
Kolbe's synthesis of sodium salt of butanoic acid gives:
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Kolbe's synthesis is used to remove the carboxylic acid group i.e. decarboxylation of the organic compound. The resultant product is alkane. Along with alkane, the synthesis produces carbon dioxide as a product. Remember that 2 moles of acid are involved in the reaction mechanism as the alkyl group undergoes dimerization.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Kolbe electrolysis or Kolbe reaction is an organic reaction named after its discoverer Hermann Kolbe. The Kolbe reaction is decarboxylative dimerization of two carboxylic acids or their ions.
The general reaction is :
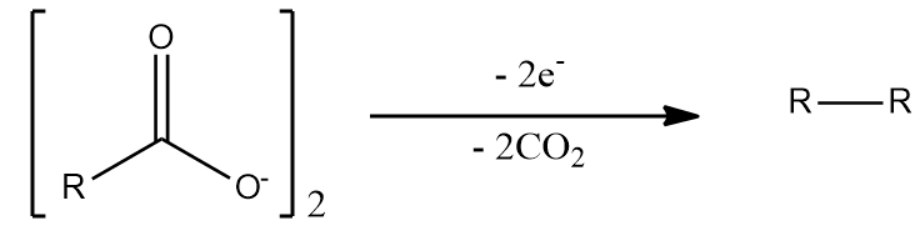
When a mixture of two unidentical carboxylic acid compounds are used, all combinations of them are seen as products. For example, Kolbe electrolysis of sodium salt of ethanoic acid and propanoic acid will give products as:
- ethane
- butane
- propane
The reaction mechanism involves a two-stage process involving the formation of free radicals. Electrochemical decarboxylation gives a radical intermediate, which then combines with the second mole of the same compound to give alkane as a product. Along with alkane, the electrolysis reaction gives carbon dioxide as a by-product.
We will now write Kolbe synthesis for two moles of sodium salt of butanoic acid to obtain the products.
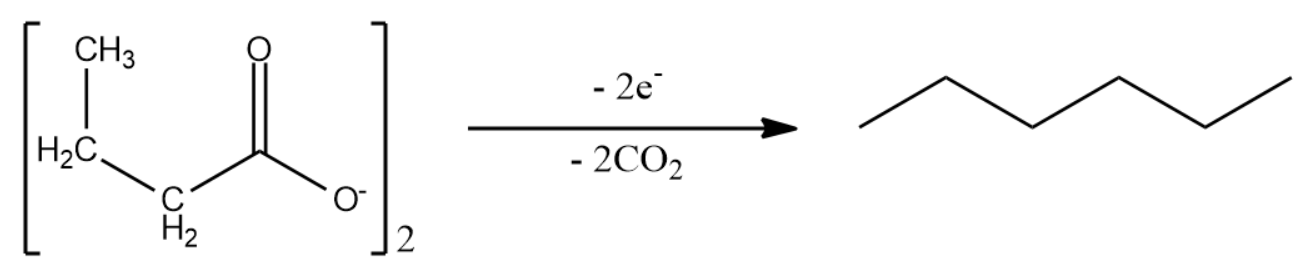
Kolbe's synthesis of sodium salt of butanoic acid gives n-hexane as the product.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Kolbe's synthesis or Kolbe's electrolysis reaction is not used for the preparation of an odd number of carbon atoms present in alkane. This is because the reaction will produce more than 1 distinct product which is part of homologous series. Hence it will be difficult to separate the required alkane from the mixture of products as their boiling points will be very close to each other.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Kolbe electrolysis or Kolbe reaction is an organic reaction named after its discoverer Hermann Kolbe. The Kolbe reaction is decarboxylative dimerization of two carboxylic acids or their ions.
The general reaction is :
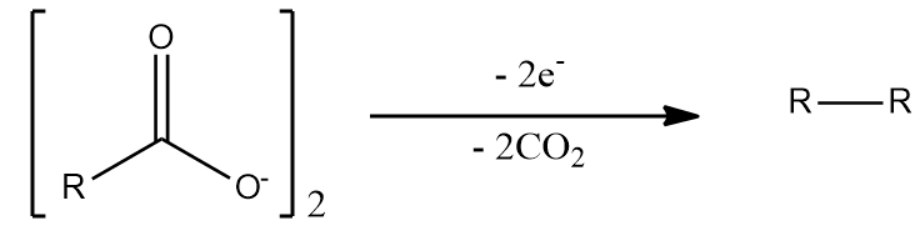
When a mixture of two unidentical carboxylic acid compounds are used, all combinations of them are seen as products. For example, Kolbe electrolysis of sodium salt of ethanoic acid and propanoic acid will give products as:
- ethane
- butane
- propane
The reaction mechanism involves a two-stage process involving the formation of free radicals. Electrochemical decarboxylation gives a radical intermediate, which then combines with the second mole of the same compound to give alkane as a product. Along with alkane, the electrolysis reaction gives carbon dioxide as a by-product.
We will now write Kolbe synthesis for two moles of sodium salt of butanoic acid to obtain the products.

Kolbe's synthesis of sodium salt of butanoic acid gives n-hexane as the product.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Kolbe's synthesis or Kolbe's electrolysis reaction is not used for the preparation of an odd number of carbon atoms present in alkane. This is because the reaction will produce more than 1 distinct product which is part of homologous series. Hence it will be difficult to separate the required alkane from the mixture of products as their boiling points will be very close to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




