
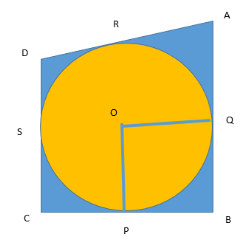
In the figure given below, a circle with center O is inscribed in a quadrilateral ABCD such that it touches the sides BC, AB, AC and CD at points P, Q, R and S respectively. If AB = 29 cm, AD = 23 cm, \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\], DS = 5 cm, then find the radius of the circle in cm.

Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: We will use the fact that: Tangents from the same external points are equal in length. Using this fact and doing some modification, we will prove that OQBP is a square and thus find the radius using given data.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We see that AD and CD touch the circle at R and S respectively and nowhere else.
Hence, we can call AD and CD the tangents to the circle.
Because tangent is a straight line or plane that touches a curve or curved surface at a point, but if extended does not cross it at that point.
Now, we will use the fact that: Tangents from the same external points are equal in length.
Now tangents AD and CD cut at R and S respectively coming from the same point D.
Hence, DR = DS ………..(1)
Similarly using the same argument again and again, we will have:-
AR = AQ ……..(2)
CP = CS ……..(3)
BQ = BP ……..(4)
Adding (1) and (2), we will get:-
DR + AR = DS + AQ ……….(5)
We can clearly see from the figure that DR + AR = AD = 23 cm (given).
Hence, (5) becomes DS + AQ = AD = 23 cm.
So, DS + AQ = 23 cm.
But we are given DS = 5 cm.
So, 5 + AQ = 23.
So, AQ = 18 cm.
Now, we know that AQ + QB = AB = 23 cm.
So, 18 cm + QB = 23 cm
SO, QB = 5 cm ………..(6)
By using (4), we will have:-
BQ = BP = 5 cm.
And we see that OQ and OP are the radii of the same circle.
Hence, OQ = OP …..(7)
We also are already given that \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\] ……..(8)
By using (6), (7) and (8):-
We have OQBP is a square.
Hence, all sides must be equal.
So, OQ = 5cm.
Hence, the radius is 5 cm.
Note: The students might just prove the sides to be equal to forget to refer to the one angle as the right angle which is a must for the quadrilateral to be a square. So, be aware to mention the given angle as well.
If the figure is not provided in such questions, after prefer drawing it first before starting off with the solution to see things better.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We see that AD and CD touch the circle at R and S respectively and nowhere else.
Hence, we can call AD and CD the tangents to the circle.
Because tangent is a straight line or plane that touches a curve or curved surface at a point, but if extended does not cross it at that point.
Now, we will use the fact that: Tangents from the same external points are equal in length.
Now tangents AD and CD cut at R and S respectively coming from the same point D.
Hence, DR = DS ………..(1)
Similarly using the same argument again and again, we will have:-
AR = AQ ……..(2)
CP = CS ……..(3)
BQ = BP ……..(4)
Adding (1) and (2), we will get:-
DR + AR = DS + AQ ……….(5)
We can clearly see from the figure that DR + AR = AD = 23 cm (given).
Hence, (5) becomes DS + AQ = AD = 23 cm.
So, DS + AQ = 23 cm.
But we are given DS = 5 cm.
So, 5 + AQ = 23.
So, AQ = 18 cm.
Now, we know that AQ + QB = AB = 23 cm.
So, 18 cm + QB = 23 cm
SO, QB = 5 cm ………..(6)
By using (4), we will have:-
BQ = BP = 5 cm.
And we see that OQ and OP are the radii of the same circle.
Hence, OQ = OP …..(7)
We also are already given that \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\] ……..(8)
By using (6), (7) and (8):-
We have OQBP is a square.
Hence, all sides must be equal.
So, OQ = 5cm.
Hence, the radius is 5 cm.
Note: The students might just prove the sides to be equal to forget to refer to the one angle as the right angle which is a must for the quadrilateral to be a square. So, be aware to mention the given angle as well.
If the figure is not provided in such questions, after prefer drawing it first before starting off with the solution to see things better.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




