
The correct order of the $O-O$ bond length in ${{O}_{2}}$, ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ and ${{O}_{3}}$ is
(1) ${{O}_{2}}>{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}>{{O}_{3}}$
(2) ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}>{{O}_{3}}>{{O}_{2}}$
(3) ${{O}_{2}}>{{O}_{3}}>{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$
(4) ${{O}_{3}}>{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}>{{O}_{2}}$
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: bond order is nothing but total number of bonds present in between the two atoms. The required answer includes concepts based on the molecular orbital theory where bond order is inversely proportional to bond length.
Complete step by step solution:
We have studied in our inorganic chemistry part that includes the chapter of finding bond order and also the structure of atoms based on several theories.
- One among those theories includes the molecular orbital theory which is well known as MOT.
- Molecular orbital theory is based on the method to depict the diagrams on the basis of their electronic structure using quantum mechanics.
- Molecular orbital theory makes use of the linear combination of atomic orbital
(LCAO).
- The diagram is based on three types of bonding. They are, bonding, antibonding and the non-bonding atomic orbital.
Now, according to the question we must find the order of bond length with the data given in terms of bond order. For this, let us draw the structures of the molecules given which is as shown below,
Structure of ${{O}_{2}}$ is as follows,

Bond order = 2
Structure of${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ is given below,
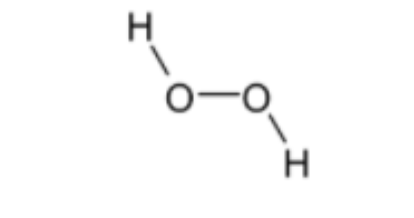
Bond order = 1
Structure of ${{O}_{3}}$ is,
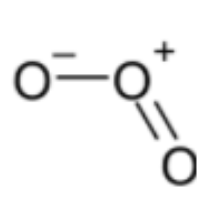
Bond order = 1.5
Therefore, increasing order of bond order is ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}<{{O}_{3}}<{{O}_{2}}$
Since, the bond angle is inversely proportional to bond order we can write the decreasing order of bond length as,
${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}>{{O}_{3}}>{{O}_{2}}$
Thus, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The principle of valence bond theory (VBT) and molecular orbital theory (MOT) are the same and not to be confused. But MOT prevails as it was successful in explaining the paramagnetic character of oxygen but not VBT.
Complete step by step solution:
We have studied in our inorganic chemistry part that includes the chapter of finding bond order and also the structure of atoms based on several theories.
- One among those theories includes the molecular orbital theory which is well known as MOT.
- Molecular orbital theory is based on the method to depict the diagrams on the basis of their electronic structure using quantum mechanics.
- Molecular orbital theory makes use of the linear combination of atomic orbital
(LCAO).
- The diagram is based on three types of bonding. They are, bonding, antibonding and the non-bonding atomic orbital.
Now, according to the question we must find the order of bond length with the data given in terms of bond order. For this, let us draw the structures of the molecules given which is as shown below,
Structure of ${{O}_{2}}$ is as follows,

Bond order = 2
Structure of${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ is given below,

Bond order = 1
Structure of ${{O}_{3}}$ is,

Bond order = 1.5
Therefore, increasing order of bond order is ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}<{{O}_{3}}<{{O}_{2}}$
Since, the bond angle is inversely proportional to bond order we can write the decreasing order of bond length as,
${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}>{{O}_{3}}>{{O}_{2}}$
Thus, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The principle of valence bond theory (VBT) and molecular orbital theory (MOT) are the same and not to be confused. But MOT prevails as it was successful in explaining the paramagnetic character of oxygen but not VBT.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




