
\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{ - C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ - C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{Br + KOH}}\left( {{\rm{alc}}{\rm{.}}} \right) \to {\rm{Product}}\]
The product in the above reaction is:
A. CH3−CH=CH2
B. CH3−CH2−CH3
C. A and B both
D. None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When a haloalkane is added to an alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution, it leads to the formation of an alkene. This reaction is called dehydrohalogenation.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this reaction, a halogen atom and a hydrogen atom from the haloalkane get removed in the form of hydrogen halide. It is an elimination reaction.
Alcoholic KOH is the concentrated alcoholic solution of KOH.
The carbon atom which holds the halogen atom is α-carbon. The carbon atom which carries the hydrogen atom is the β-carbon. The hydrogen atom is removed from β-carbon, this reaction is likewise called the β-elimination reaction.
For example - dehydrobromination of bromoethane
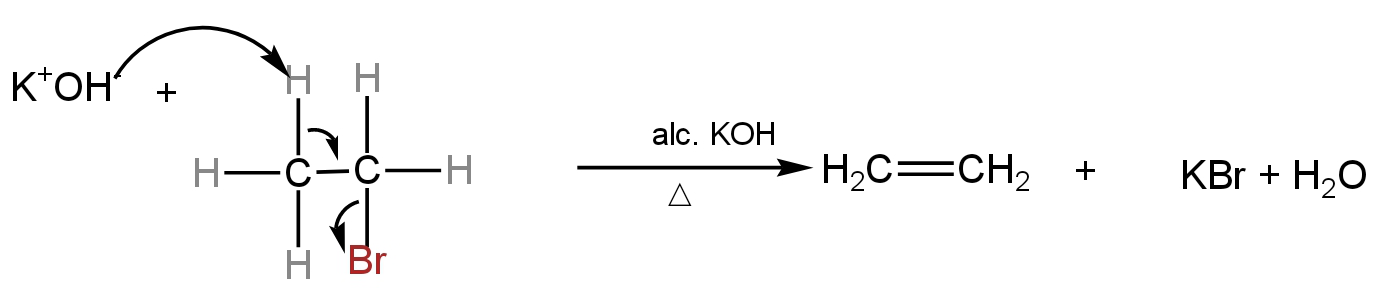
Image: Dehydrobromination of bromoethane leading to the formation of ethene.
In the given reaction, the α-carbon loses the bromine atom and the β-carbon loses the hydrogen atom.
The resulting product is an alkene.
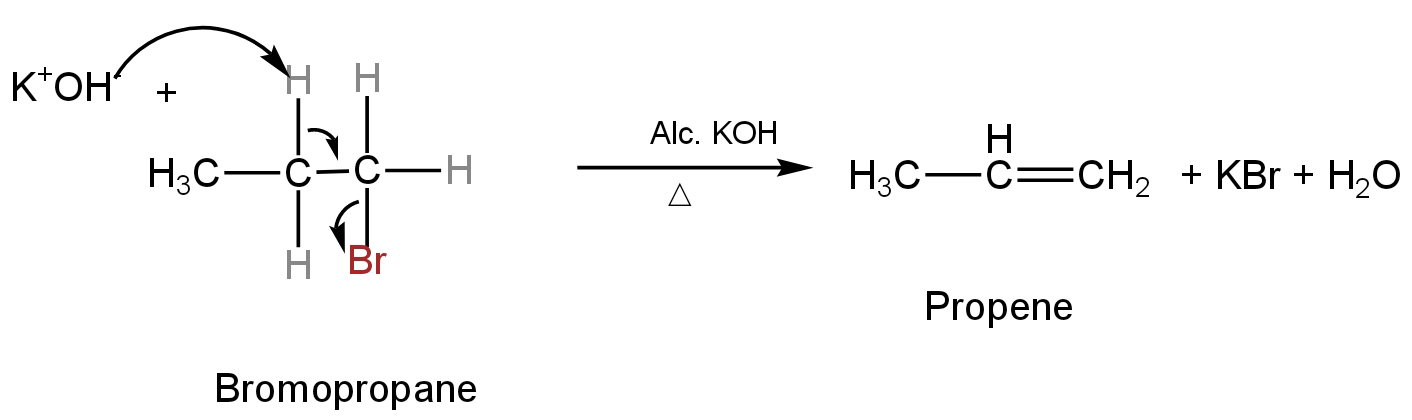
Image: Dehydrobromination of bromopropane.
A. Propene is the main product in this reaction. So, A is correct.
B. Propane cannot be the product of this type of elimination reaction. So, B is incorrect.
C. In an elimination reaction, only an alkene is formed as the product. So, C is incorrect.
So, option A is correct.
Note: While attempting the question, one must retain in mind that the product of this type of elimination reaction is an alkene. Alkane is not formed during this type of reaction. The halide is removed from the α-carbon and the hydrogen atom is removed from the carbon atom next to the α-carbon i.e., β-carbon.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this reaction, a halogen atom and a hydrogen atom from the haloalkane get removed in the form of hydrogen halide. It is an elimination reaction.
Alcoholic KOH is the concentrated alcoholic solution of KOH.
The carbon atom which holds the halogen atom is α-carbon. The carbon atom which carries the hydrogen atom is the β-carbon. The hydrogen atom is removed from β-carbon, this reaction is likewise called the β-elimination reaction.
For example - dehydrobromination of bromoethane

Image: Dehydrobromination of bromoethane leading to the formation of ethene.
In the given reaction, the α-carbon loses the bromine atom and the β-carbon loses the hydrogen atom.
The resulting product is an alkene.

Image: Dehydrobromination of bromopropane.
A. Propene is the main product in this reaction. So, A is correct.
B. Propane cannot be the product of this type of elimination reaction. So, B is incorrect.
C. In an elimination reaction, only an alkene is formed as the product. So, C is incorrect.
So, option A is correct.
Note: While attempting the question, one must retain in mind that the product of this type of elimination reaction is an alkene. Alkane is not formed during this type of reaction. The halide is removed from the α-carbon and the hydrogen atom is removed from the carbon atom next to the α-carbon i.e., β-carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




