
When the polynomial $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1 $ is divided by $ \left( x+1 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+1 \right) $ then the remainder is ax+b, then a+b is equal to
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Here, in this question, we can use the fact that the dividend is equal to the product of the divisor and the quotient when added with the remainder, that is,
$ p\left( x \right)=g\left( x \right)\times q\left( x \right)+r\left( x \right) $ where p $ \left( x \right) $ , g $ \left( x \right) $ , q $ \left( x \right) $ and r $ \left( x \right) $ are the dividend, divisor, quotient and remainder respectively and do the long division method to get the quotient and remainder.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this given question, we are asked to divide $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1 $ by $ \left( x+1 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+1 \right) $ and find the sum of a and b if the remainder is ax+b.
We are going to use the fact that the dividend is equal to the product of the divisor and the quotient when added with the remainder, that is,
$ p\left( x \right)=g\left( x \right)\times q\left( x \right)+r\left( x \right) $ where p $ \left( x \right) $ , g $ \left( x \right) $ , q $ \left( x \right) $ and r $ \left( x \right) $ are the dividend, divisor, quotient and remainder respectively……………………….(1.1)
Here, we are, going to perform the long division method to divide $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1 $ by $ \left( x+1 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+1 \right) $ to find our answers as the quotient and remainder (ax+b) then the sum of a and b. In the long division method, the first term of the quotient is chosen such that after multiplying with it the divisor (the polynomial by which the other polynomial is being divided) and then subtracting from the dividend (the polynomial to be divided), the highest power of x from the dividend gets cancelled out. We continue in this way with the resulting remainder as the new dividend until the power of the remainder becomes less than the power of the divisor.
First of all let us divide $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1 $ by $ {{x}^{2}}-x+1 $.
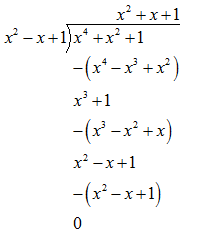
Thus, dividing $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1 $ by $ {{x}^{2}}-x+1 $ , we get the remainder as 0 and the quotient as \[{{x}^{2}}+x+1\]………………….(1.2)
Now, we divide \[{{x}^{2}}+x+1\] by $ \left( x+1 \right) $ .
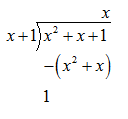
From the above, we see that upon dividing \[{{x}^{2}}+x+1\] by $ \left( x+1 \right) $ we get the remainder as 1……………………(1.3)
So, using (1.2), we can write
$ \dfrac{{{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1}{\left( x+1 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+1 \right)}=\dfrac{1}{\left( x+1 \right)}\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1}{{{x}^{2}}+x+1} \right)=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+x+1}{x+1} $
And as the division in the last term has been performed in (1.3), we know that the remainder after performing the division should be equal to 1=0x+1.
Thus, comparing the remainder to the form given in the question, ax+b, we find that a=0 and b=1 and thus a+b=0+1=1 which matches option (a). Hence, (a) is the correct answer to this question.
Note: In this sort of question, we must be very careful while doing the long division process about changing the signs of the terms in the quotient. The divisor should be multiplied by the quotient and the resulting whole polynomial should be subtracted from the dividend. If even a single sign is changed in the wrong way, the whole answer could be different and wrong.
$ p\left( x \right)=g\left( x \right)\times q\left( x \right)+r\left( x \right) $ where p $ \left( x \right) $ , g $ \left( x \right) $ , q $ \left( x \right) $ and r $ \left( x \right) $ are the dividend, divisor, quotient and remainder respectively and do the long division method to get the quotient and remainder.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this given question, we are asked to divide $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1 $ by $ \left( x+1 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+1 \right) $ and find the sum of a and b if the remainder is ax+b.
We are going to use the fact that the dividend is equal to the product of the divisor and the quotient when added with the remainder, that is,
$ p\left( x \right)=g\left( x \right)\times q\left( x \right)+r\left( x \right) $ where p $ \left( x \right) $ , g $ \left( x \right) $ , q $ \left( x \right) $ and r $ \left( x \right) $ are the dividend, divisor, quotient and remainder respectively……………………….(1.1)
Here, we are, going to perform the long division method to divide $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1 $ by $ \left( x+1 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+1 \right) $ to find our answers as the quotient and remainder (ax+b) then the sum of a and b. In the long division method, the first term of the quotient is chosen such that after multiplying with it the divisor (the polynomial by which the other polynomial is being divided) and then subtracting from the dividend (the polynomial to be divided), the highest power of x from the dividend gets cancelled out. We continue in this way with the resulting remainder as the new dividend until the power of the remainder becomes less than the power of the divisor.
First of all let us divide $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1 $ by $ {{x}^{2}}-x+1 $.
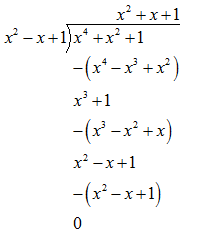
Thus, dividing $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1 $ by $ {{x}^{2}}-x+1 $ , we get the remainder as 0 and the quotient as \[{{x}^{2}}+x+1\]………………….(1.2)
Now, we divide \[{{x}^{2}}+x+1\] by $ \left( x+1 \right) $ .
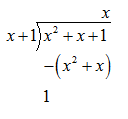
From the above, we see that upon dividing \[{{x}^{2}}+x+1\] by $ \left( x+1 \right) $ we get the remainder as 1……………………(1.3)
So, using (1.2), we can write
$ \dfrac{{{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1}{\left( x+1 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+1 \right)}=\dfrac{1}{\left( x+1 \right)}\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+1}{{{x}^{2}}+x+1} \right)=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+x+1}{x+1} $
And as the division in the last term has been performed in (1.3), we know that the remainder after performing the division should be equal to 1=0x+1.
Thus, comparing the remainder to the form given in the question, ax+b, we find that a=0 and b=1 and thus a+b=0+1=1 which matches option (a). Hence, (a) is the correct answer to this question.
Note: In this sort of question, we must be very careful while doing the long division process about changing the signs of the terms in the quotient. The divisor should be multiplied by the quotient and the resulting whole polynomial should be subtracted from the dividend. If even a single sign is changed in the wrong way, the whole answer could be different and wrong.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





