
The enolic form of ethyl acetoacetate as below has-
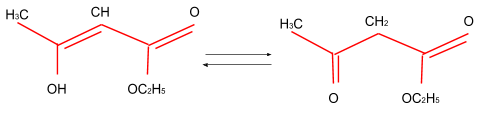
(A) 9 sigma bonds and 2 pi-bonds
(B) 9 sigma bonds and 1 pi-bonds
(C) 18 sigma bonds and 2 pi-bonds
(D) 16 sigma bonds and 1 pi-bonds
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: First, we will draw a simplified view of the chemical structure of ethyl acetoacetate in order to understand the bonds between each element better. Once done so, simply count the bonds between the elements.
Complete step by step solution:
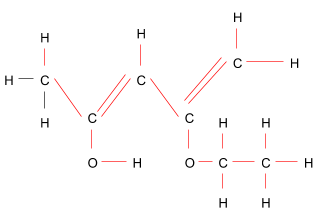
> Sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ bonds are the strongest form of covalent chemical bond. These are made up of head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals. Sigma bonding is more clearly described for diatomic molecules using the symmetry group language and tools. Through this systematic solution, the bond becomes symmetrical with respect to the orientation of the bond axis.
> Sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent bonding due to the close overlap of orbitals, and the electrons in such bonding are often referred to as sigma electrons.
Usually, a single bond is a sigma bond, whereas a multiple bond is a sigma bond with pi or other bonds. A double bond contains a sigma and a pi bond, while a triple bond has a sigma and two pi bonds.
After counting the bonds very carefully, we come to this conclusion-
The above structure has 18 sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ bonds and 2 pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bonds.
Hence it is clear that option C is the correct option.
Note: Pi bonds are covalent chemical bonds where two orbital lobes on one atom overlap two orbital lobes on another atom and this overlap happens laterally. Both of such atomic orbitals have zero electron density on a common nodal plane, going through the two bonded nodes. The same plane is also a nodal plane for the pi bond molecular orbital. Pi Bonds that develop in double and triple bonds, but in most cases do not shape in single bonds.
Complete step by step solution:

> Sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ bonds are the strongest form of covalent chemical bond. These are made up of head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals. Sigma bonding is more clearly described for diatomic molecules using the symmetry group language and tools. Through this systematic solution, the bond becomes symmetrical with respect to the orientation of the bond axis.
> Sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent bonding due to the close overlap of orbitals, and the electrons in such bonding are often referred to as sigma electrons.
Usually, a single bond is a sigma bond, whereas a multiple bond is a sigma bond with pi or other bonds. A double bond contains a sigma and a pi bond, while a triple bond has a sigma and two pi bonds.
After counting the bonds very carefully, we come to this conclusion-
The above structure has 18 sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ bonds and 2 pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bonds.
Hence it is clear that option C is the correct option.
Note: Pi bonds are covalent chemical bonds where two orbital lobes on one atom overlap two orbital lobes on another atom and this overlap happens laterally. Both of such atomic orbitals have zero electron density on a common nodal plane, going through the two bonded nodes. The same plane is also a nodal plane for the pi bond molecular orbital. Pi Bonds that develop in double and triple bonds, but in most cases do not shape in single bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




