
The single, double, and triple bond lengths of carbon in carbon dioxides are respectively.
(a) \[1.15,1.15,\]and \[1.10\] Angstrom
(b) \[1.22,1.15,\]and \[1.10\] Angstrom
(c) \[1.10,1.15,\]and \[1.22\] Angstrom
(d) \[1.15,1.10,\]and \[1.22\] Angstrom
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Based on sharing of elections during the chemical bond formation. The chemical bond can be classified into three types (a) single bond, (b) double bond, and (c) triple bond, respectively.
Complete step by step solution:We all know atoms involved in chemical bond formation. On the other hand, we can say that atoms combined to complete their octet.
On the basis of the requirement of the electron by the atoms to complete their octet, they can form single, double and triple bonds respectively.
Carbon dioxide is a linear molecule which has a \[C{O_2}\]formula.
The structure of carbon dioxide is composed of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
At room temperature, the carbon dioxide molecule exists in gaseous form.
The structure of carbon dioxide exists in three resonating forms and in its resonating structure it has single, double and triple bonds respectively.
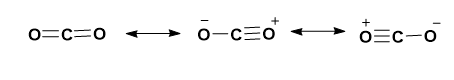
Image: Resonating structure of carbon dioxide.
Because of the three resonating structures, the carbon dioxide has single, double and triple bonds.
The bond length for single, double, and triple bonds will be \[1.22,1.15\] and \[1.10\] Angstrom respectively.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (b) will be the correct option:
Note: The carbon di-oxide is a nonpolar molecule due to linear and symmetrical structure.
Carbon dioxide is known as an electrophile in organic chemistry.
The carbon dioxide molecule has \[s{p^2}\]hybridization with linear geometry and shape.
Complete step by step solution:We all know atoms involved in chemical bond formation. On the other hand, we can say that atoms combined to complete their octet.
On the basis of the requirement of the electron by the atoms to complete their octet, they can form single, double and triple bonds respectively.
Carbon dioxide is a linear molecule which has a \[C{O_2}\]formula.
The structure of carbon dioxide is composed of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
At room temperature, the carbon dioxide molecule exists in gaseous form.
The structure of carbon dioxide exists in three resonating forms and in its resonating structure it has single, double and triple bonds respectively.
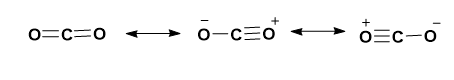
Image: Resonating structure of carbon dioxide.
Because of the three resonating structures, the carbon dioxide has single, double and triple bonds.
The bond length for single, double, and triple bonds will be \[1.22,1.15\] and \[1.10\] Angstrom respectively.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (b) will be the correct option:
Note: The carbon di-oxide is a nonpolar molecule due to linear and symmetrical structure.
Carbon dioxide is known as an electrophile in organic chemistry.
The carbon dioxide molecule has \[s{p^2}\]hybridization with linear geometry and shape.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




