobic sols.
9. What is the range of particle size in colloids?
Ans: The colloidal particles have a diameter in the range between 1 and 1000 nm.
10. What is the charge present in arsenious sulphide?
Ans: Negative charge is present on arsenious sulphide.
Practical Based Questions (MCQs)
To prepare a colloidal solution of starch, which of the following is important?
Iodine solution
Starch paste
Cold water
-20℃ temperature
Ans: Starch paste
Arsenic sulphide formula is_____
As4S6
As3S
As5S7
As2S3
Ans: As2S3
Arsenious sulphide sol is prepared by passing
Ferrous sulphide gas
Hydrogen peroxide gas
Hydrogen sulphide gas
Carbon dioxide gas
Ans: Hydrogen sulphide gas
A colloidal solution of platinum is prepared by____
Bredig’s method
Solvation method
Hydrolysis
Combustion
Ans: Bredig’s method
What does hydrolysis mean?
Chemical breaking of a compound due to water
Lysis of compound due to hydrogen
Ligation of a compound due to water
The chemical breakdown of the compound due to water vapour
Ans: Chemical breaking of a compound due to water
Sols can be destroyed using which of the following?
Adding water
Adding inert metals
By increasing the dispersion medium
By adding electrolytes
Ans: By adding electrolytes
Orpiment is _____in colour
Pink
Orange
Yellow
Black
Ans: Yellow
A red-orange mineral of arsenious sulphide is
Realgar
Arsenious sulphide
Orpiment
Arsenious oxide
Ans: Realgar
State which of the following is false.
Colloidal solutions are true solutions
The emulsion is a type of colloidal solution
Gas particles trapped in a solid medium are known as foam.
Starch forms a lyophilic sol.
Ans: Colloidal solutions are true solutions
Find the odd man out
Starch
Protein
Aluminium hydroxide
Gelatin
Ans: Aluminium hydroxide
Conclusion
From the above experiment, we can conclude that colloidal solutions are made of two parts: a dispersed phase and the dispersion medium. The dispersed phase remains suspended in the dispersed medium. Sols are of two types lyophobic, which are solvent hating and hence remain suspended in the solution due to the presence of charges on their surface. Arsenious sulphide is an example of a negatively charged sol, i.e. its colloidal particles have a negative charge on their surface. As2S3 is a yellow-coloured colloidal solution which has various industrial applications.
FAQs on Class 12 Chemistry To Prepare Colloidal Solution Of Arsenious Sulphide Experiment
1. What is the fundamental principle behind preparing arsenious sulphide sol for the Class 12 practical exam?
The preparation of arsenious sulphide (As₂S₃) sol is based on the principle of double decomposition. In this method, a saturated solution of arsenious oxide (As₂O₃) is treated with hydrogen sulphide (H₂S) gas. The resulting reaction forms the insoluble As₂S₃, which remains dispersed in the medium as a colloid.
2. From an exam perspective, what is the chemical equation for the preparation of arsenious sulphide sol?
The key chemical reaction that you must know for your viva voce is the double decomposition between arsenious oxide and hydrogen sulphide gas. The balanced equation is:
As₂O₃ + 3H₂S → As₂S₃(sol) + 3H₂O
Here, As₂S₃(sol) represents the formation of the colloidal solution.
3. How is the prepared arsenious sulphide sol purified, and why is this step important for marks?
The sol is purified using dialysis. This step is crucial because the prepared sol contains soluble impurities like excess H₂S. To purify it, the sol is placed in a parchment or cellophane bag, which is then suspended in a beaker of fresh, continuously flowing water. The small impurity ions pass through the membrane, leaving the larger colloidal particles behind. This purification ensures the stability of the sol.
4. What are the most important precautions to mention during the viva for the arsenious sulphide experiment?
For full marks on safety and procedure, you should mention the following precautions:
- Hydrogen sulphide (H₂S) is a highly poisonous gas, so the experiment must be conducted in a fume hood.
- The apparatus, especially the conical flask, must be thoroughly cleaned before use.
- H₂S gas should be bubbled through the arsenious oxide solution slowly to ensure proper formation of the colloid.
5. Why is arsenious sulphide (As₂S₃) sol considered a negatively charged colloid?
Arsenious sulphide sol is a negatively charged colloid due to the preferential adsorption of ions from the dispersion medium. During its formation, the As₂S₃ particles adsorb the common sulphide ions (S²⁻) from the hydrogen sulphide (H₂S) solution. This creates a negative layer on the particles, resulting in a stable, negatively charged sol.
6. What type of colloid is arsenious sulphide sol, and what is its appearance?
Arsenious sulphide sol is a lyophobic colloid, meaning it has little affinity for the solvent (water). It is also classified as a multimolecular colloid because it's formed by the aggregation of many small As₂S₃ molecules. The sol has a distinct, bright yellow colour and is translucent.
7. How can you confirm that the prepared solution is a colloid and not a true solution?
The colloidal nature can be confirmed by observing the Tyndall effect. When a strong beam of light is passed through the yellow arsenious sulphide sol in a dark room, the path of the light becomes visible due to the scattering of light by the colloidal particles. This phenomenon is not observed in a true solution.






































